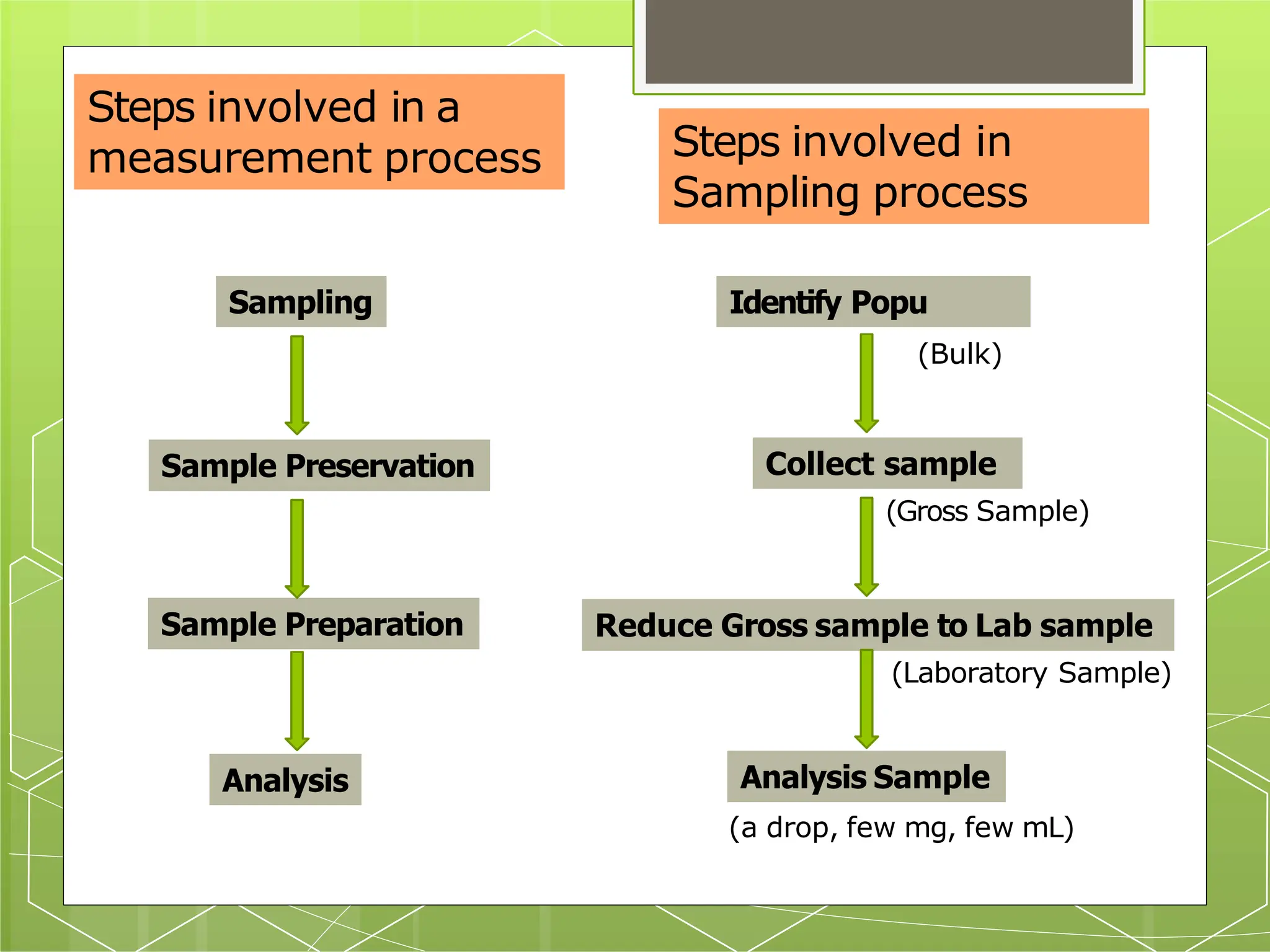
The document discusses the concepts of sampling, including types of samples (solid, liquid, gas) and the importance of homogeneity to ensure accurate analysis. It outlines the process of reducing a gross sample to a laboratory sample and lists different methods of analysis based on sample size. Key considerations for effective sampling and sample preservation are emphasized to maintain the integrity of the samples.