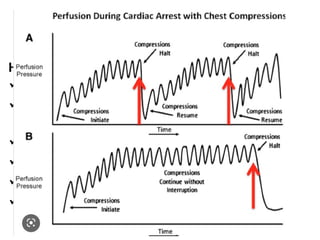
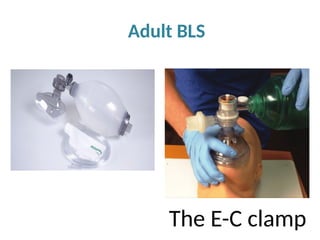
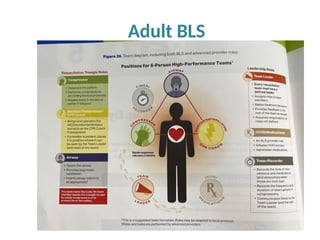
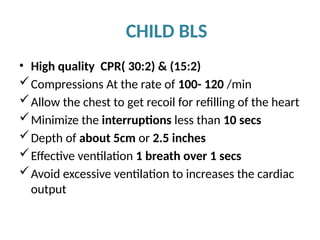
The document outlines the principles and procedures of Basic Life Support (BLS) for various age groups, highlighting the importance of immediate response to cardiac arrest and choking scenarios. It details the steps for adult and child BLS, including CPR techniques, the use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED), rescue breathing, and considerations for special situations such as pregnancy. Importantly, it emphasizes the chain of survival, calling for early emergency response activation and effective teamwork during resuscitation efforts.