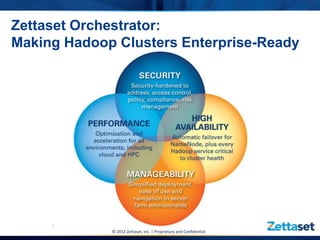
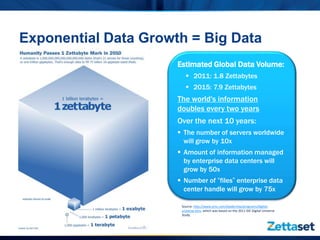
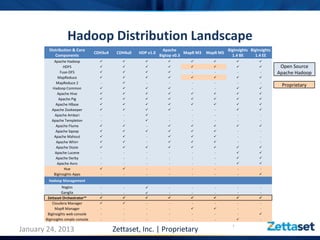
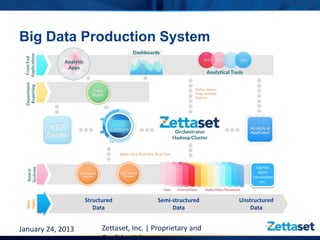
This document discusses Zettaset's initiative to create a secure Hadoop environment, highlighting the limitations of existing Apache Hadoop distributions in security and compliance. It emphasizes the need for enterprise-class security measures, including better access control and compliance management, which Zettaset Orchestrator aims to address. The summary also touches on the exponential growth of big data and the importance of threat modeling in protecting data assets.