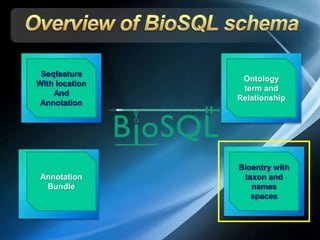
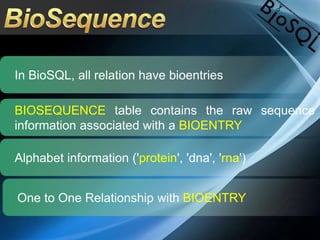
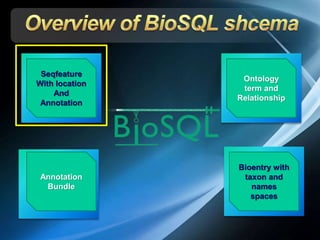
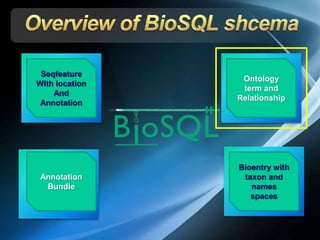
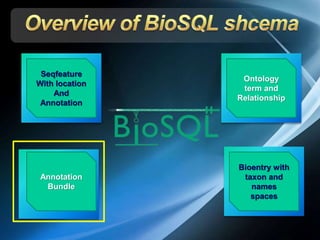
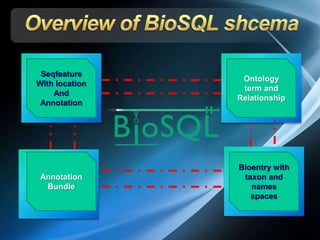
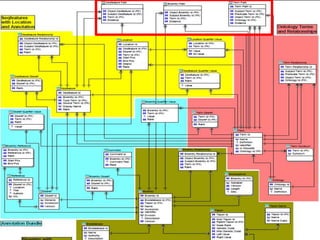
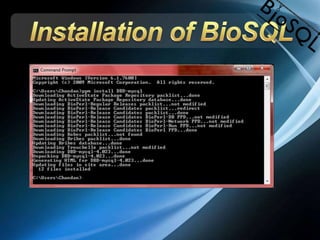
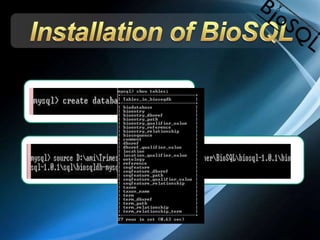
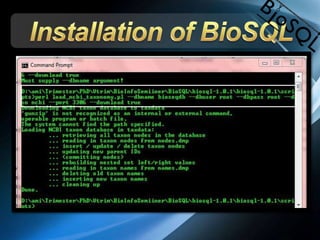
The document discusses BioSQL, a generic relational data model for storing biological data in a relational database. It provides an overview of the BioSQL schema, which defines standardized relation types to store entities like biological entries, sequences, sequence features, annotations, ontologies, and taxonomic information. The data model aims to provide a flexible yet standardized storage solution and is compatible with various programming languages. However, it is best suited for single-user installations and does not consider aspects like protein structure prediction.