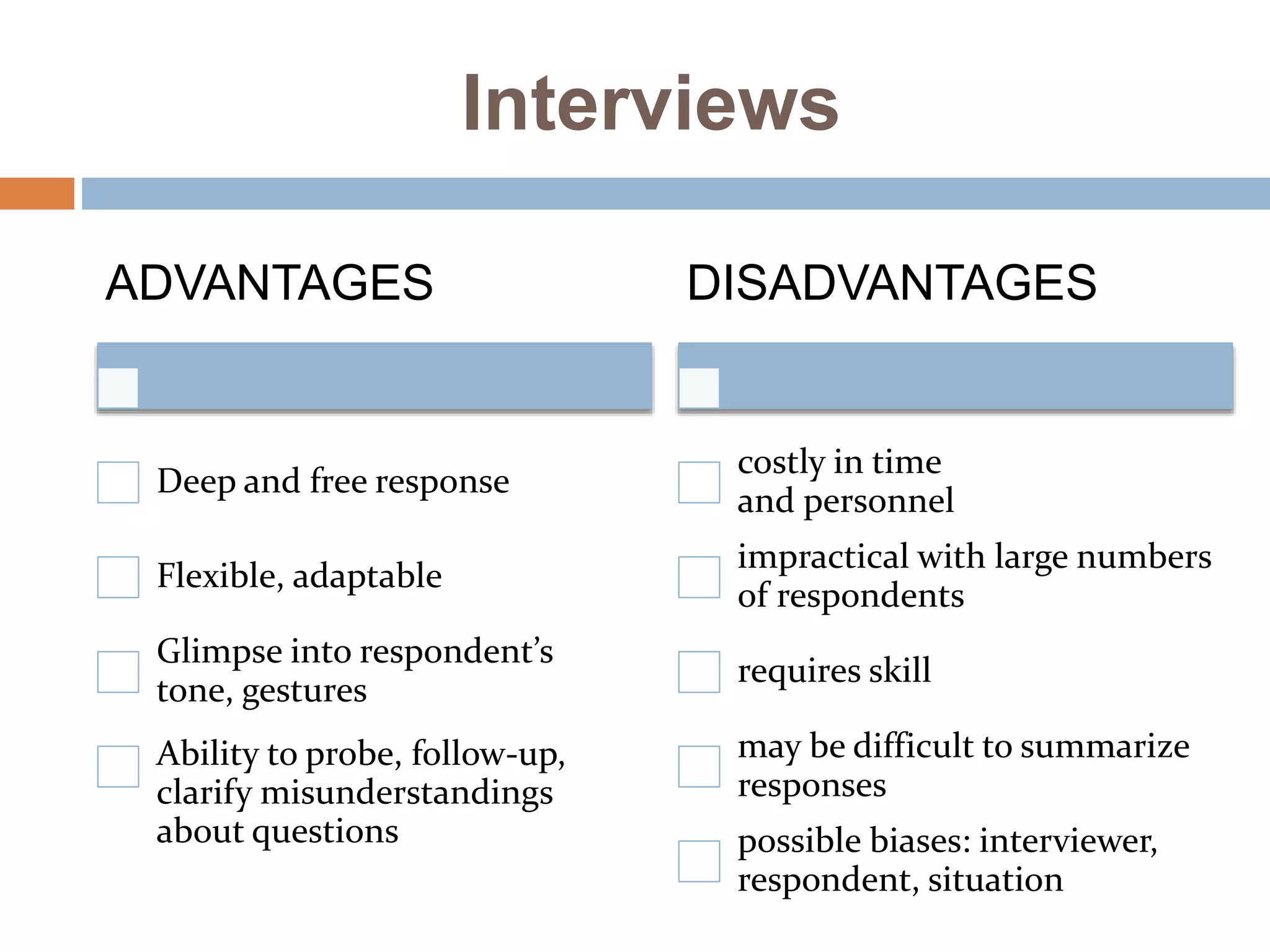
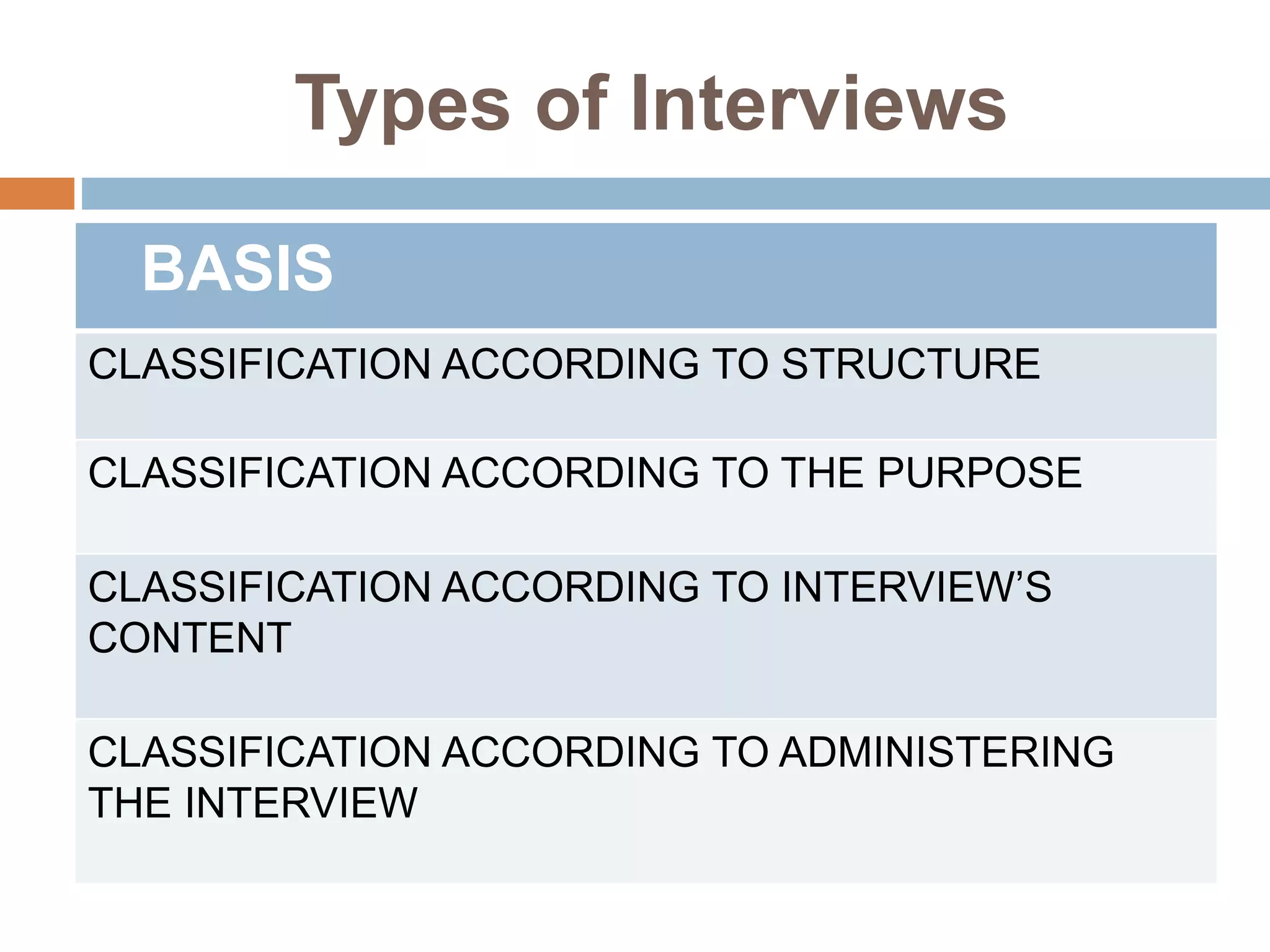
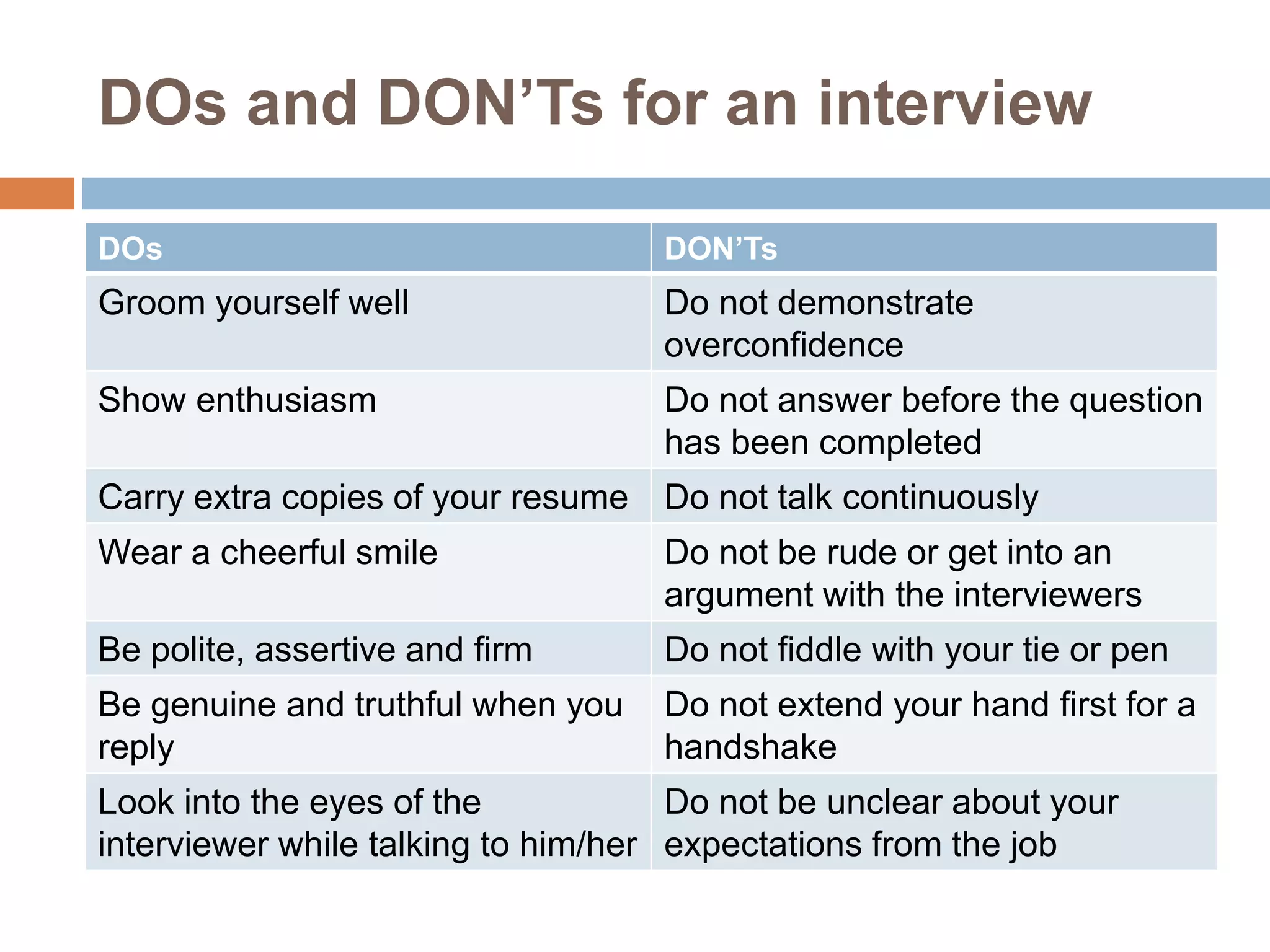
The document discusses different types of interviews. It begins by defining an interview as a formal meeting where a person is asked questions, typically for a job or educational program. There are then several classifications of interviews discussed: by structure (structured, unstructured, semi-structured); by purpose (stress, appraisal, exit); by administration (one-on-one, sequential, group, panel); and by content (situational, job-related, behavioral, psychological). Common interview styles like telephone and video conferencing are also noted. The document provides tips for interviewees on preparation, etiquette during the interview, and following up after.