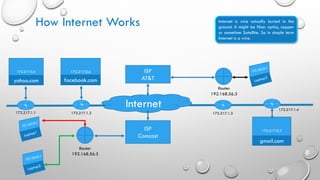
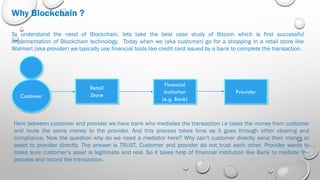
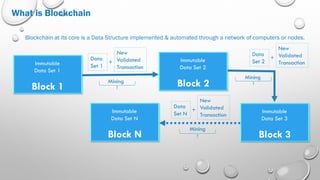
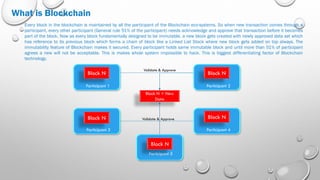
Blockchain technology allows for direct peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries by maintaining an immutable distributed digital ledger. It solves issues like slow settlement, high costs, and lack of trust between transacting parties through automation and cryptography. Each participant holds an identical copy of the blockchain, which consists of blocks of validated transaction data linked together. A new block is only added when a majority of participants reach consensus, preventing hacking of the immutable record. Potential applications beyond digital currencies include land titles, micropayments, and electronic health records.