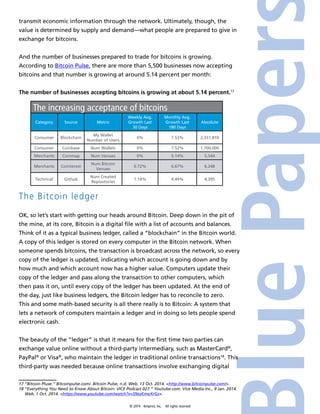
Bitcoin is a digital currency that allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for third-party intermediaries, such as banks, offering low fees and reliable payment options. Despite skepticism surrounding its value and stability, its unique security features, underpinned by cryptographic algorithms, have garnered a growing acceptance among businesses and consumers. The structure of bitcoin relies on a blockchain ledger that records all transactions, providing transparency and security while maintaining user anonymity.