Embed presentation



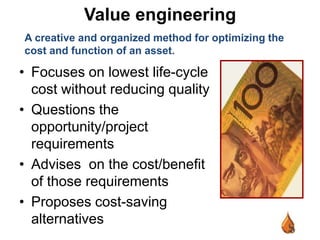
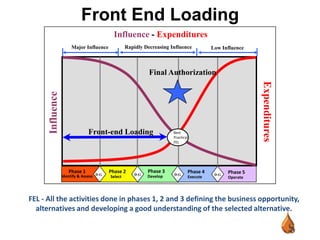
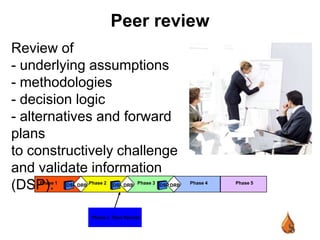


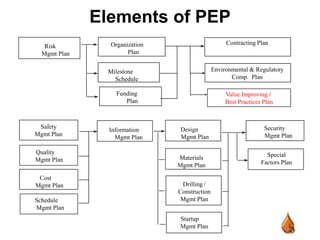
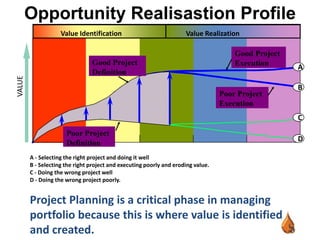

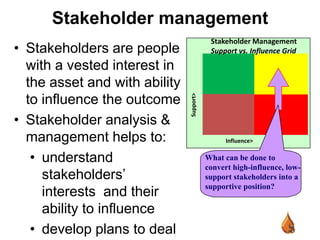




This document outlines best practices for upstream asset management in the oil and gas industry. It discusses defining assets, both tangible like reservoirs and facilities, and intangible like data and relationships. It emphasizes the importance of tools, value engineering, peer review, decision review boards, project execution plans, stakeholder management, benchmarking, and lessons learned reviews to effectively plan, develop, operate, and improve assets over their lifecycle. The goal is to integrate disciplines, make sound decisions, ensure safety, cost efficiency, and operational excellence.














