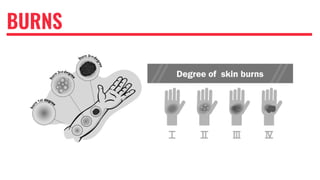
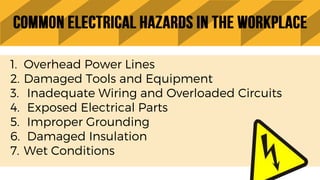
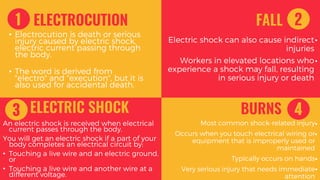
The document provides guidance on safety procedures for hazardous activities and industries. It discusses different types of hazardous energy including electrical, chemical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and thermal energy. It outlines the steps to develop a hazardous energy control program which includes gathering information, performing task and hazard analyses, implementing controls, and training employees. It also discusses lockout/tagout procedures and provides electrical safety tips for construction workers.