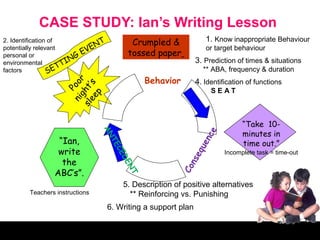
This document provides information on behavioral management strategies for children with challenging behaviors. It discusses functional behavior assessments and using their components to develop behavioral plans. Some key points covered include identifying the antecedents and functions of problematic behaviors, using positive reinforcement and modeling to teach new behaviors, setting clear classroom rules, and creating individualized behavior modification plans with rewards for improving targeted behaviors. The overall aim is to understand why behaviors occur and develop supports to help children learn more appropriate ways of interacting.