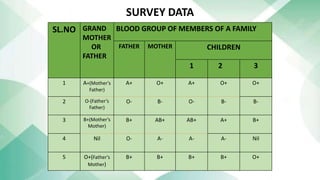
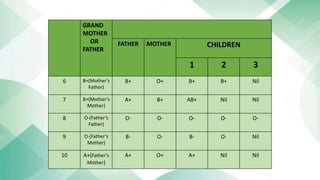
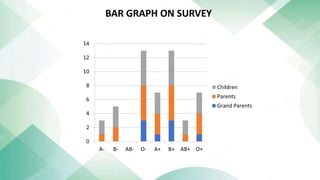
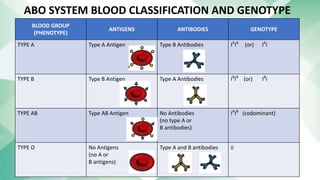
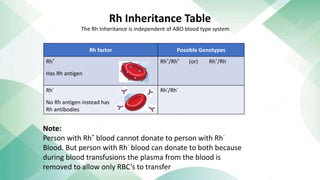
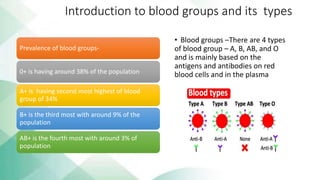
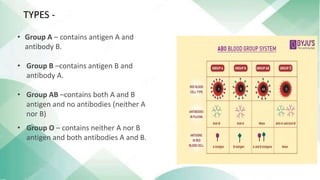
The document discusses blood groups and related diseases. It provides objectives, survey data on family blood types, a bar graph showing survey results, information on ABO blood group classification and genotypes. It then discusses diseases related to different blood groups like higher risk of cardiovascular and pancreatic diseases for some groups. Preventive measures discussed include annual checkups, exercise, diet and more. In conclusion, resistance to disease is complex and depends on multiple factors including blood type, health, lifestyle and vaccinations.