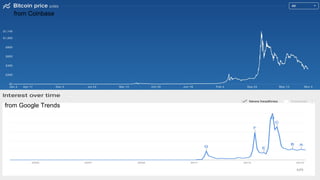
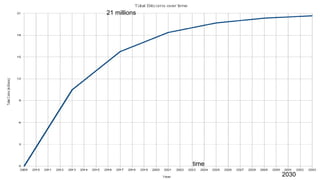
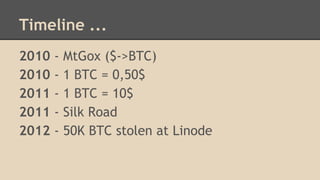
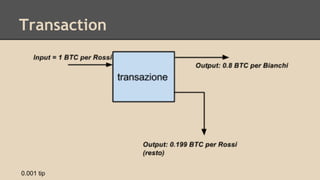
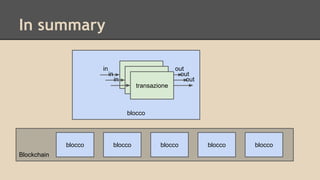
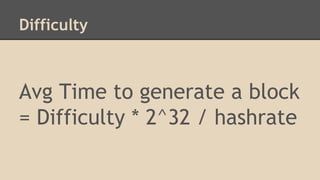
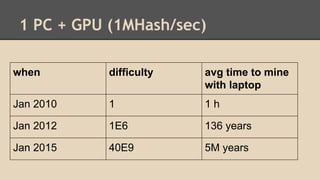
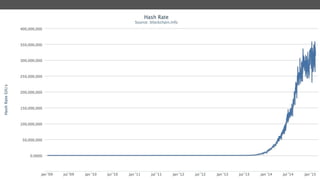
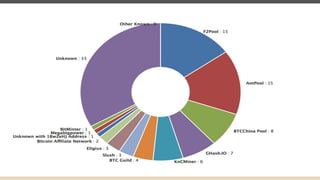
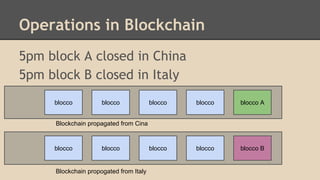
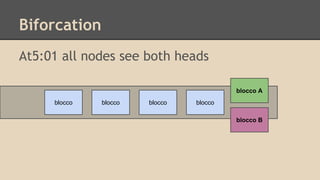
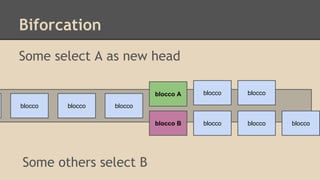
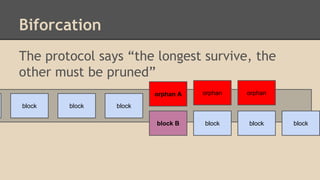
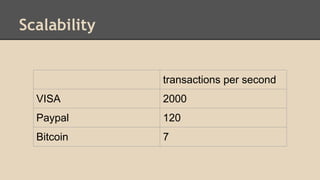
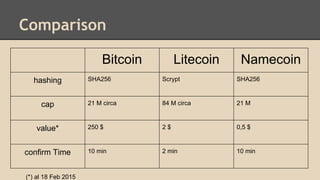
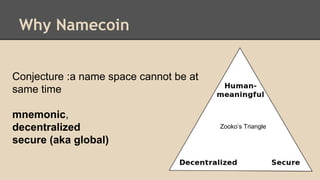
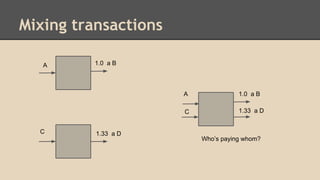
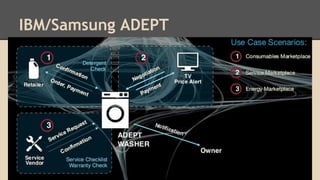
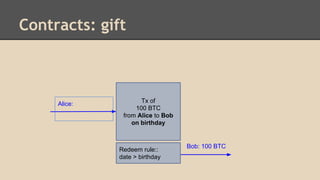
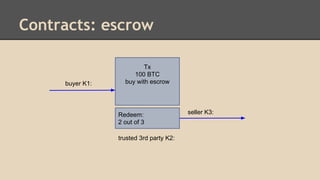
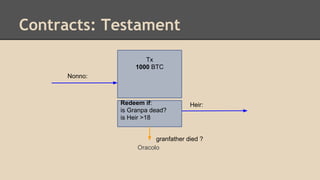
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin enable new forms of digital money and financial contracts. Bitcoin introduced a trustless digital currency using cryptography to secure a distributed public ledger called the blockchain. Miners on the Bitcoin network process transactions and add them to blocks which get added to the immutable blockchain roughly every 10 minutes. Over time, the blockchain has grown large as a record of all transactions, posing scalability challenges. New applications like smart contracts and alternative currencies like Namecoin build on this innovation to enable decentralized applications and services.