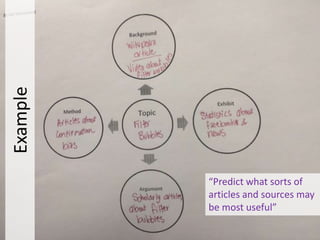
The document introduces the BEAM method for organizing research sources, which categorizes sources as Background, Exhibit/Evidence, Argument, or Method. It defines each BEAM element and provides examples of the types of sources that could fit into each category. The document then guides the reader through applying the BEAM framework to brainstorm potential sources for their own research topic.