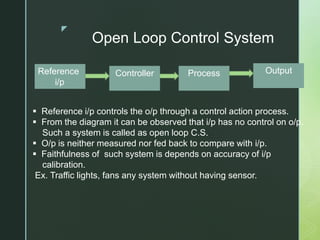
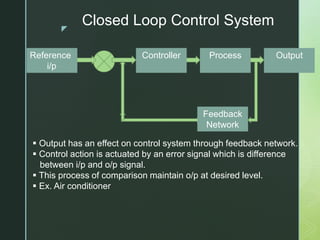
A control system uses feedback to regulate physical components and achieve a desired output from a given input. It has an input, output, and control action to achieve objectives. Control systems can be open-loop or closed-loop. Open-loop systems do not measure or feedback output, so accuracy depends on input calibration. Closed-loop systems compare input to measured output and use error signals to maintain output at the desired level, making them more accurate but also more complex and expensive.


![A control system must have :
Input
Output
Ways to obtain i/p and o/p objectives
Control action
Any system can be characterised mathematically by
1. Transfer Function
2. State Model
Laplace transform of o/p
Transfer Function=
Laplace transform of i/p Initial
condition=0
L[c(t)]
L[r(t)]
=
C(s)
R(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slideshare1-180307194811/85/Basics-of-Control-System-3-320.jpg)