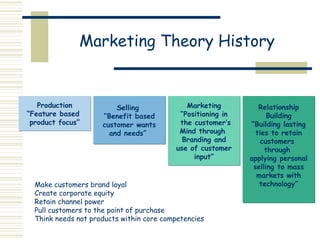
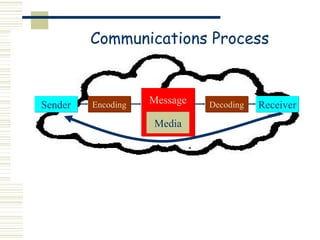
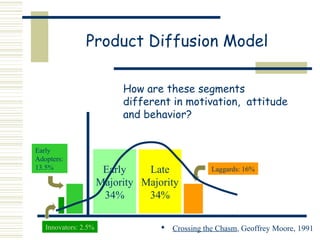
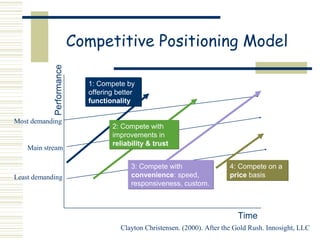
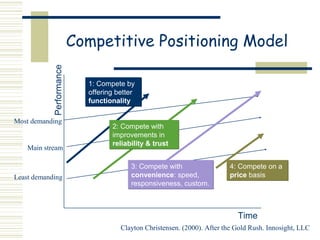
Marketing is the process of identifying, stimulating, and satisfying customer needs and wants. It has evolved from a production focus to a customer focus, positioning products in customers' minds through branding and using customer input. The goal is to build lasting customer relationships through personal selling and technology to retain customers. Basic marketing frameworks include analyzing the marketing environment, communications processes, message effectiveness, customer profiles, buying stages, product adoption rates, competitive positioning, and developing marketing communications strategies.