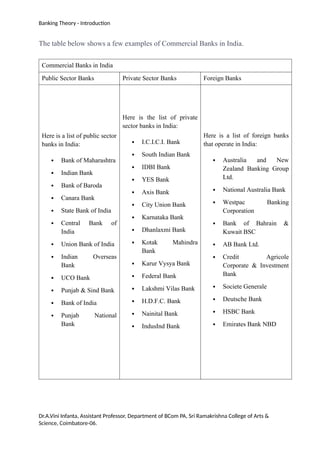
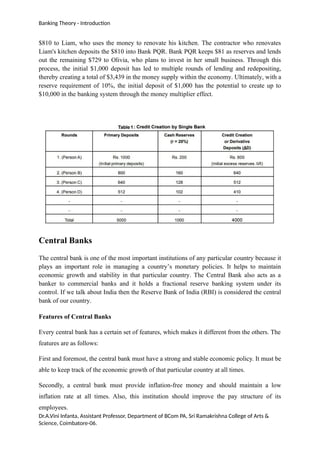
Banking refers to financial institutions providing services like deposit acceptance, loans, and transaction facilitation essential for economic activity. In India, banks are classified into types including central banks, commercial banks, cooperative banks, and payment banks, each with specific roles and services. The document discusses various banking functions, types of bank accounts, and the concept of credit creation within the banking system.