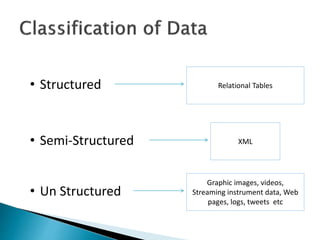
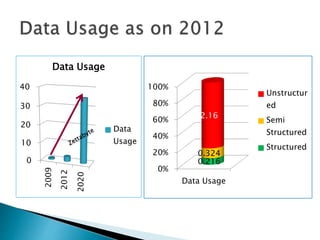
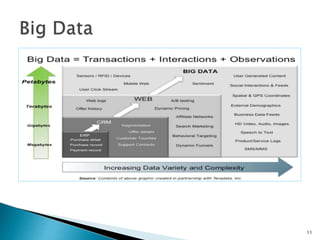
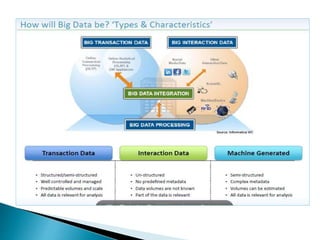
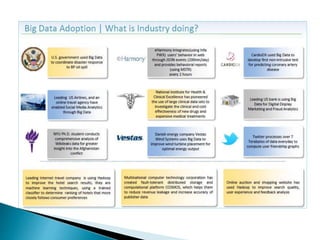
The document discusses the rise of real-time analytics processing (RTAP) and big data. It notes that big data comes from a variety of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured sources and is growing exponentially. Examples show huge amounts of data being generated every day from sources like social media, sensors, and mobile devices. It emphasizes that not all this unstructured data is useful and highlights challenges like integrating diverse data sources and adapting solutions quickly. The document promotes RTAP platforms as a way to leverage universal data sources, power sophisticated analytics, and gain business agility and value from large and variable datasets.