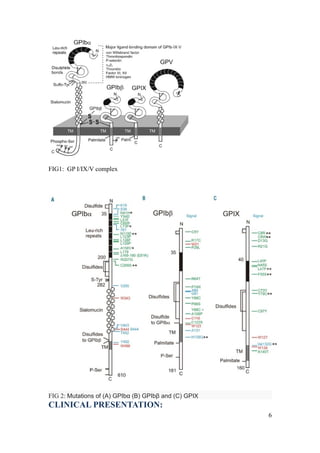
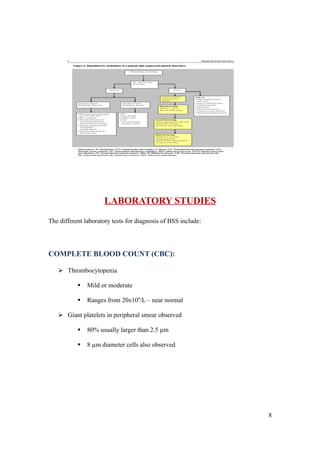
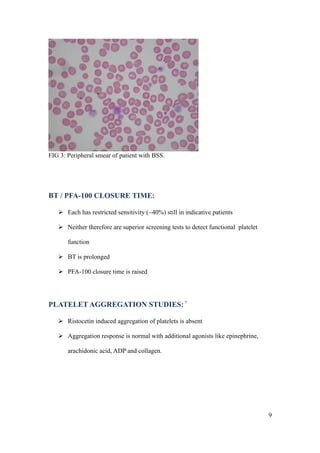
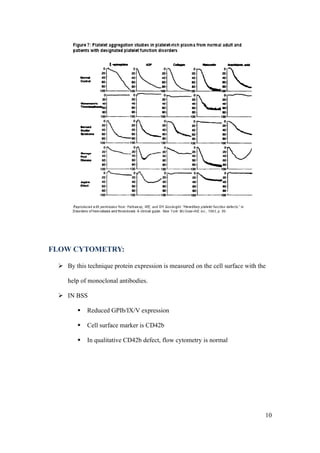
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare inherited bleeding disorder characterized by thrombocytopenia and giant platelets. It is caused by mutations in the glycoprotein Ib/IX/V complex, which binds von Willebrand factor and is essential for platelet adhesion. Patients present with bruising, epistaxis, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Diagnosis involves finding giant platelets, prolonged bleeding times, and absent ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. Management focuses on prevention of bleeding episodes through hormonal contraceptives, antifibrinolytics, and desmopressin. Severe bleeding may require platelet transfusions or recombinant factor VIIa.