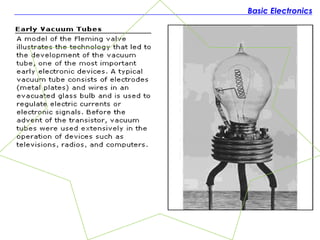
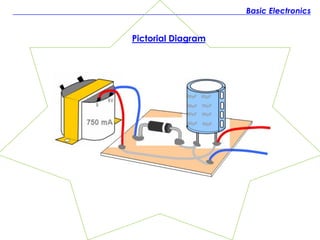
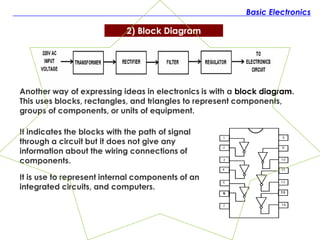
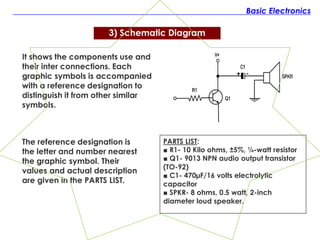
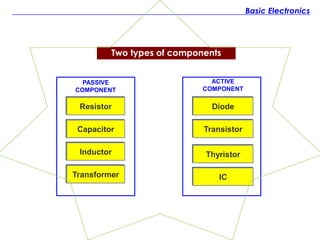
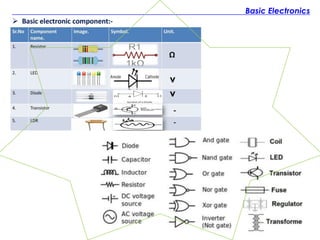
The document discusses the history and fundamentals of electronics, highlighting key developments such as Thomas Edison's discovery of the 'Edison effect' in 1883 and the demonstration of the first transistor in 1947 by Walter H. Brattain and John Bardeen. It explains basic electronic concepts, including circuit diagrams like pictorial, block, and schematic diagrams used for illustrating electronic components and their wiring. Additionally, it categorizes electronic components into passive and active types, providing examples and specifications for each.