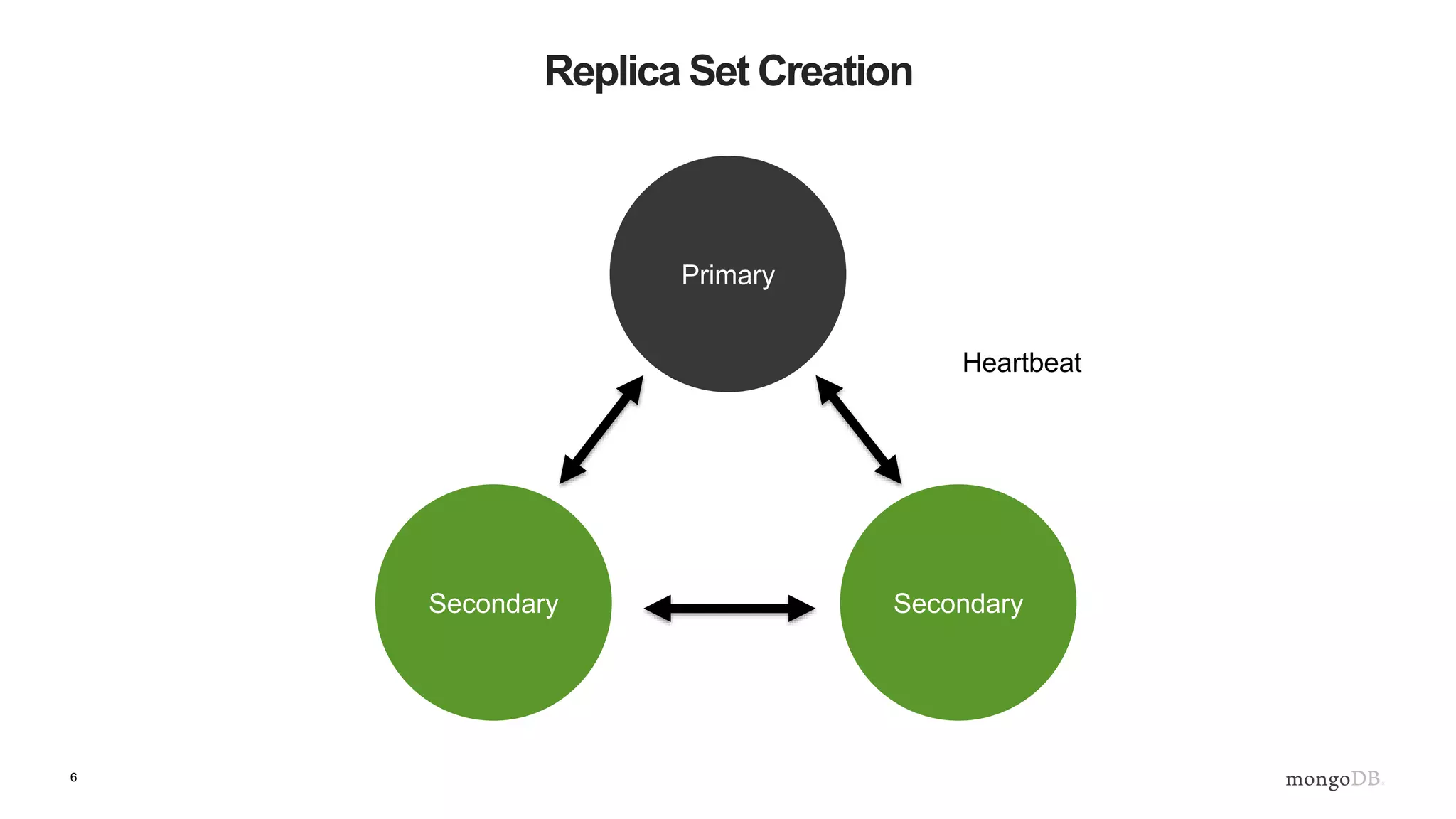
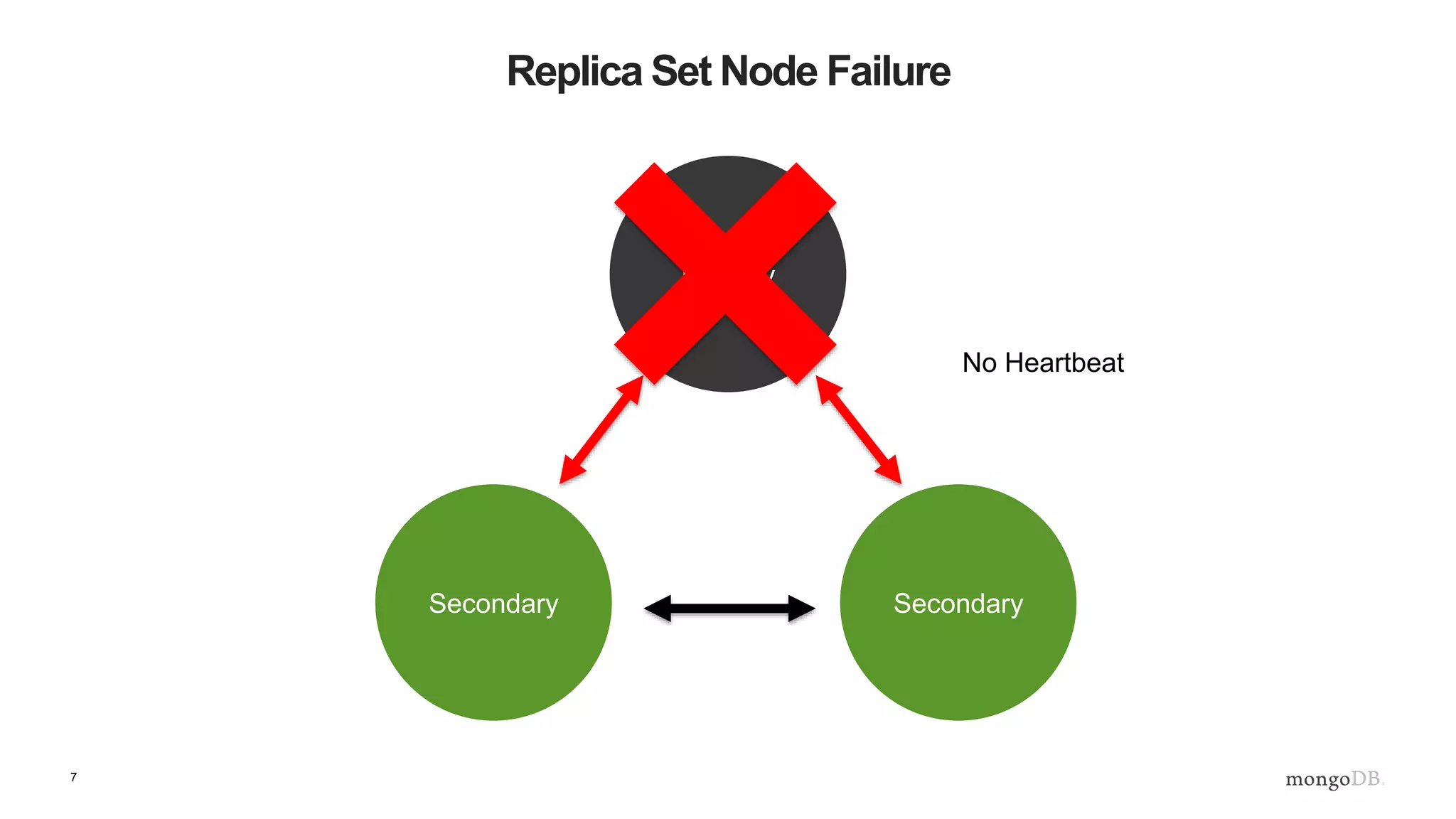
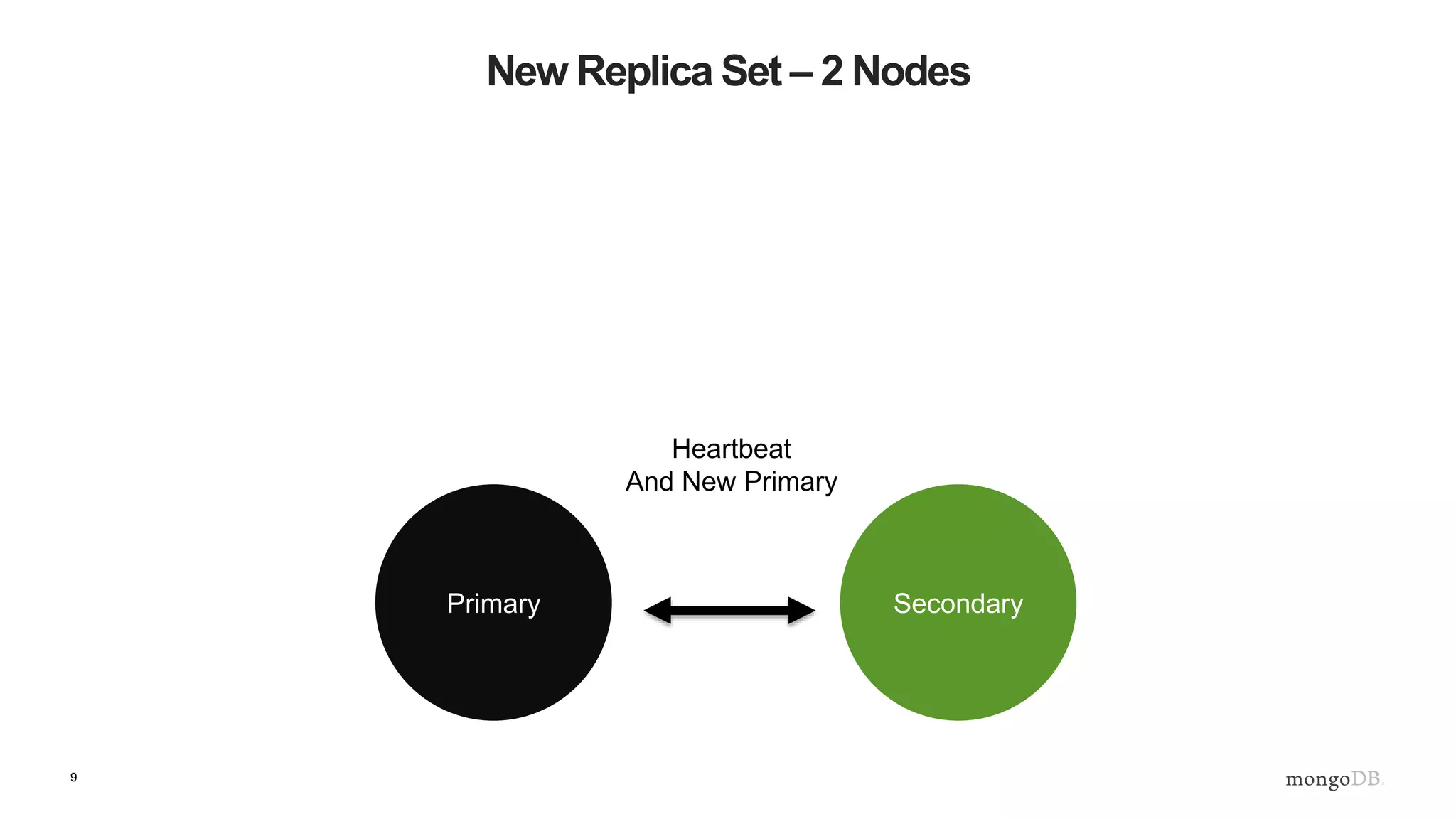
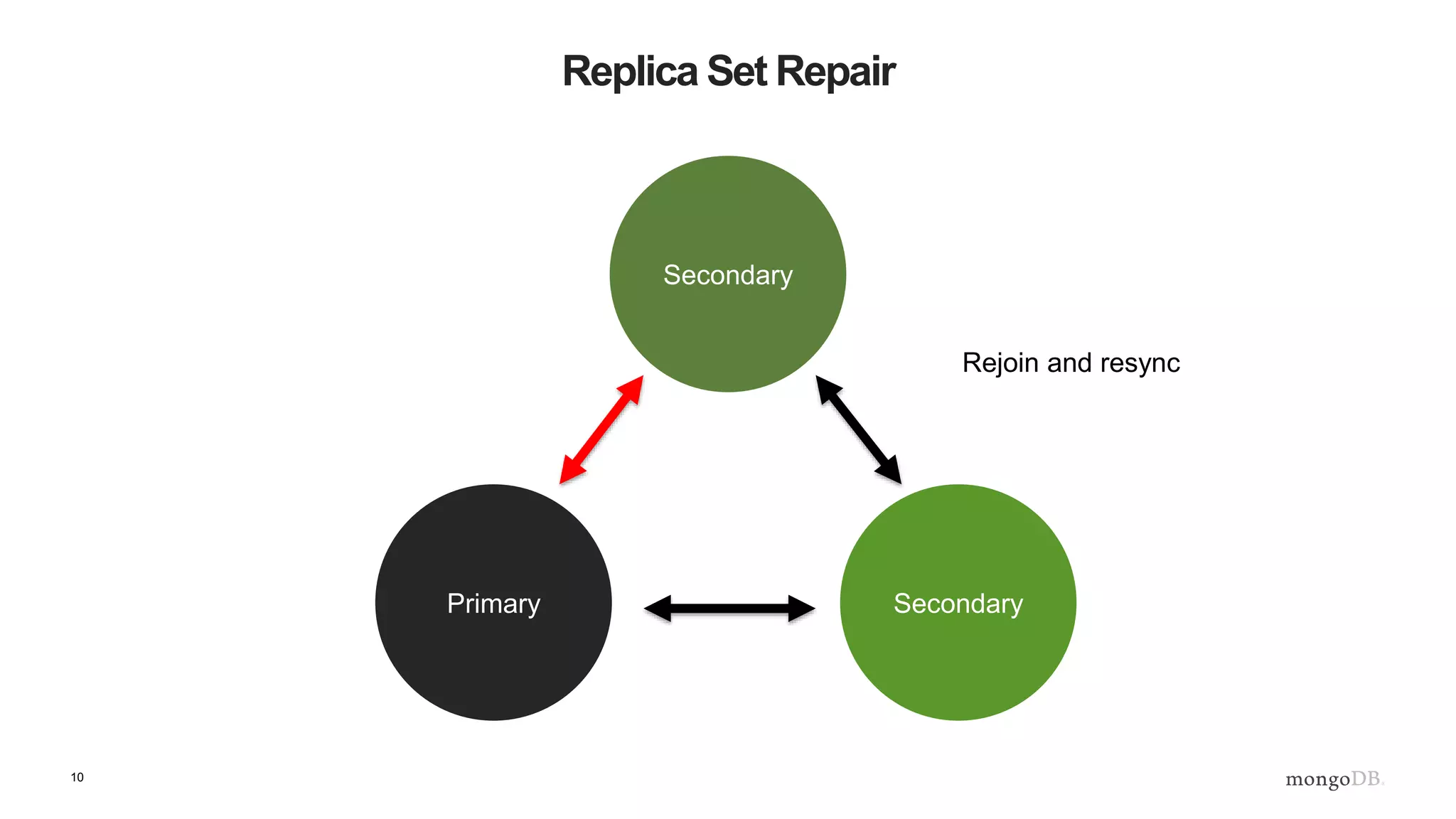
The document provides an overview of MongoDB's replica sets, explaining their importance for data durability and high availability. It covers the lifecycle of replica sets, client-side interactions, and error handling protocols in development. Additionally, it includes practical examples and references to further reading on server discovery and monitoring in MongoDB.

















![23
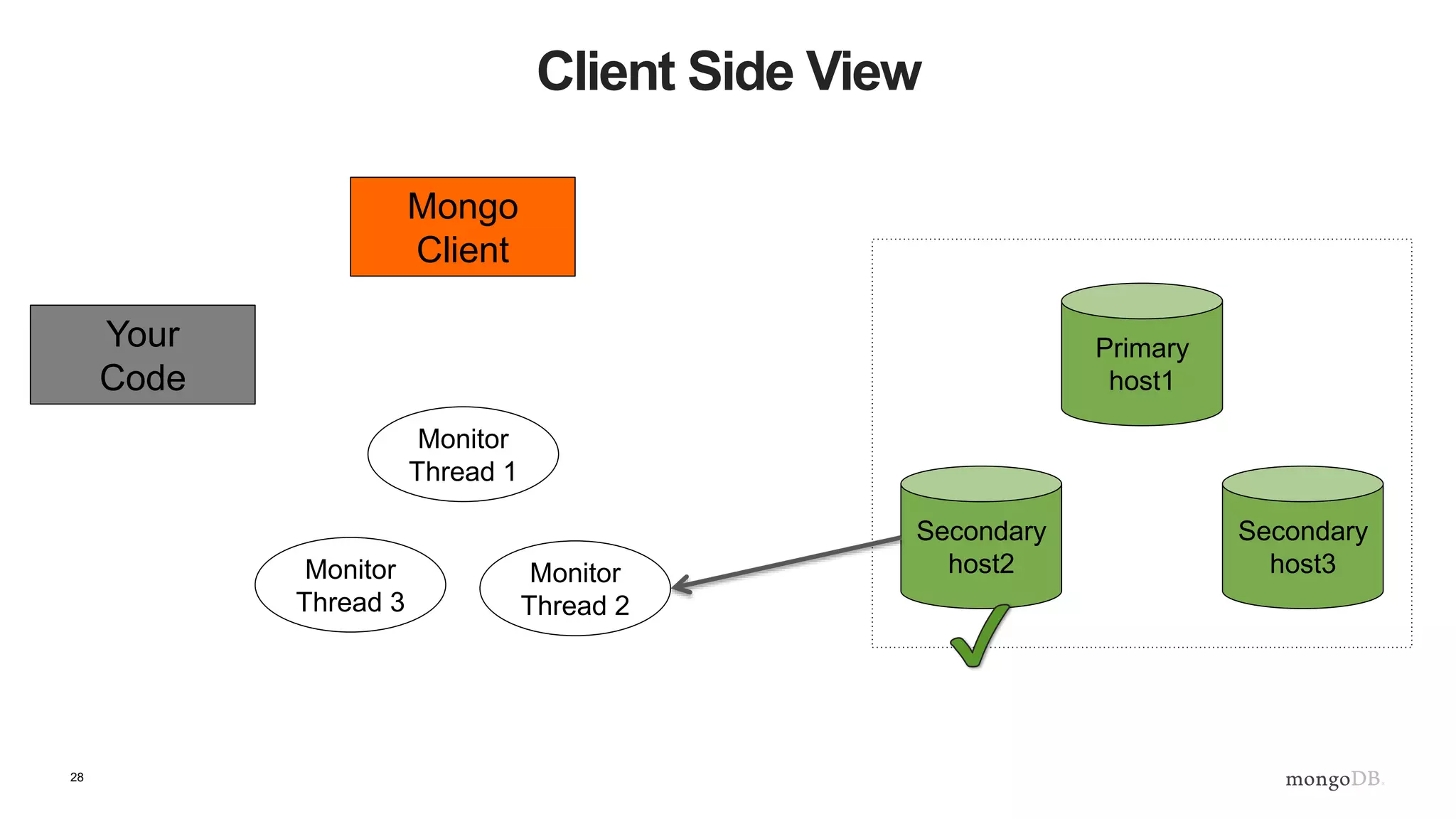
Client Side View
Secondary
host2
Secondary
host3
Primary
host1
Mongo
Client
Monitor
Thread 1
Monitor
Thread 2
{ ismaster : False,
secondary: True,
hosts : [ host1, host2, host3 ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b2b-webinar-3-replica-sets-1-170518103133/75/Back-to-Basics-German-3-Einfuhrung-in-Replica-Sets-23-2048.jpg)
![24
What Does ismaster show?
>>> pprint.pprint( db.command( "ismaster" ))
{u'hosts': [u'JD10Gen-old.local:27017',
u'JD10Gen-old.local:27018',
u'JD10Gen-old.local:27019'],
u'ismaster' : False,
u'secondary': True,
u'setName' : u'replset',
…}
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b2b-webinar-3-replica-sets-1-170518103133/75/Back-to-Basics-German-3-Einfuhrung-in-Replica-Sets-24-2048.jpg)







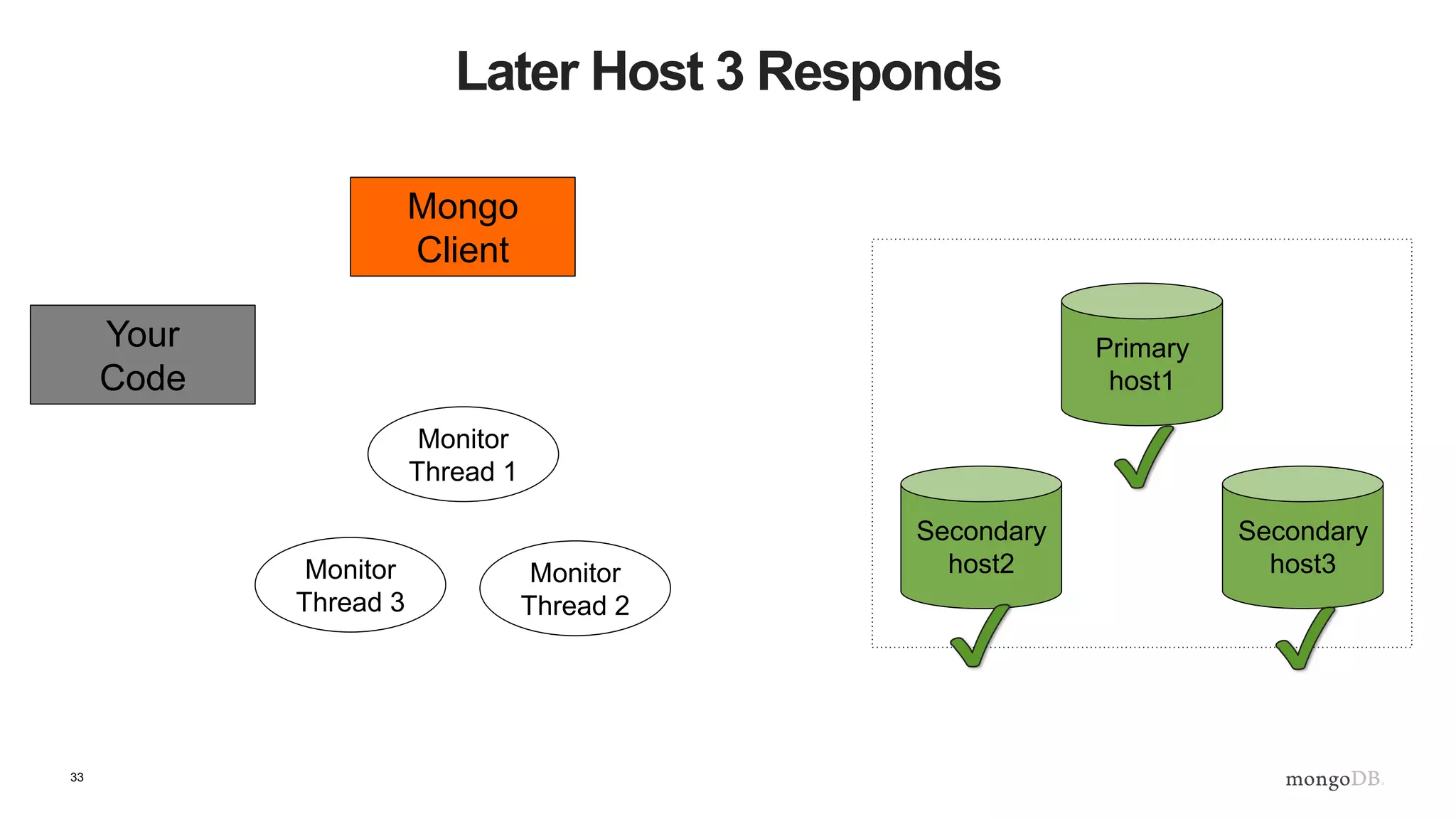

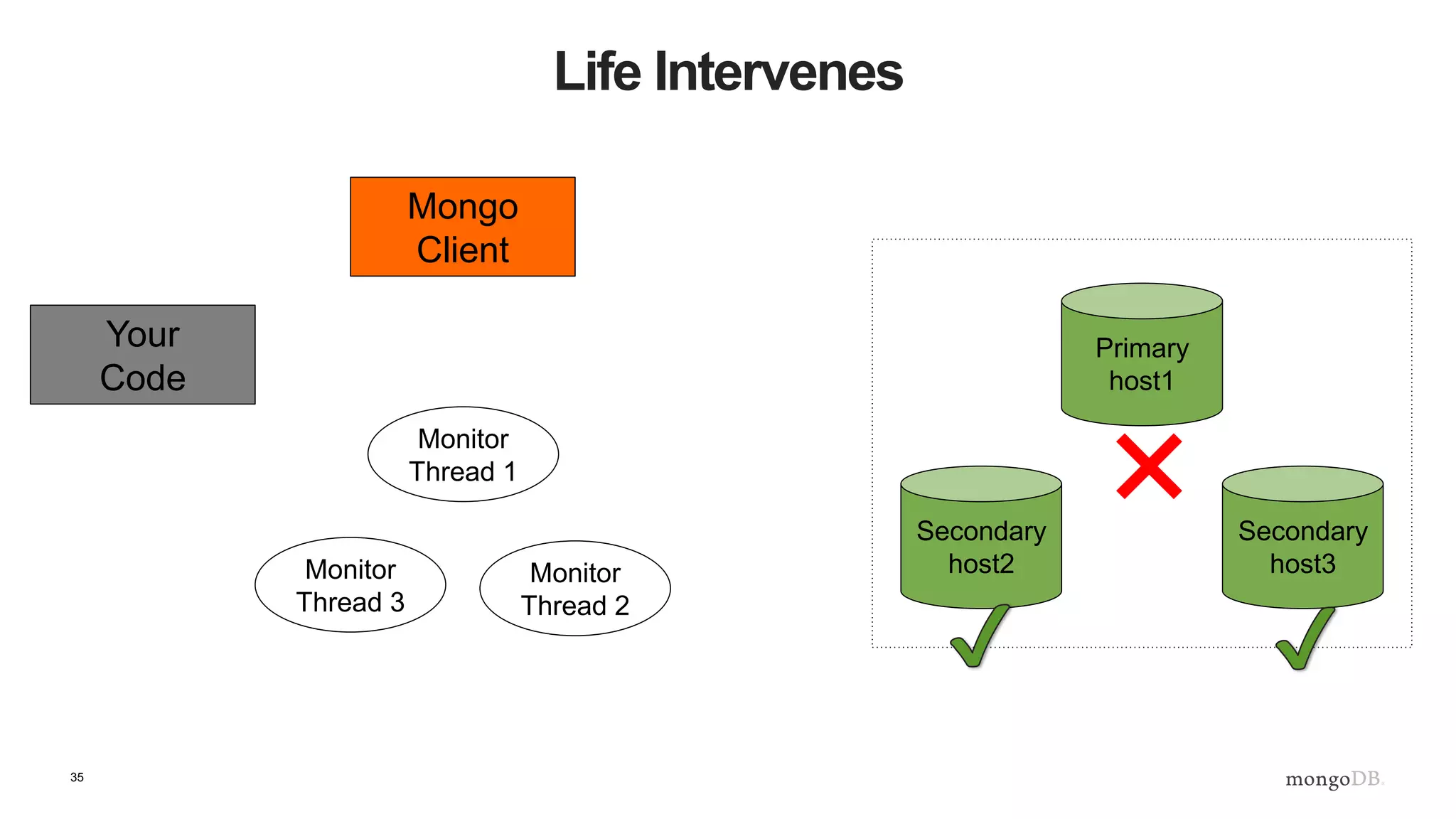
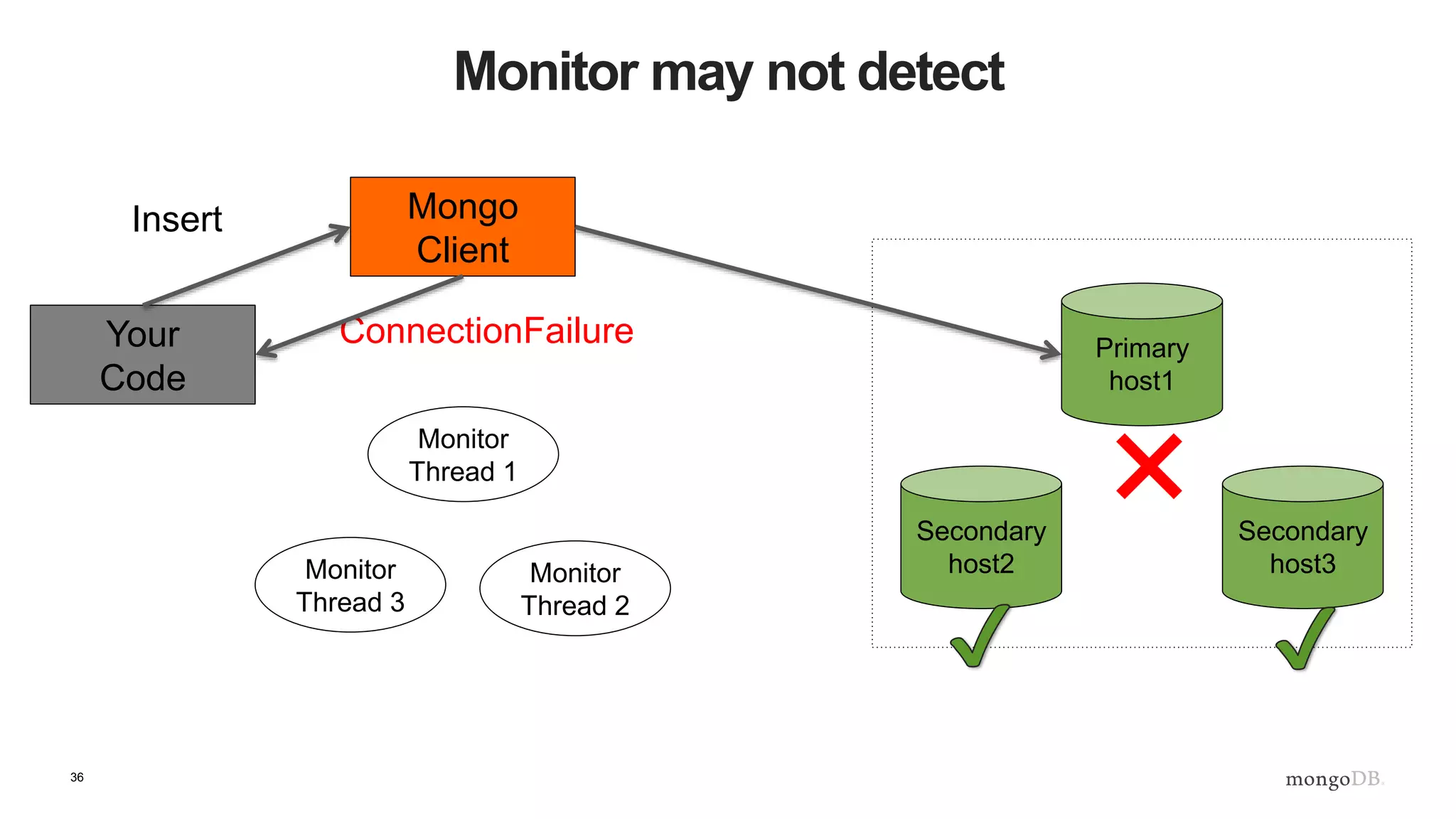
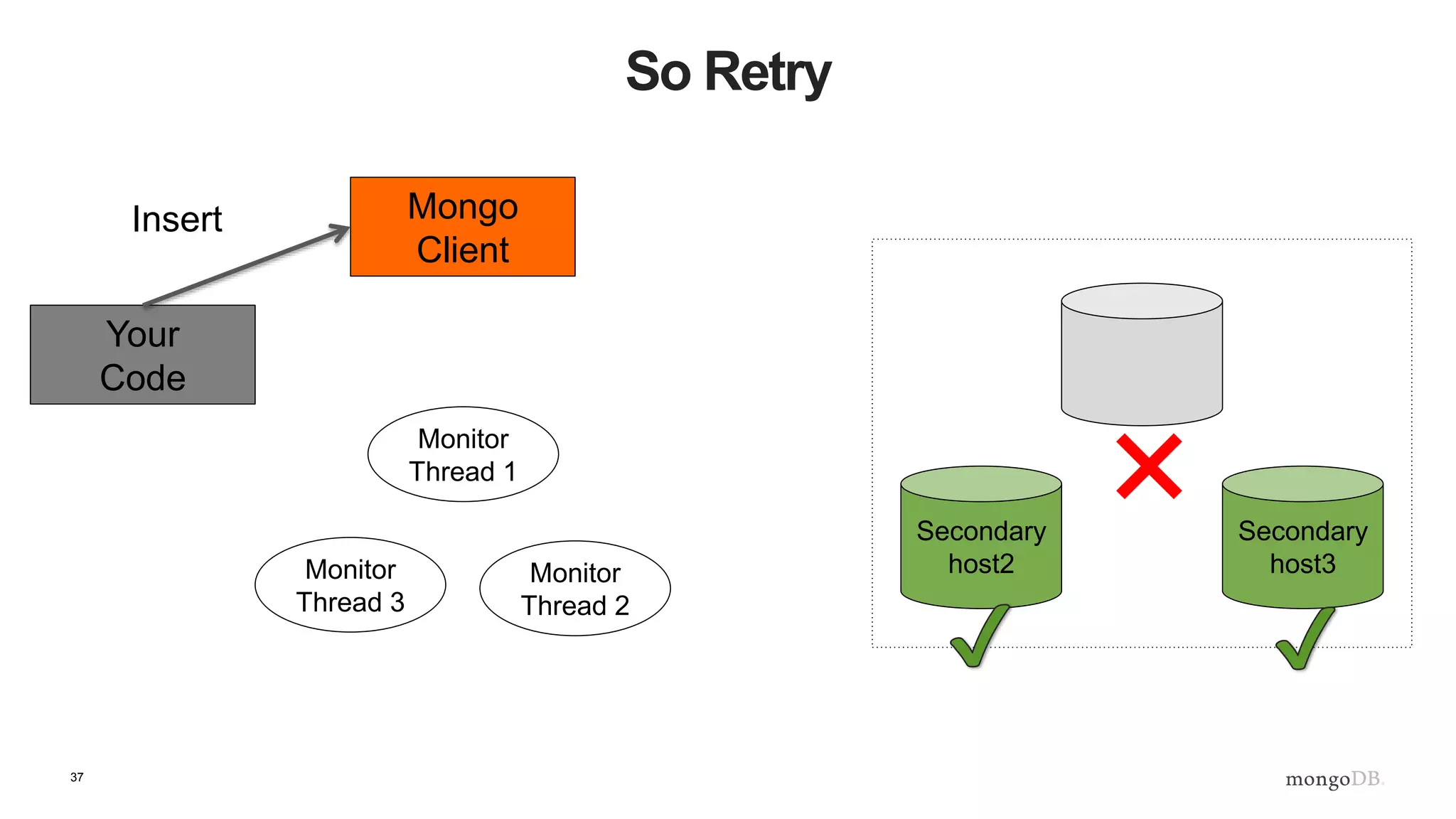





![43
What Does This Mean? - Inserts
def insert_with_recovery( collection, doc ) :
doc[ "_id" ] = ObjectId()
try:
collection.insert_one( doc )
except pymongo.errors.ConnectionFailure, e:
logging.info( "Connection error: %s" % e )
try:
collection.insert_one( doc )
except DuplicateKeyError:
pass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b2b-webinar-3-replica-sets-1-170518103133/75/Back-to-Basics-German-3-Einfuhrung-in-Replica-Sets-43-2048.jpg)


