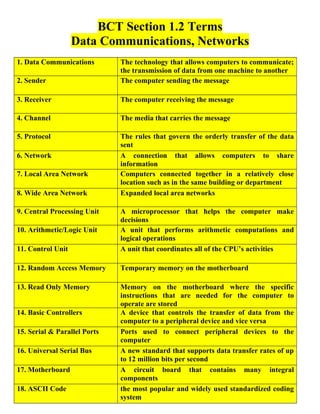
This document defines key terms related to data communications and computer networks. It describes terms such as sender, receiver, channel, protocol, network, local area network, wide area network, components of a central processing unit, types of computer memory, basic controllers, ports, buses, motherboards, ASCII code, bytes, megabytes, and gigabytes. The document provides definitions for 20 important data communications and computer networking terms.