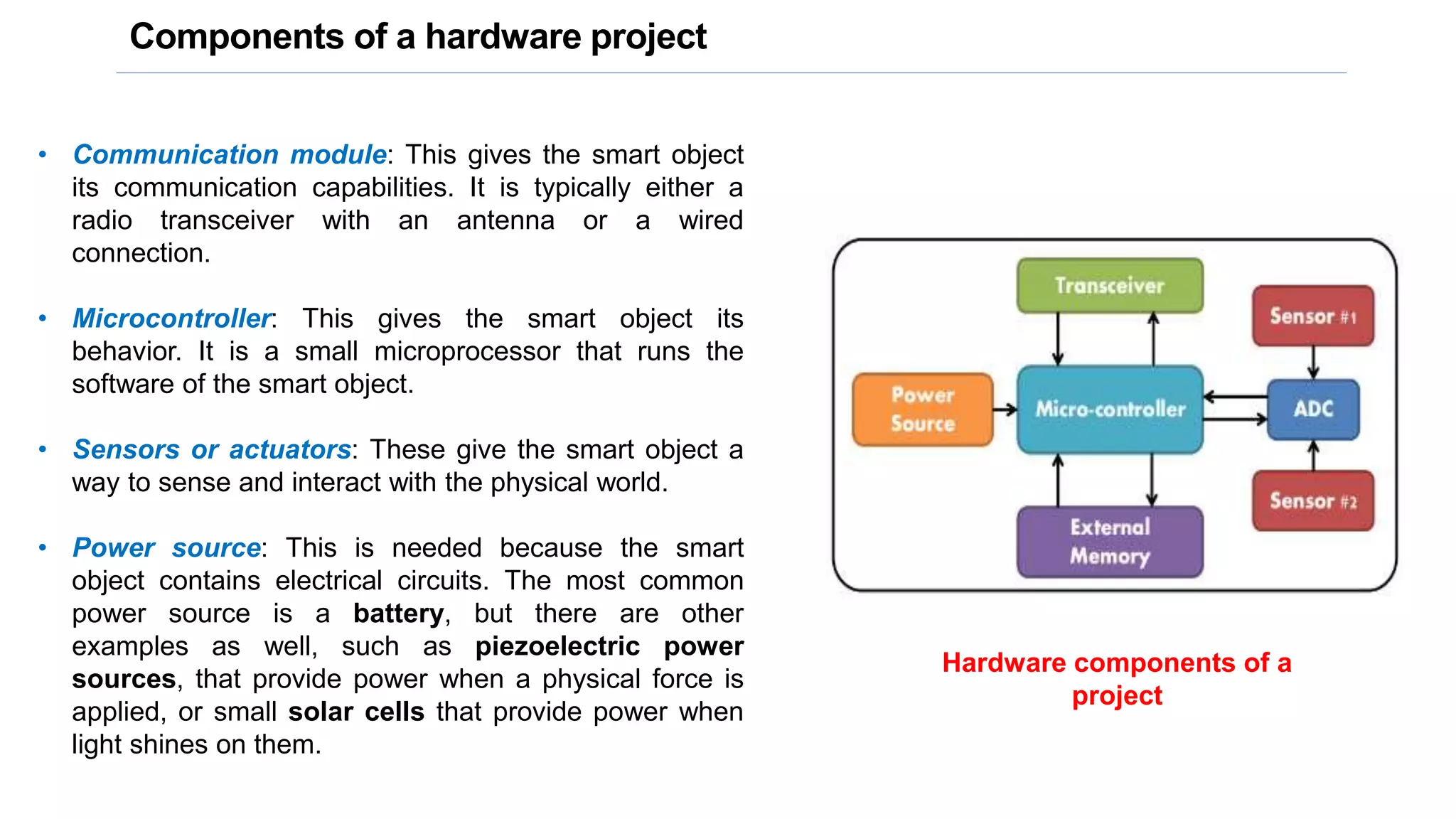
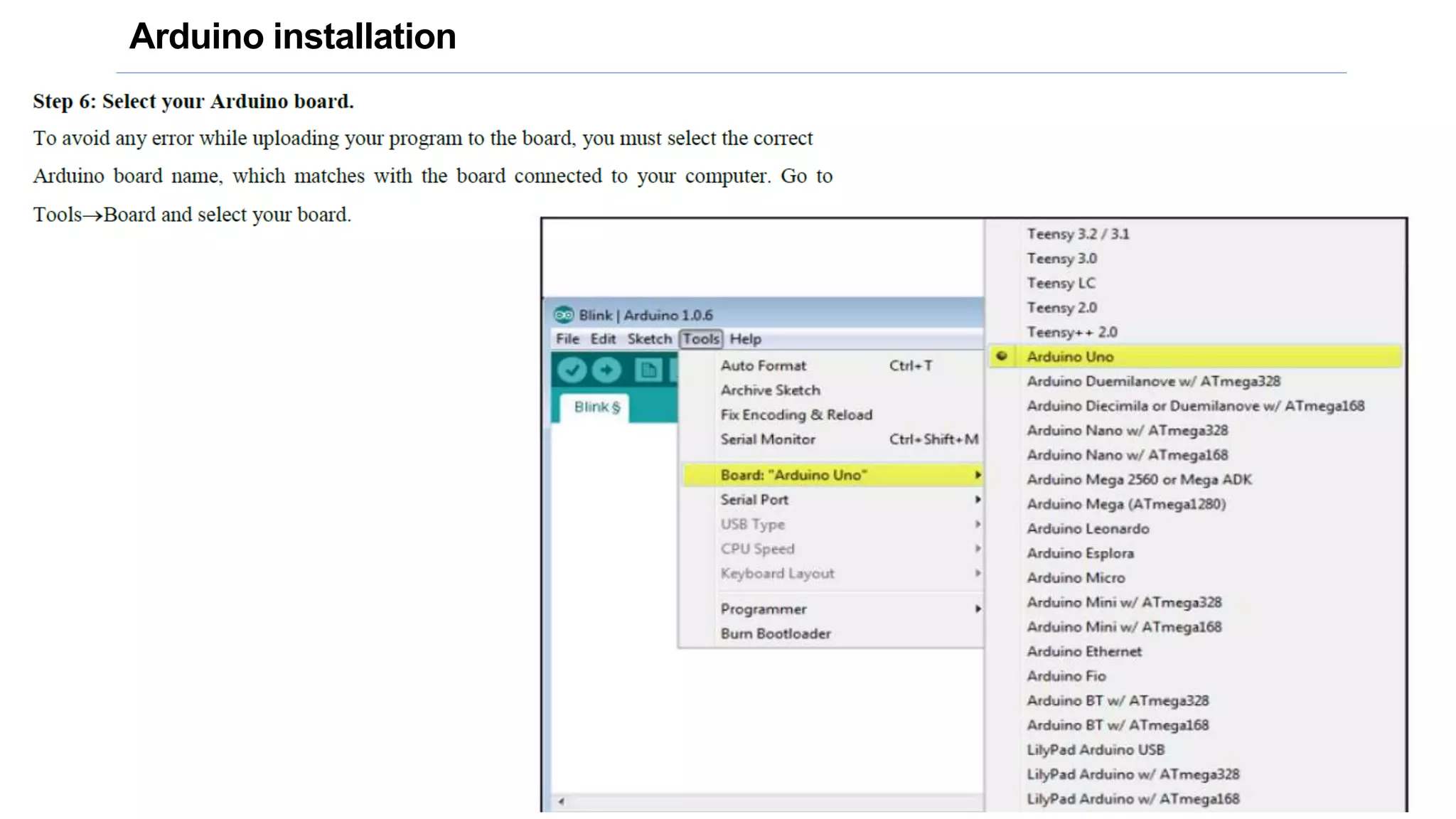
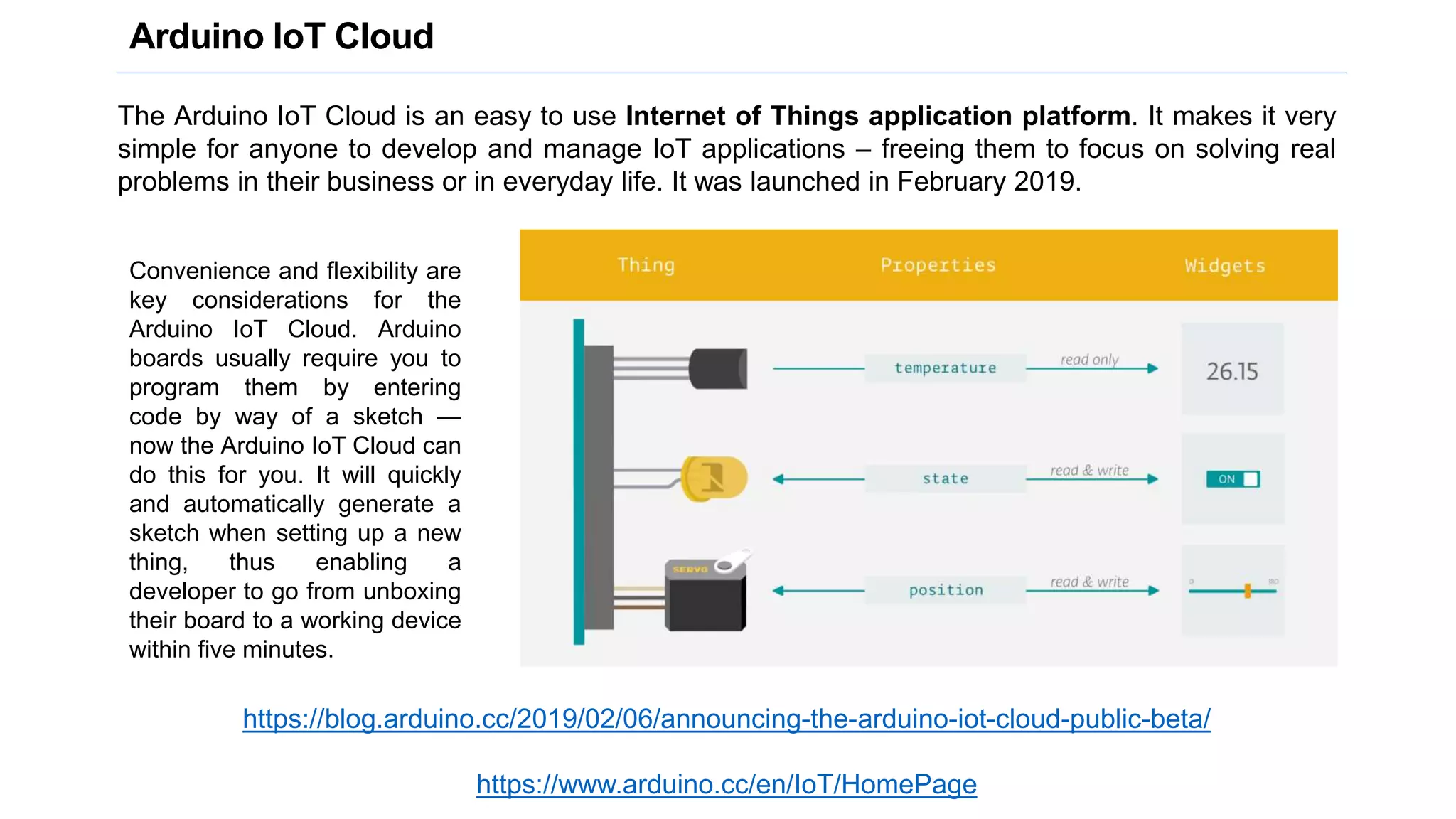
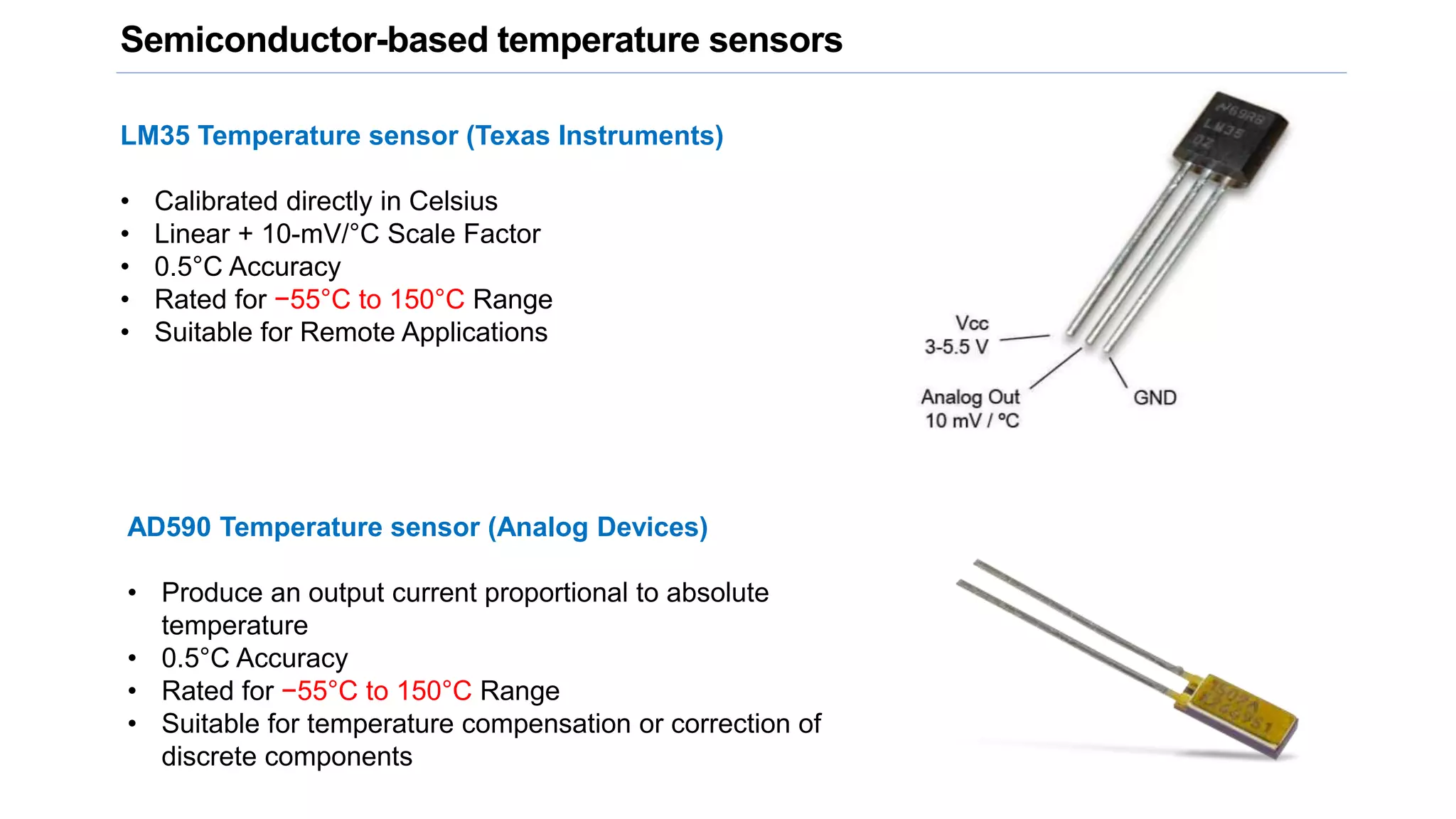
This document provides an overview of an ICT workshop on Arduino hardware platforms. It discusses the key components of a hardware project, including communication modules, microcontrollers, sensors/actuators, and power sources. It then describes the Arduino platform in more detail, including common Arduino boards, specifications of the Arduino Uno, the Arduino IDE, and how to connect Arduino to sensors and actuators. It also provides examples of temperature and other sensors that can be used in Arduino projects.