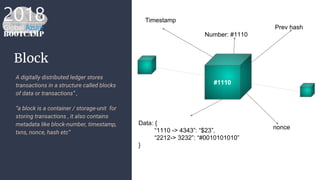
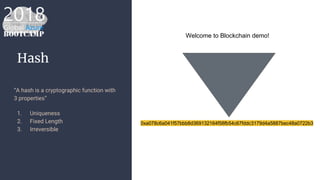
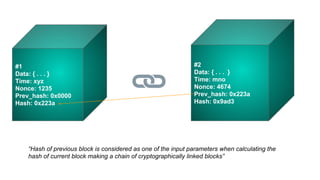
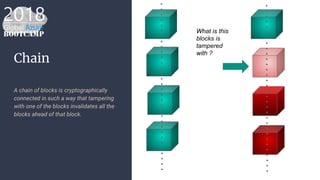
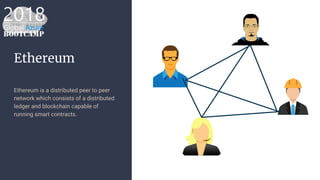
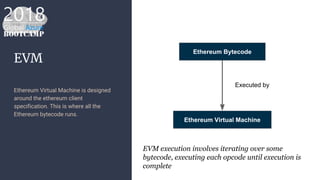
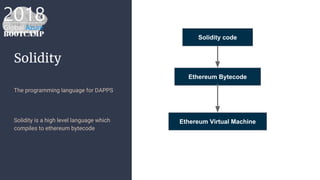
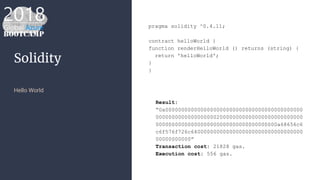
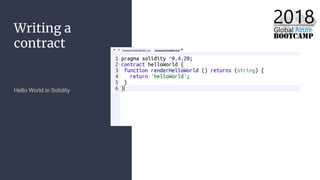
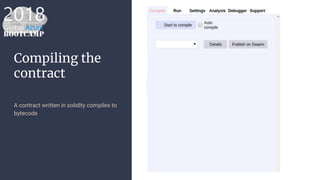
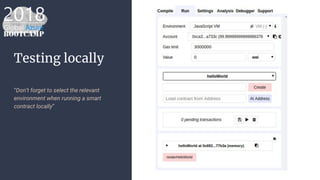
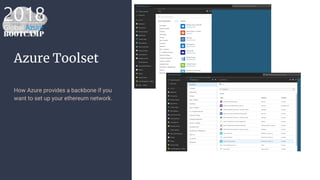
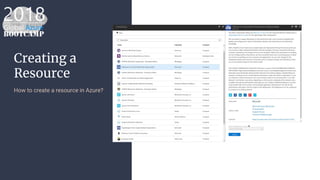
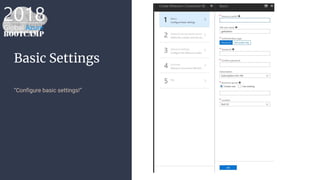
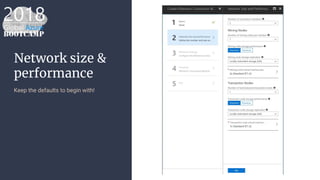
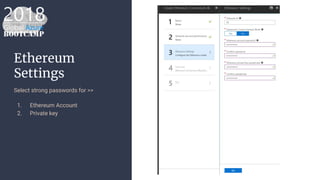
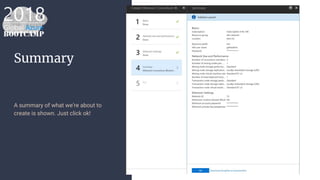
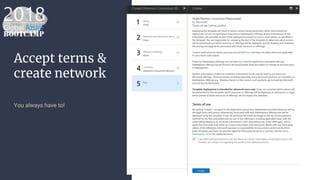
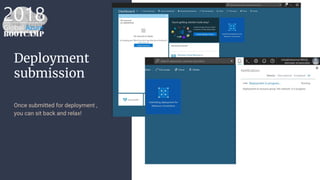
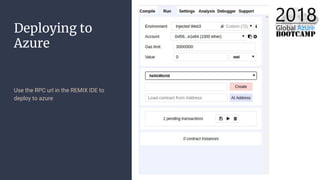
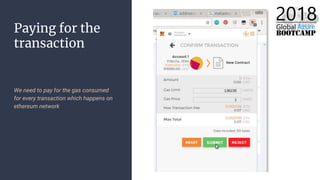
The document outlines the process of deploying a smart contract on the Azure Ethereum blockchain, detailing the components of blockchain such as transactions, ledgers, and smart contracts. It explains Ethereum's decentralized nature and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), as well as providing guidance on writing contracts in Solidity and using Azure tools for deployment. Additionally, it discusses practical applications, including a supply chain use case, and highlights key elements like gas pricing for transaction execution.



![Contracts
“I trust the broker [ 3rd party ] so I’m
willing to make the deal happen at 3%
brokerage”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchain-180425170949/85/Blockchain-4-320.jpg)
![Decentralization
Imagine buying a sunglasses
20 years back . . . .
Only 1 shop in the area [
centralized ]
High price
Hard to trust the quality as
there’s no way to measure
Today . . . .
Multiple websites / apps with all
time access [ decentralized ]
Competitive price with
comparison
Trust relatively high because of
huge competition / reputation
issue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchain-180425170949/85/Blockchain-5-320.jpg)

![#1
genesis
#2 #3 #4
What is Blockchain?
“A digitally distributed ledger which stores cryptographically linked blocks of data [ transactions ] in a
way which makes the data immutable , final and tamper-proof”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchain-180425170949/85/Blockchain-8-320.jpg)