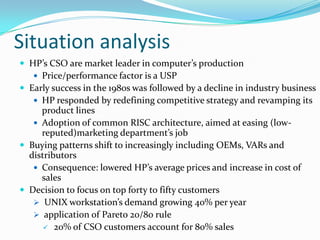
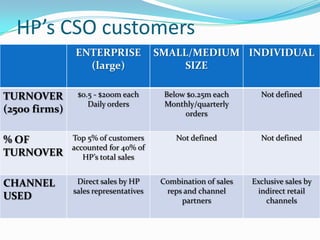
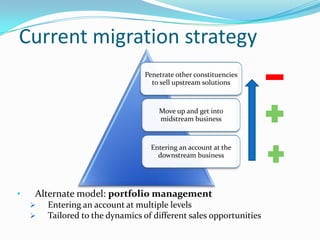
The document discusses Hewlett Packard's Computer Systems Organisation and its approach to selling to enterprise customers. It finds that HP is strongest in downstream repurchase opportunities but needs to improve in midstream replacement/expansion and upstream innovation opportunities. It recommends that HP adopt a portfolio management approach where it enters accounts at multiple levels tailored to the dynamics of different sales opportunities, rather than its current approach of starting downstream and moving up. This represents a change from treating salespeople as a cost center to developing long-term consultative relationships with enterprise customers.