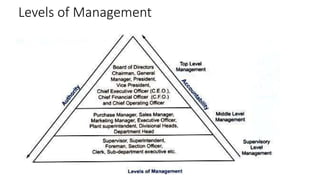
This document discusses the nature and significance of management. It covers the meaning of management, its nature as a universal and goal-oriented process, and its importance in every field. The document also discusses management as a science, art, and profession. It describes the levels, functions, and areas of management including marketing, human resources, and financial management.