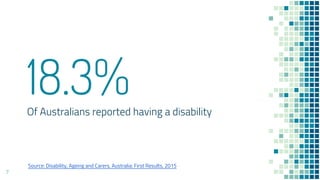
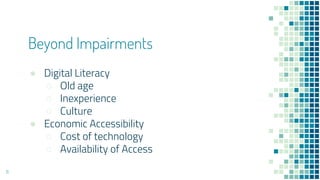
The document serves as a beginner's guide to digital accessibility, highlighting its importance and real-world implications for individuals with disabilities. It covers legal considerations, core design principles, and practical steps to create accessible digital products, emphasizing empathy and collaboration among teams. The guide also includes exercises for understanding accessibility firsthand and encourages ongoing learning and engagement with accessibility experts.













![Case: Sydney Olympics Website (1999)
“The HREOC's ruling set a precedent that creating a
website intended for use by and to inform the
general public, where such a website is more
accessible to a sighted user than the same intent
and information is not available for a user who is
blind by virtue of disability” [Applies to
Commonwealth Government Websites]
17
Source: A Cautionary Tale of Inaccessibility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginnersguidetoaccessibility-170705063737/85/Beginners-Guide-to-Accessibility-17-320.jpg)