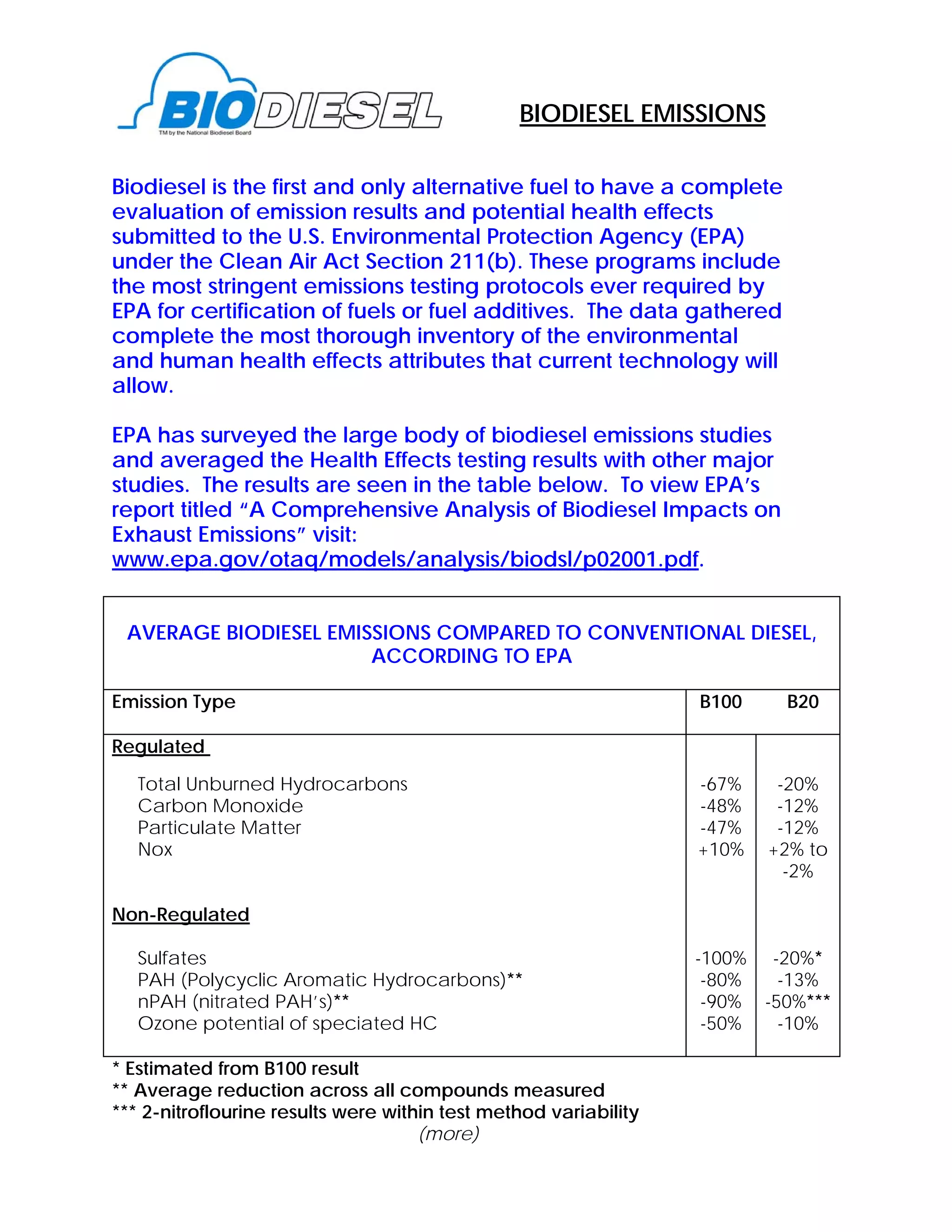
Biodiesel has been extensively tested by the EPA and is shown to significantly reduce harmful emissions compared to conventional diesel. EPA data shows biodiesel reduces particulate matter by 47% and carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons each by about 50%. It also essentially eliminates sulfur emissions and reduces cancer-causing PAHs and nPAHs by 75-90%. The only pollutant that may increase is NOx, which increases about 10% for pure biodiesel but biodiesel allows use of technologies to control NOx not possible with conventional diesel.