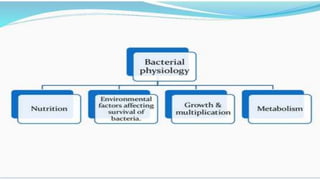
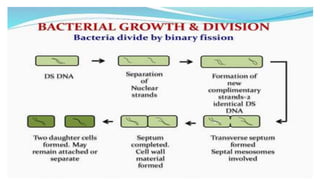
Bacterial physiology and genetics were discussed. Key points include:
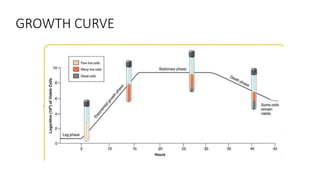
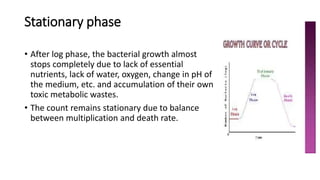
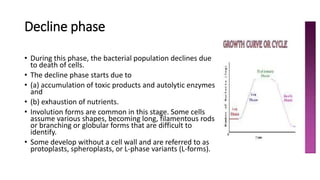
1) Bacteria grow through an orderly increase in constituents and multiply through cell division. Growth is measured by a growth curve with four phases: lag, log, stationary, and decline.
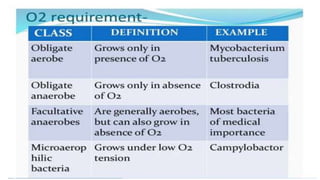
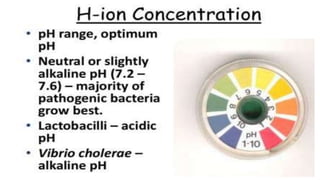
2) Bacteria require nutrients, temperature, oxygen levels, and other environmental factors for growth.
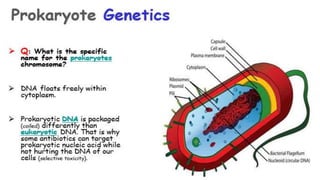
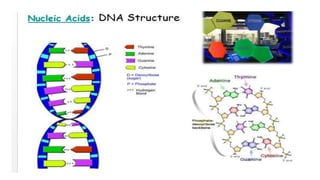
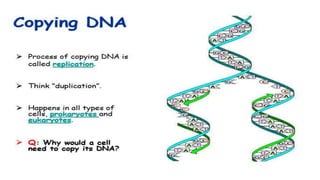
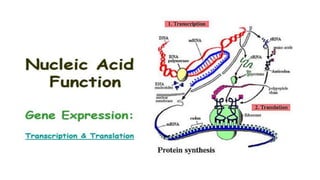
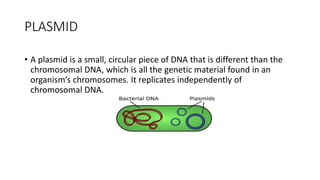
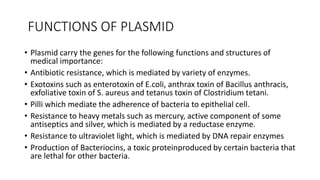
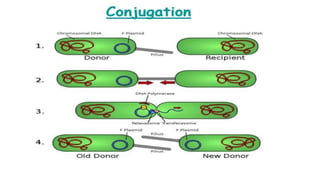
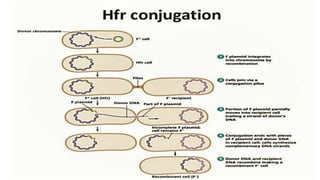
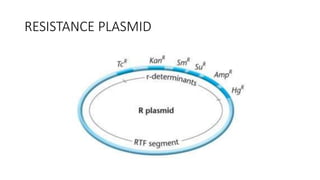
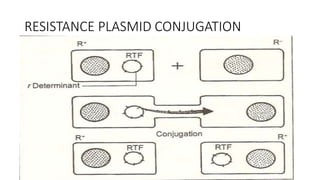
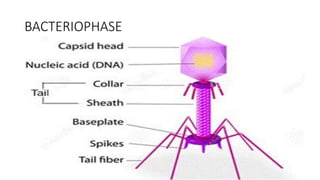
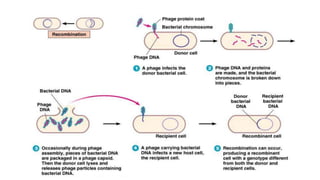
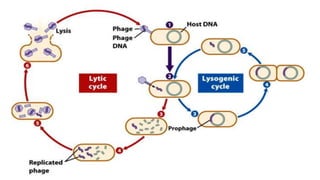
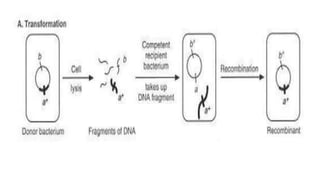
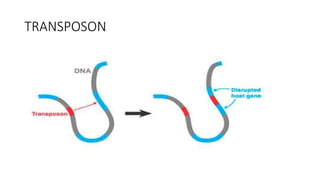
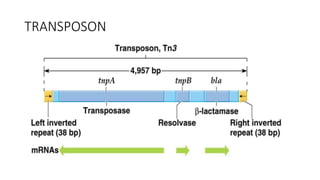
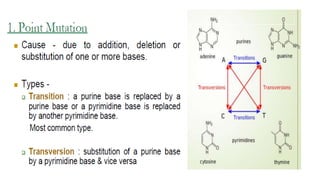
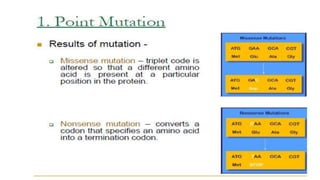
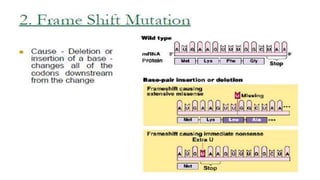
3) Genetic variations occur through mutations, conjugation, transduction, and transformation. Plasmids and transposons allow horizontal gene transfer.
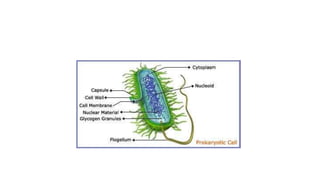
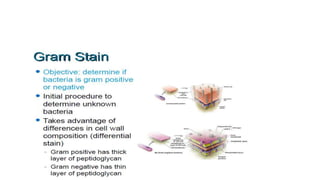
4) Staining techniques like Gram staining and acid-fast staining are used to differentiate bacteria based on cell wall structure.