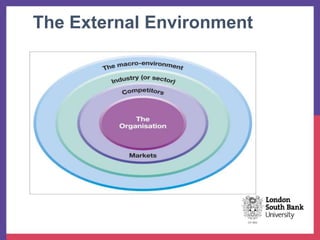
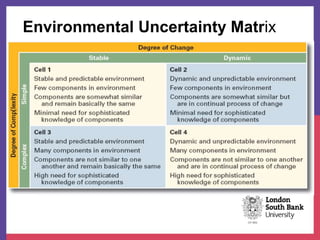
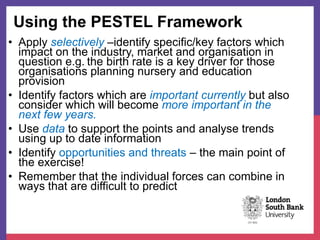
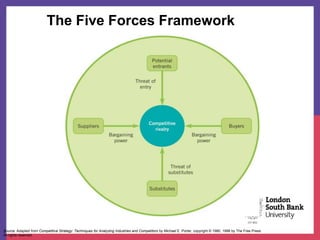
This document provides an overview of analyzing an organization's external environment. It discusses the macro and micro external environments, and frameworks for assessing them. The PESTEL framework categorizes macro factors into political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal categories. Porter's Five Forces analyzes the micro environment through the lenses of competitive rivalry, potential new entrants, substitution threats, supplier power and buyer power. Understanding how these external forces impact an industry is crucial for strategic planning and decision making.