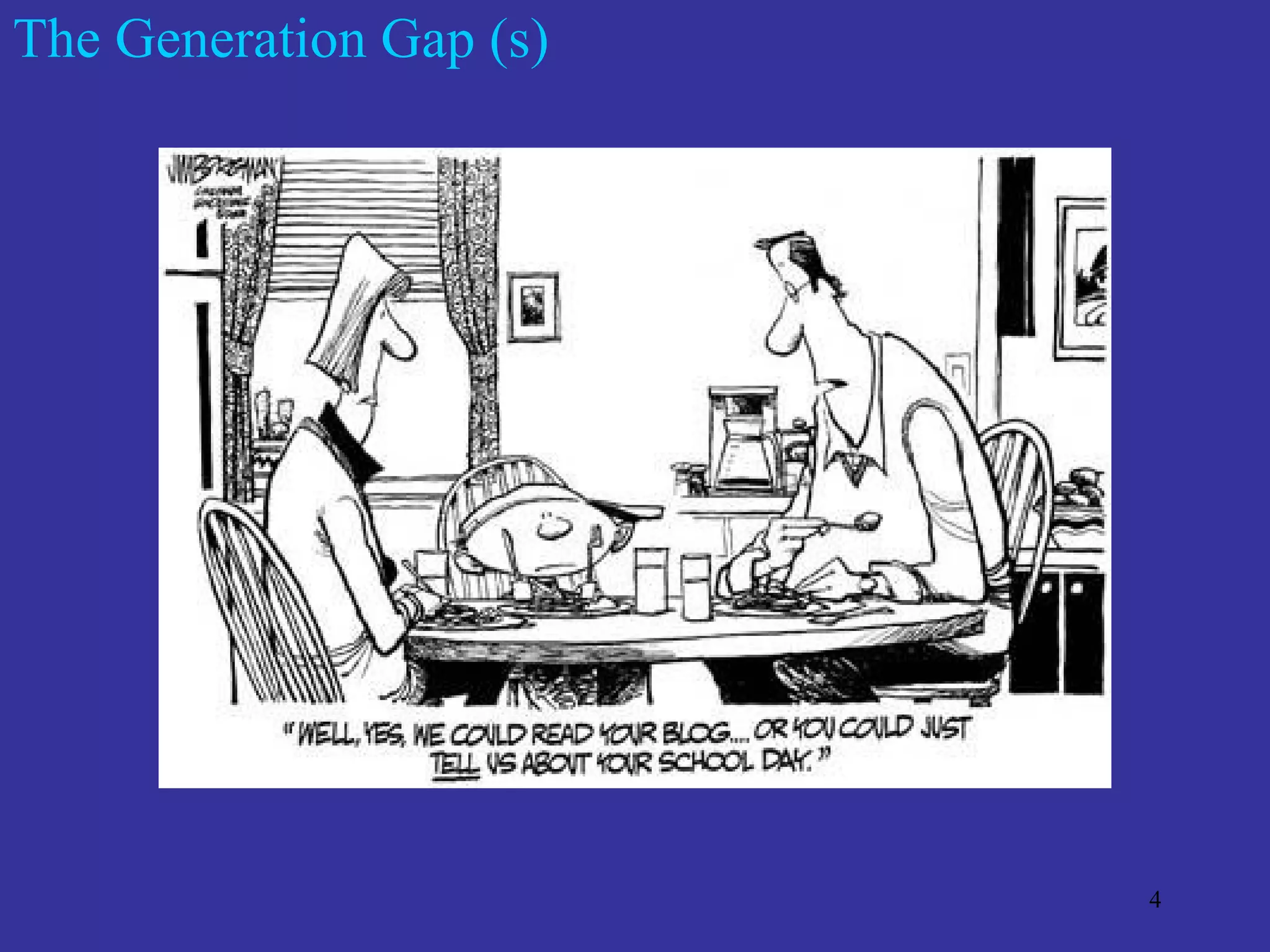
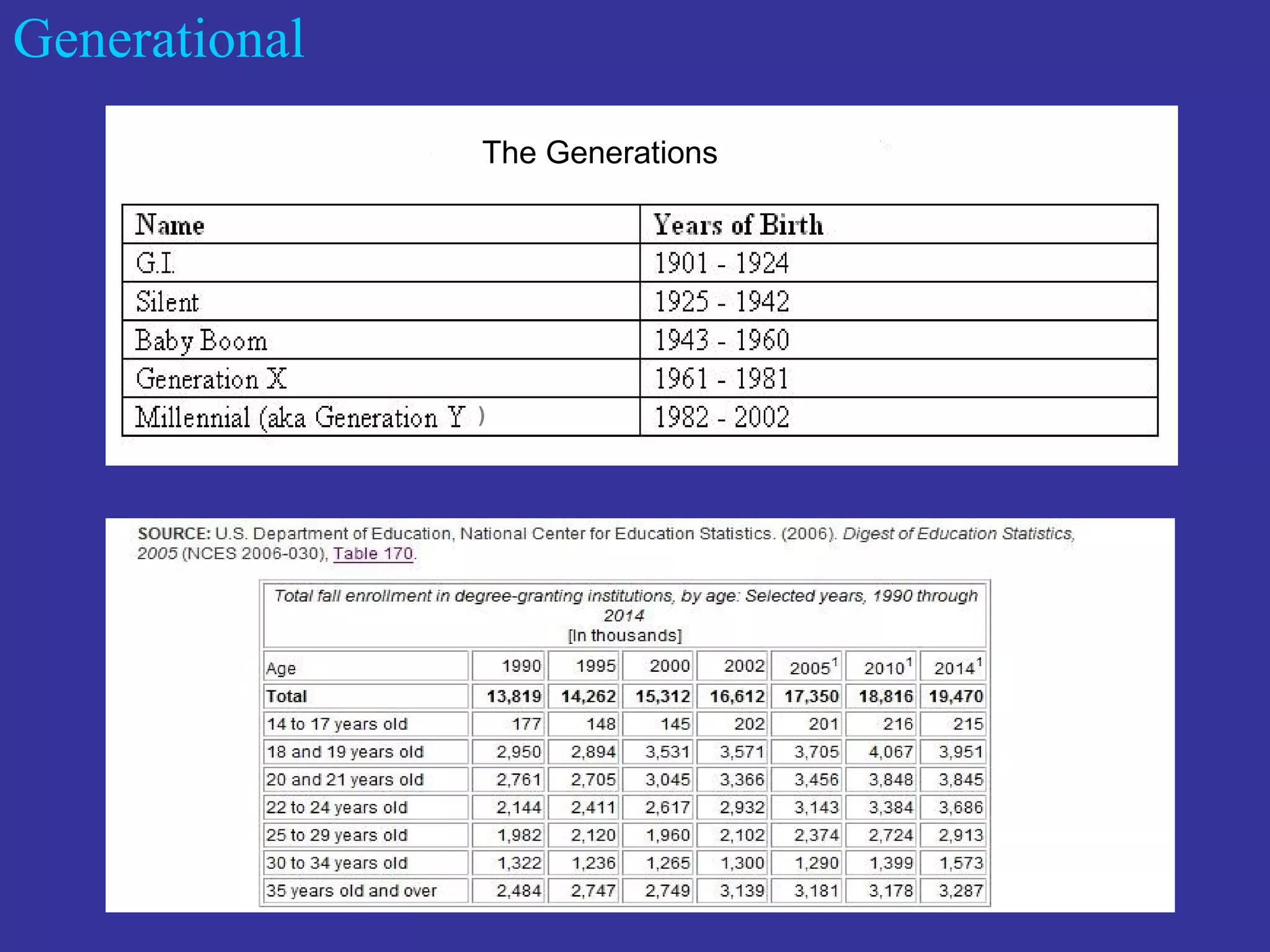
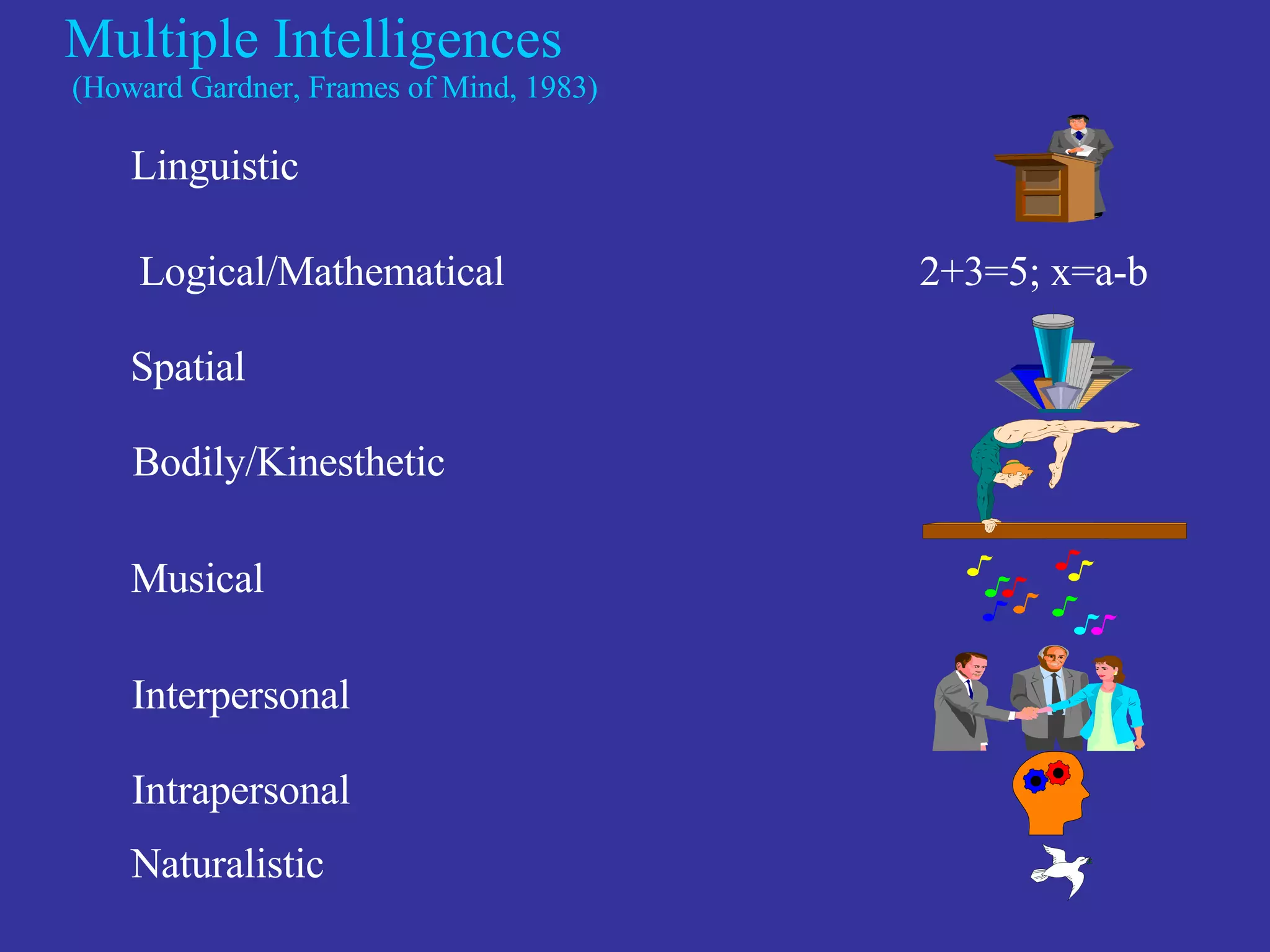
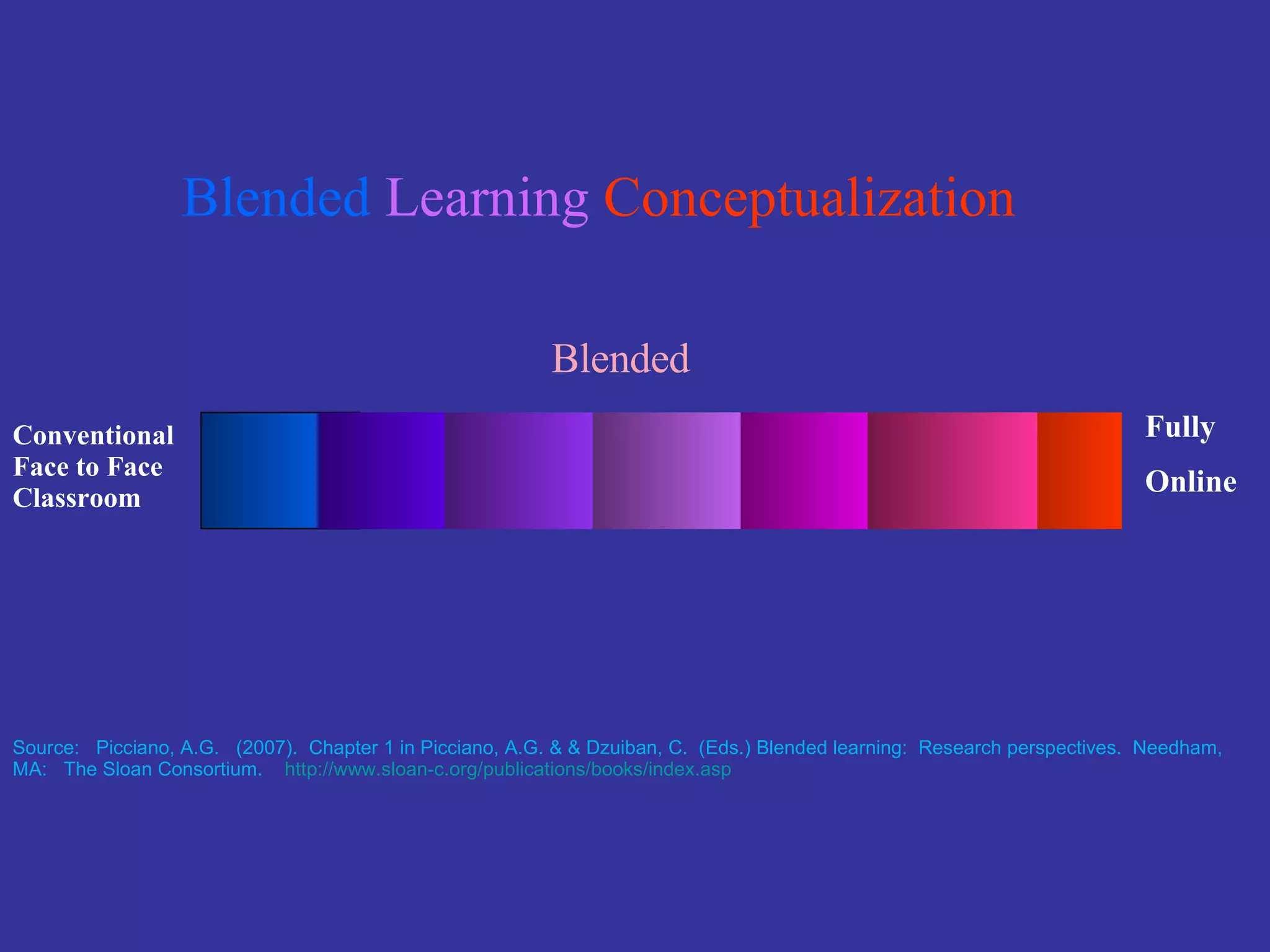
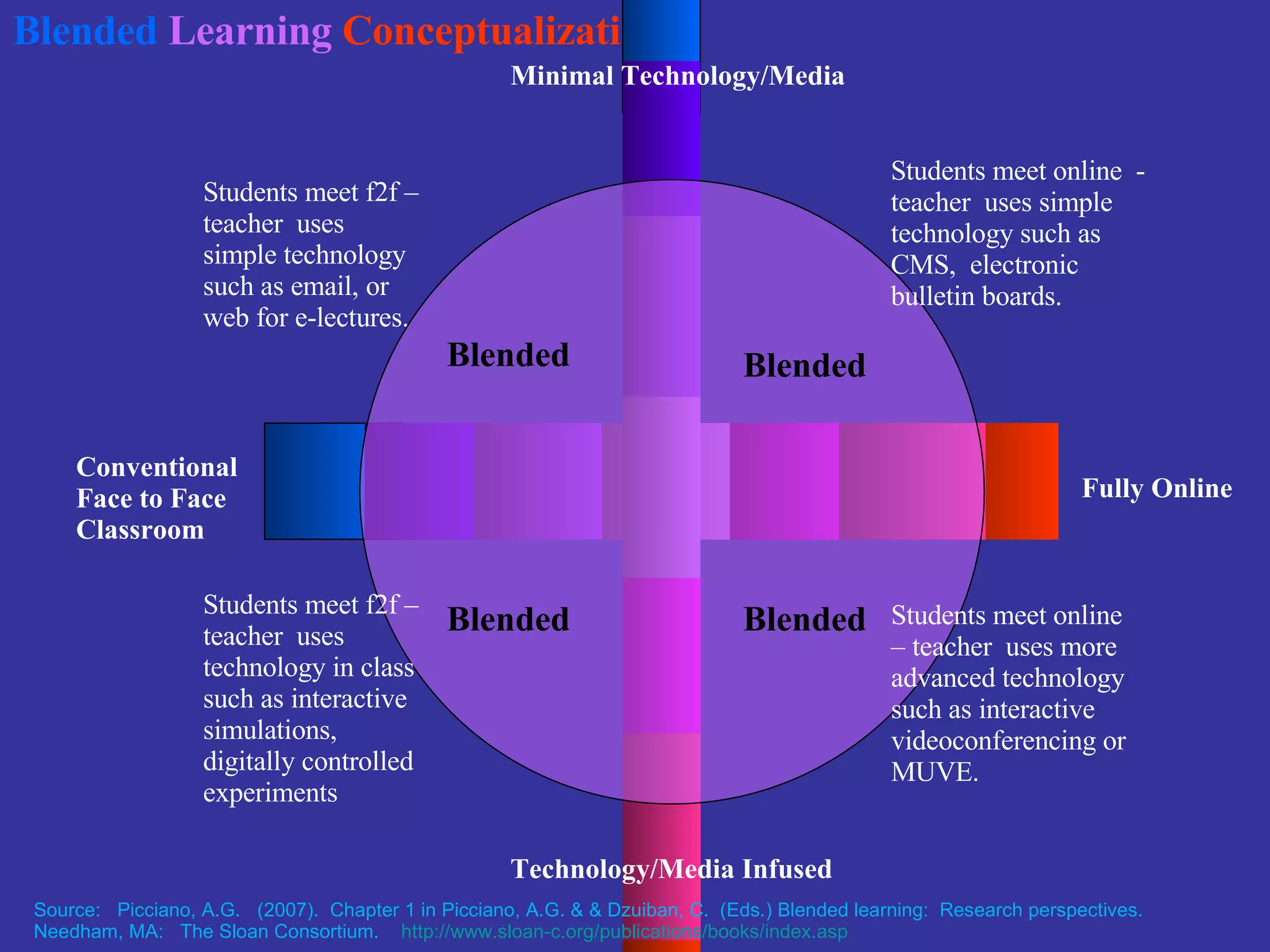
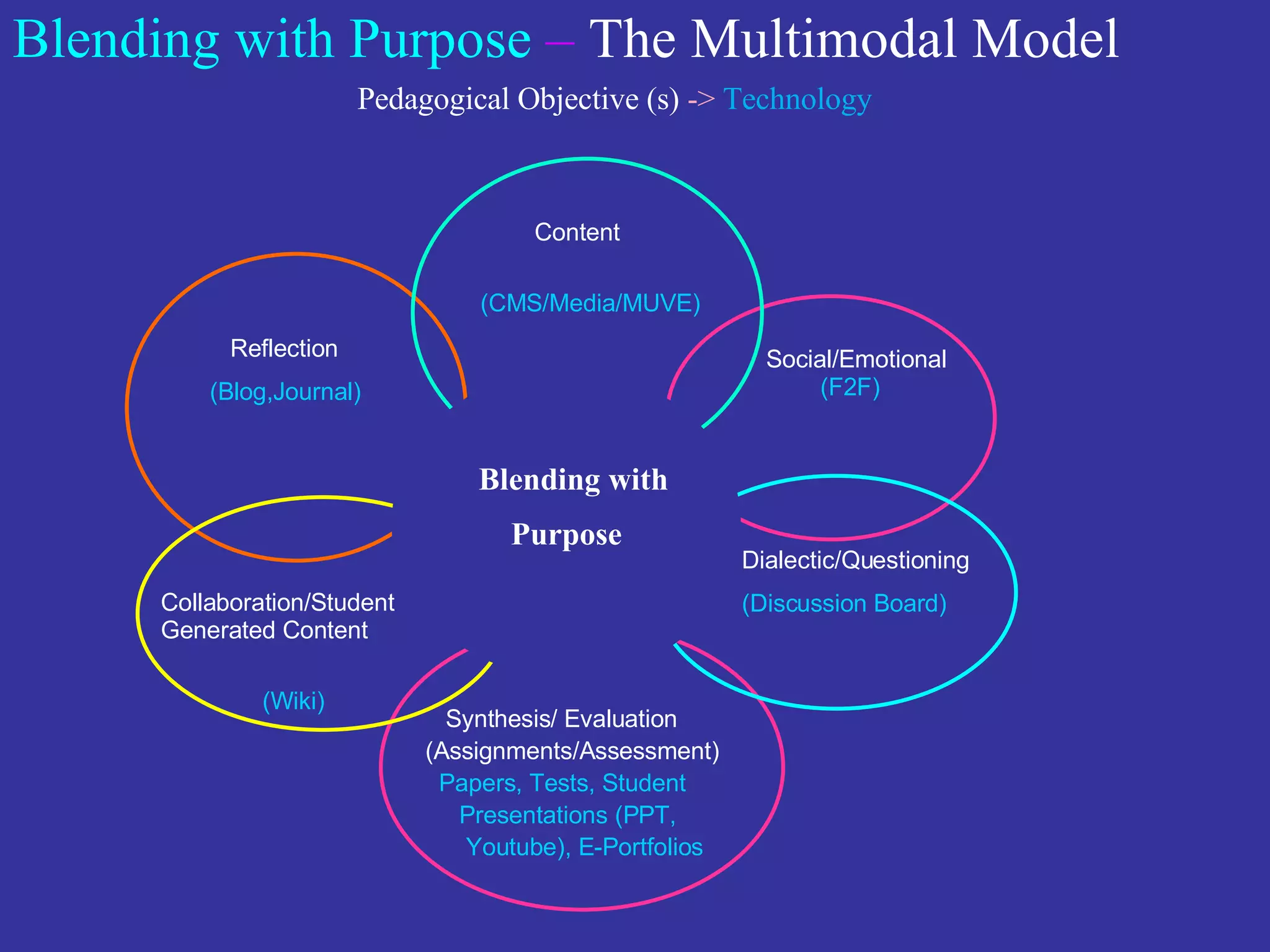
The document discusses the multimodal model of blended learning and its alignment with different learning and teaching styles. It emphasizes the importance of using multiple modalities to engage students effectively while addressing diverse learning preferences and needs. Additionally, it highlights institutional perspectives on implementing blended learning, including the evaluation of effectiveness and the potential benefits for students and faculty.