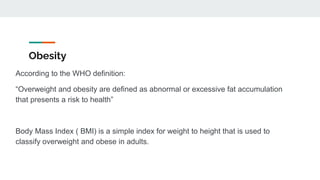
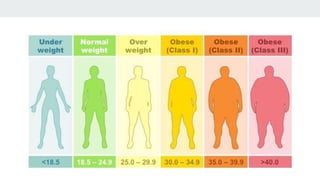
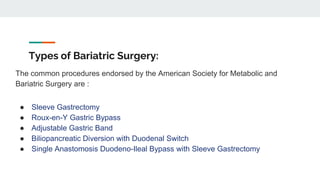
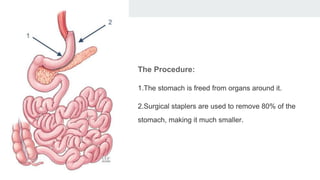
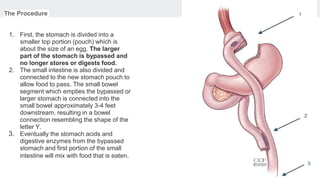
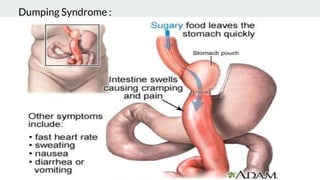
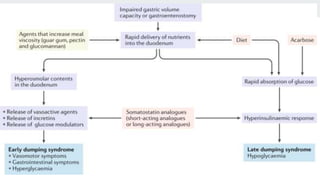
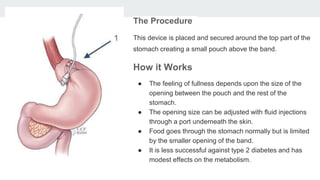
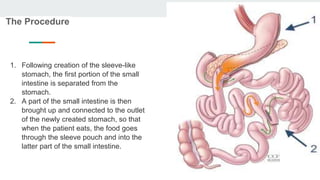
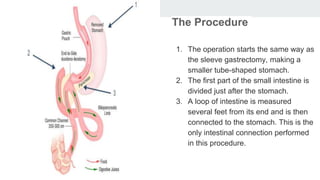
Bariatric surgery procedures like sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding are recommended for individuals with a BMI over 35 or over 30 with obesity-related conditions. These procedures create a smaller stomach pouch or bypass part of the small intestine to induce weight loss. Sleeve gastrectomy removes 80% of the stomach to restrict intake. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass divides the stomach and reconnects the small intestine to bypass part of the stomach. The adjustable gastric band constricts the top of the stomach but can require frequent adjustments. All procedures aim to treat obesity and related diseases but have risks like nutritional deficiencies or complications.