BIOL 364 - assignment 2
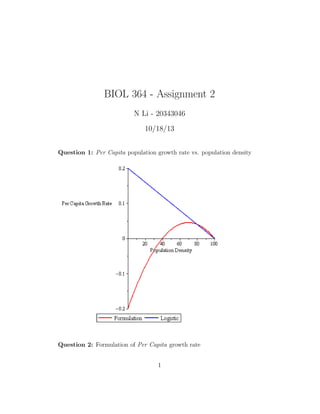
- 1. BIOL 364 - Assignment 2 N Li - 20343046 10/18/13 Question 1: Per Capita population growth rate vs. population density Question 2: Formulation of Per Capita growth rate 1
- 2. Behaviours that need to be accounted for: 1. rate of decline is curvilinear 2. decline is not monotonic 3. Per Capita growth rates increase at low population levels, then decline later 4. Allee effect accounted for We consider an existing model for our formulation: 1 N dN dt = r N C − 1 1 − N K (1) (1) where: • N: population level • C: critical population size • K: carrying capacity • r: biological rate of growth For completeness, we impose the biological constraint requiring: 0 < C < N Putting the Per Capita growth rate in functional form, we have: Rp-c = r N C − 1 1 − N K (2) note: This formulation satisfies all required behaviours (see question 1) Question 3: Inclusion of Per Capita growth rate into Logistic model To begin, we’ll work off of the the logistic model. We see that the following relation is true: Rp-c N C − 1 = r 1 − N K (3) 2
- 3. To simplify expression (3), let’s define a new parameter δ = N C − 1 With this simplification, we can relate the formulation to the logistic model by the following: dNlogistic dt = NRp-c δ (4) Question 4: Phase-Line analysis To begin, recall: dN dt = rN N C − 1 1 − N K The critical pts are: N* = 0, C, K From which, the following phase-line graph can be generated: note: for details see question 5 Question 5: Local Stability analysis Using the condition for local stability of continuous time models, we have: df dN N = N* < 0 (5) where f is given by: 3
- 4. f = rN N C − 1 1 − N K (6) Carry out the expansion: f = r N2 C − N3 CK − N + N2 K (7) Then: df dN = 2rN C − 3rN2 CK − r + 2rN K (8) It follows that: 1. df dN N =0 = −r < 0, =⇒ r > 0 is stable 2. df dN N =C = r − 1 < 0, =⇒ r < 1 is stable 3. df dN N =K = r(1 − K C ) < 0, =⇒ r > 0 is stable Analysis 1. d dt ≈ df dN N =0 gets smaller for r > 0 2. d dt ≈ df dN N =C gets larger for r > 1 3. d dt ≈ df dN N =K gets smaller for r > 0 These stability conditions =⇒ 1. N* = 0: Perturbations decrease, so 0 is stable 2. N* = C: Perturbations increase, so C is unstable 3. N* = K: Perturbations decrease, so K is stable Together, these results give rise to the Phase-Line in question 4. 4
- 5. References [1] Allee effect Model http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allee_effect(1) ∴ 5