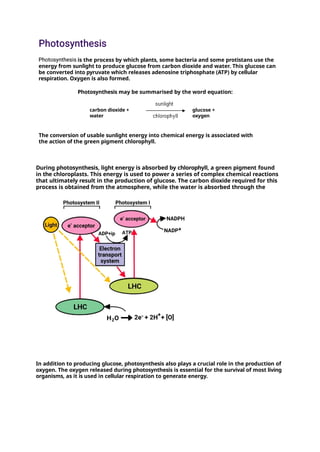
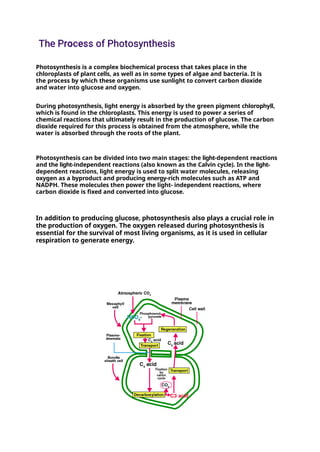
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, some bacteria, and certain protists convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. The process occurs in chloroplasts and comprises two main stages: light-dependent reactions that generate ATP and NADPH, and light-independent reactions, or the Calvin cycle, that convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules. Factors affecting photosynthesis include light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, water availability, and nutrient levels, and its significance extends to ecological balance, human agriculture, and potential biofuel production.