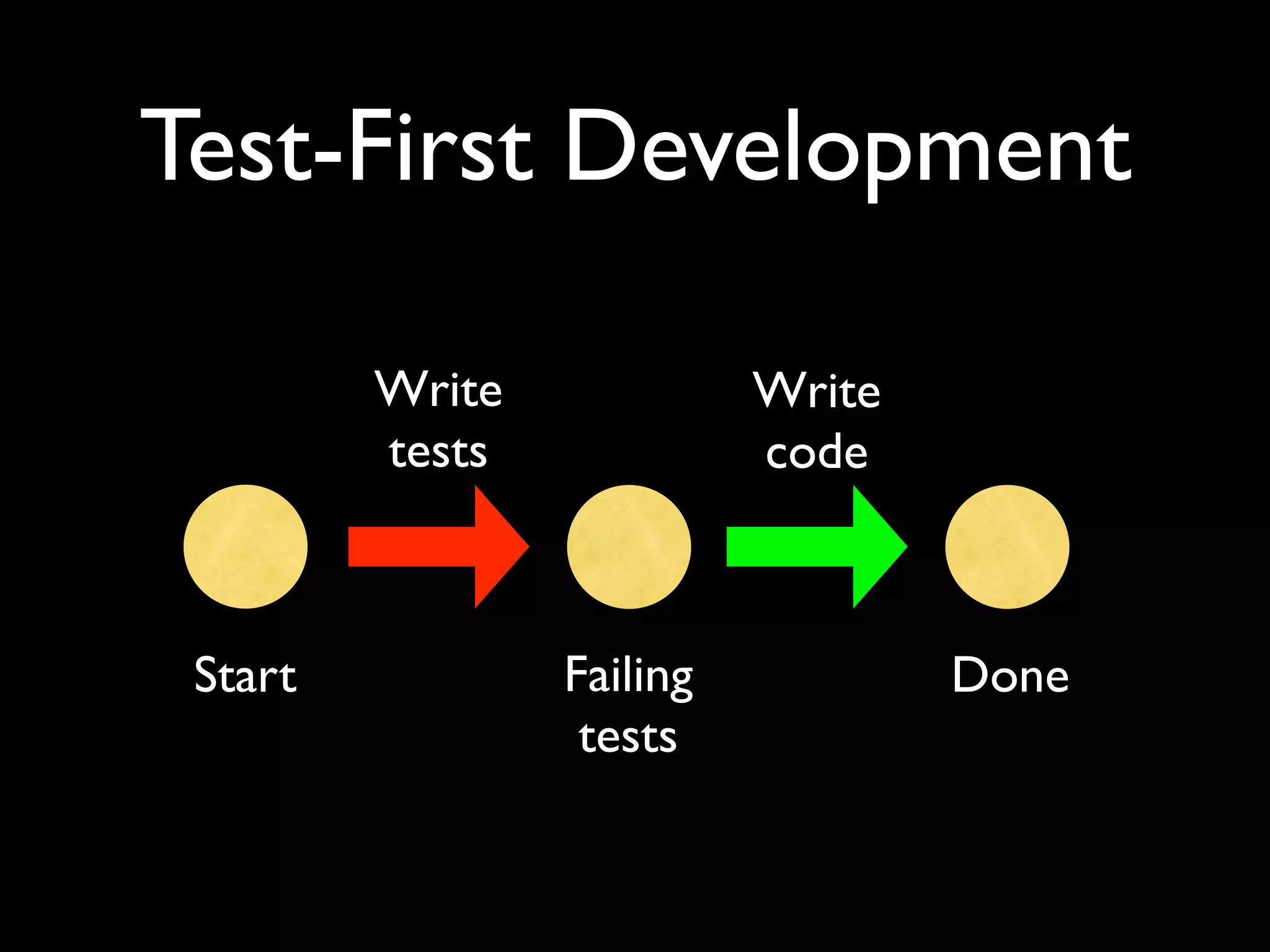
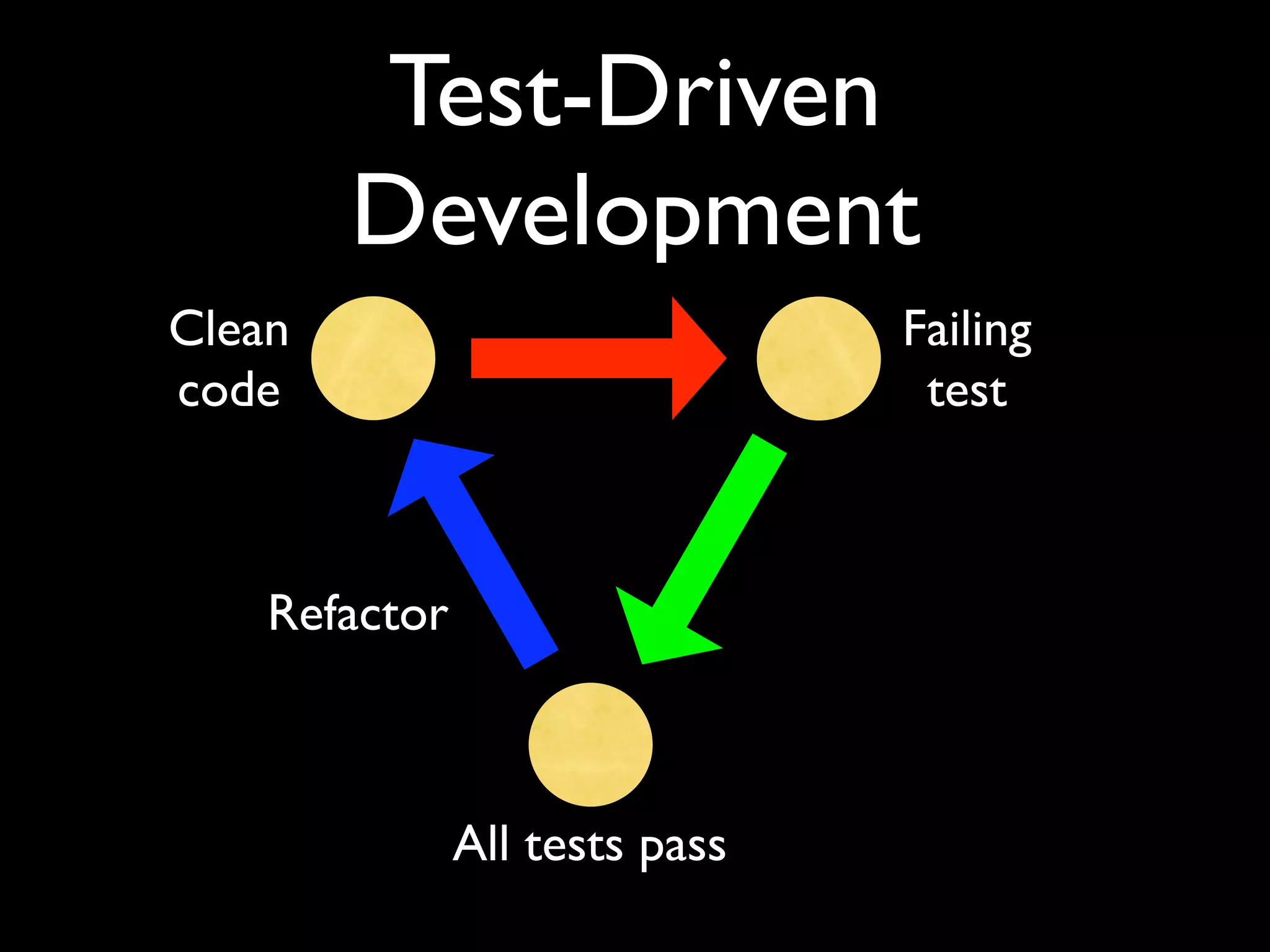
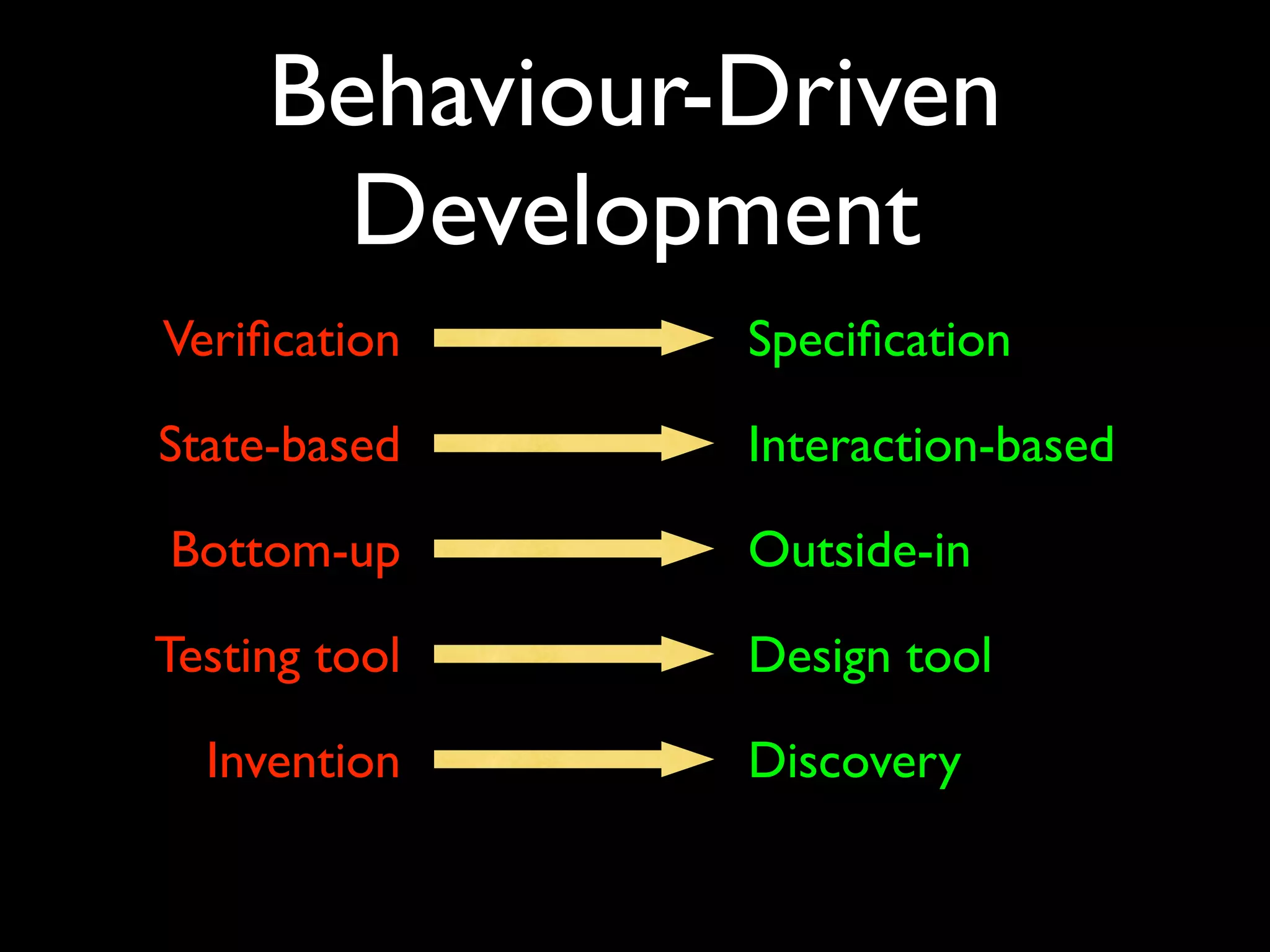
This document provides an overview of test-driven development (TDD) and behavior-driven development (BDD), beginning with common misconceptions about TDD and how it differs from traditional testing approaches. It discusses how TDD is a design activity that focuses on emergent design and driving design with tests. Key principles of TDD/BDD are explained, such as writing tests before code, the red-green-refactor cycle, and outside-in development. The document also covers test automation, mock objects, different testing tools and frameworks, and best practices for TDD/BDD.




















![Describing Features
Given /^an account called '(w*)' containing £(d*)$/ do |name, amount|
@@accounts ||= {}
@@accounts[name] = Account.new(amount.to_i)
end
When /^I transfer £(d*) from (w*) to (w*)$/ do |amount, from, to|
AccountController.new.transfer @@accounts[from], @@accounts[to], amount.to_i
end
Then /^the '(w*)' account should contain £(d*)$/ do |name, amount|
@@accounts[name].balance.should == amount.to_i
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdd-for-dso-1227123516572504-8-121204154440-phpapp02/75/Bdd-for-dso-1227123516572504-8-29-2048.jpg)