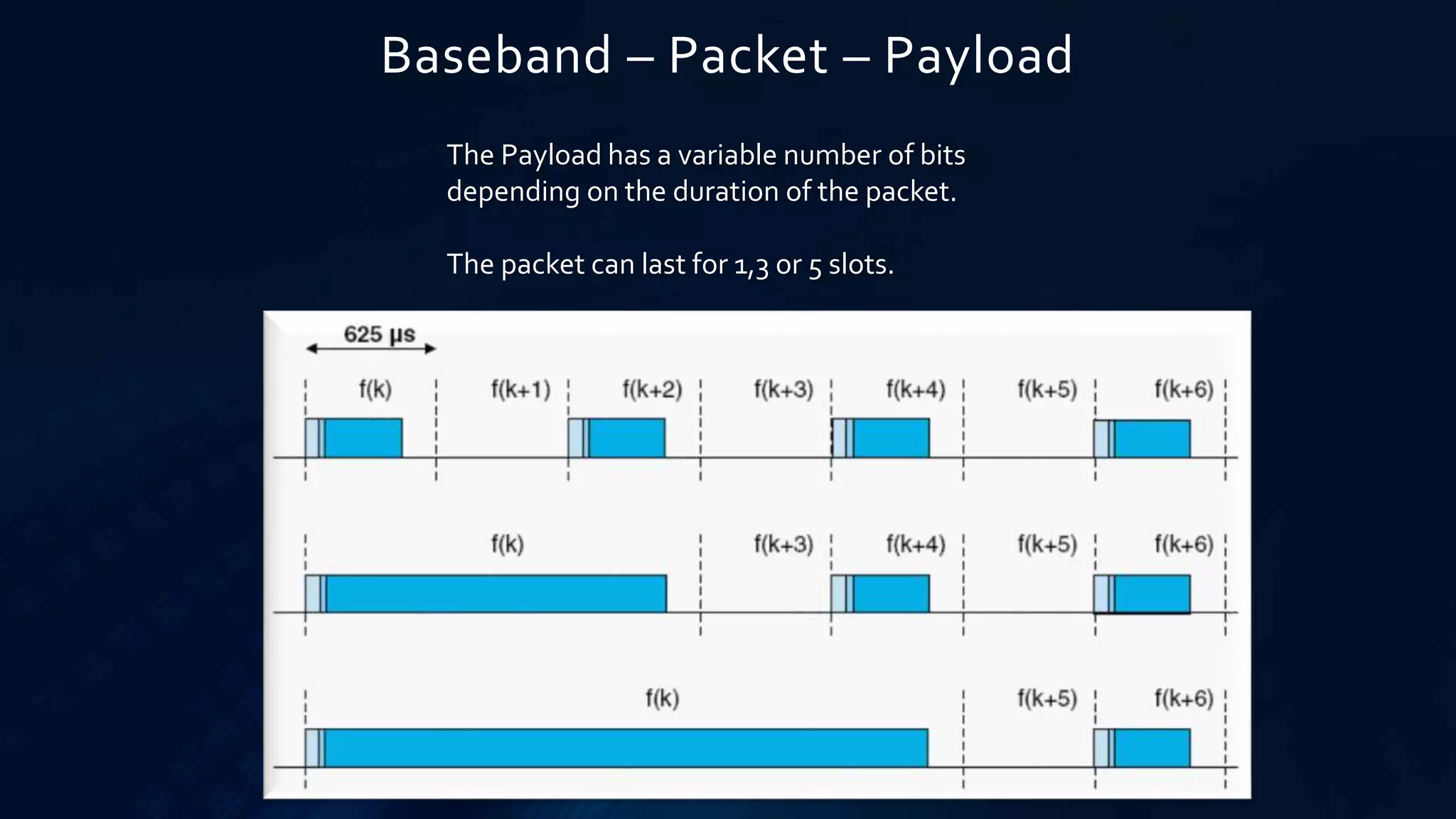
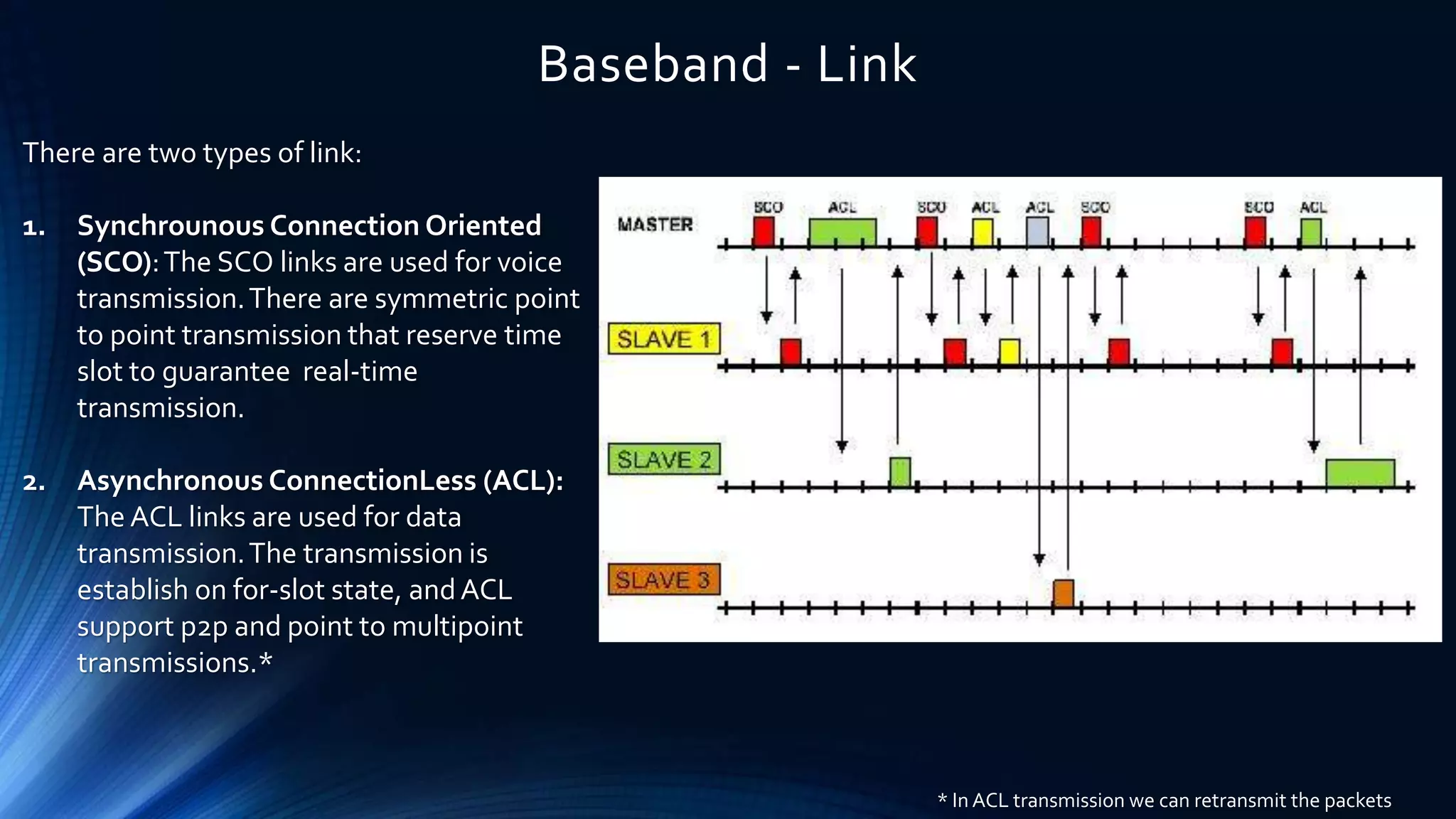
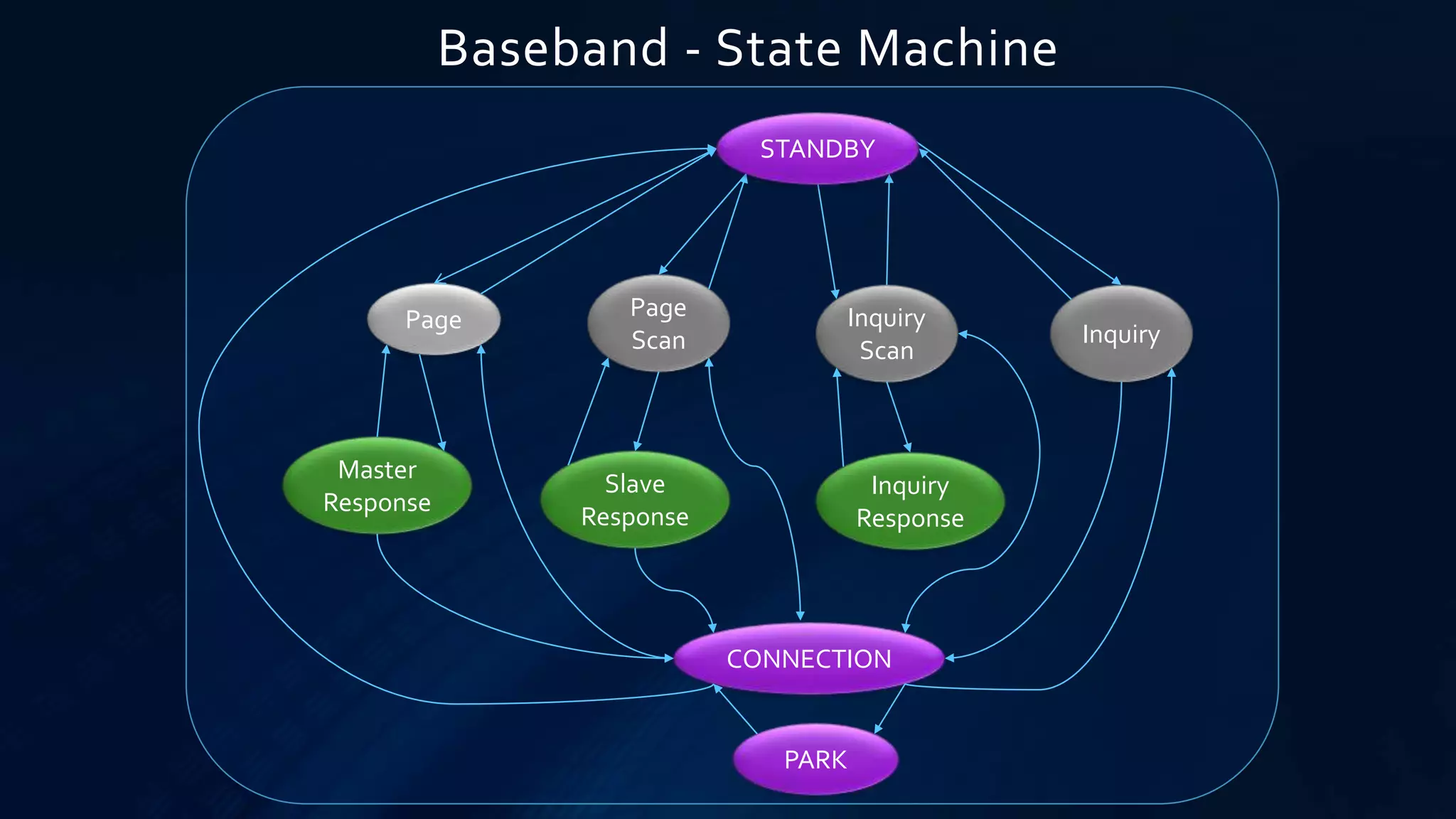
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Bluetooth technology, covering its definition, history, protocols, and operational characteristics. Bluetooth is an open standard for wireless communication that uses frequency-hopping spread spectrum for data exchange over short distances. It discusses various Bluetooth protocols, device classifications, and packet transmission methods within piconets and scatternets.













![Baseband – Packet – Header
Header contains some information about the packet.
3 bits: Slave address on the piconet
1 bit: positive or negativeACK
1 bit: flow (0 Stop in ACL packets)
1 bit: sequence number (not interested)
4 bit: identify 16 possible payload types:
- Null (Access Code + Payload)
- ID (Only Access Code)
- Pool (Slaves must answer)
- FHS (Frequency Hopping Synchronization)
- 12 Synchronized or Asynchronized Packets
8 bits: + 36 redundancy bits [FEC 1/3]*
*FEC is Forwared Error Connection, essentially in FEC 1/3 every bit is transmited for three times.With this technique we can correct a single error for every three bits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blueberry-200524121714/75/Bluetooth-18-2048.jpg)