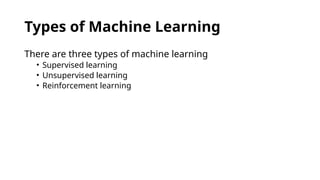
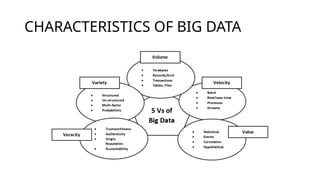
The document outlines the differences between traditional computer software and machine learning, emphasizing that machine learning relies on training with large datasets rather than explicit coding. It describes the types of machine learning, such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, along with various applications for these techniques. Additionally, it discusses characteristics and importance of big data, encapsulated by the concepts of volume, velocity, veracity, and value.