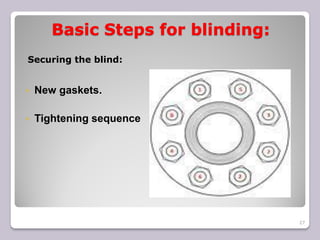
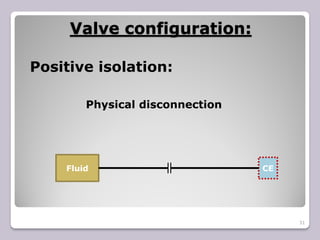
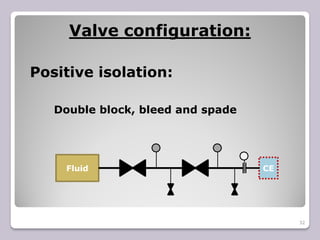
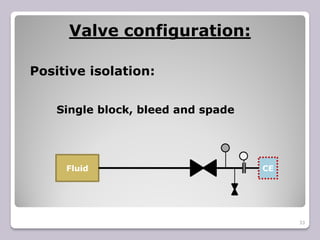
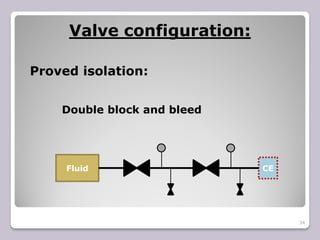
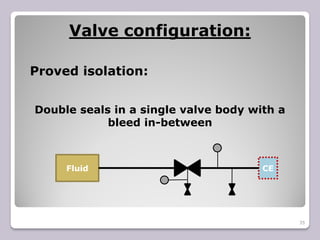
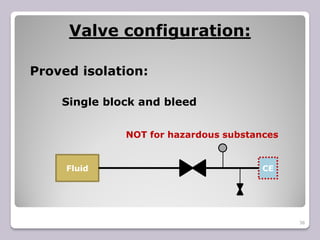
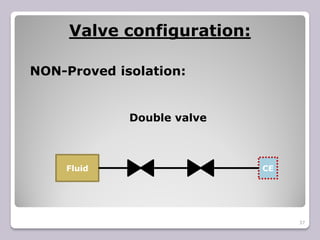
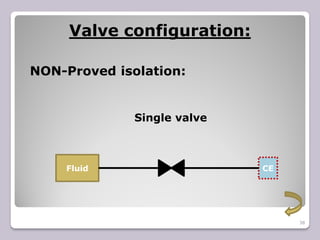
The document outlines the processes of blinding and de-blinding, emphasizing risk assessment, hazard identification, and the use of specific tools for safe operation. It details key stages of process isolation and the importance of preparing for blinding tasks with appropriate safety measures. Additionally, it discusses various valve configurations and standards regarding isolation to prevent hazardous incidents.