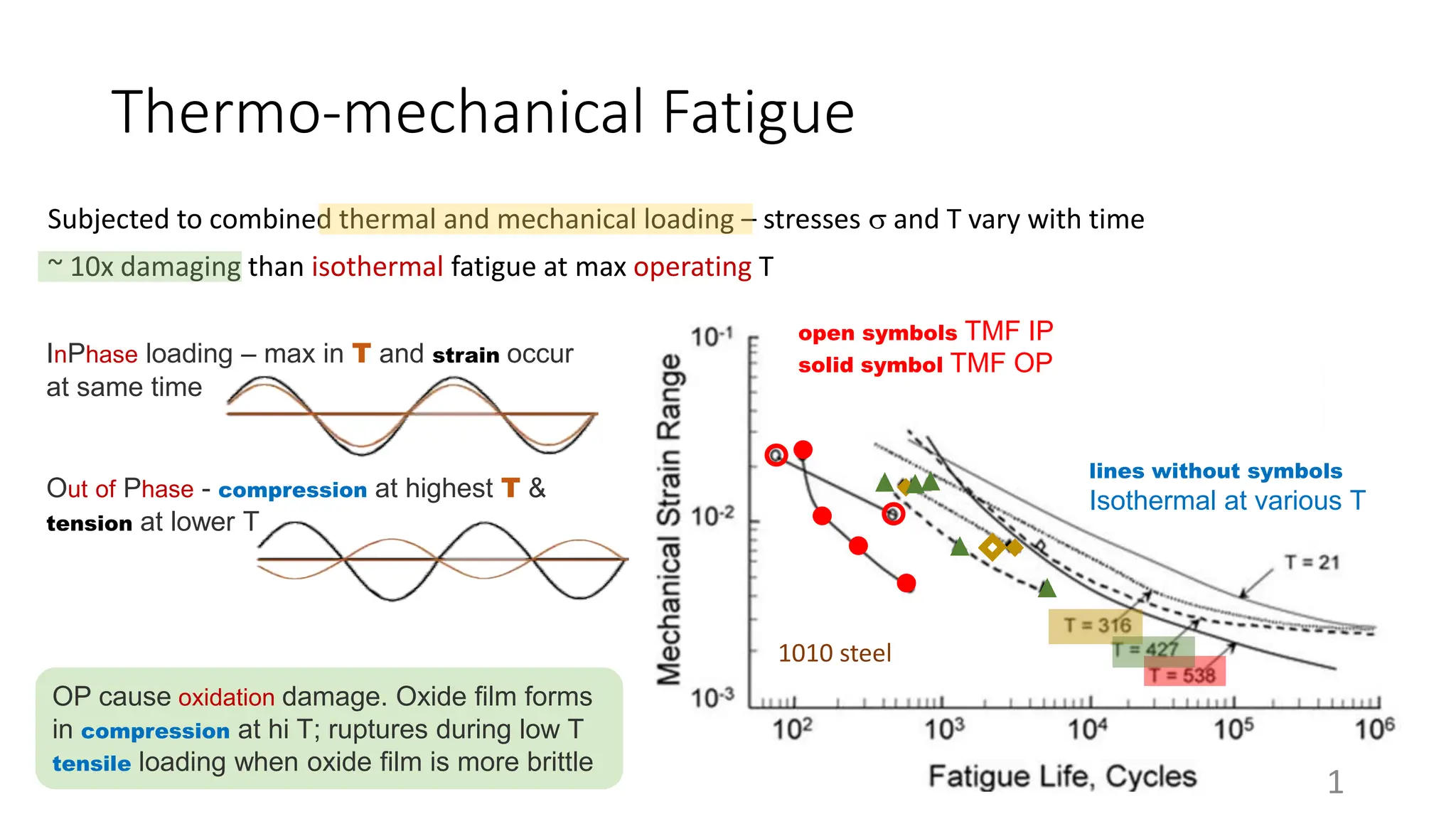
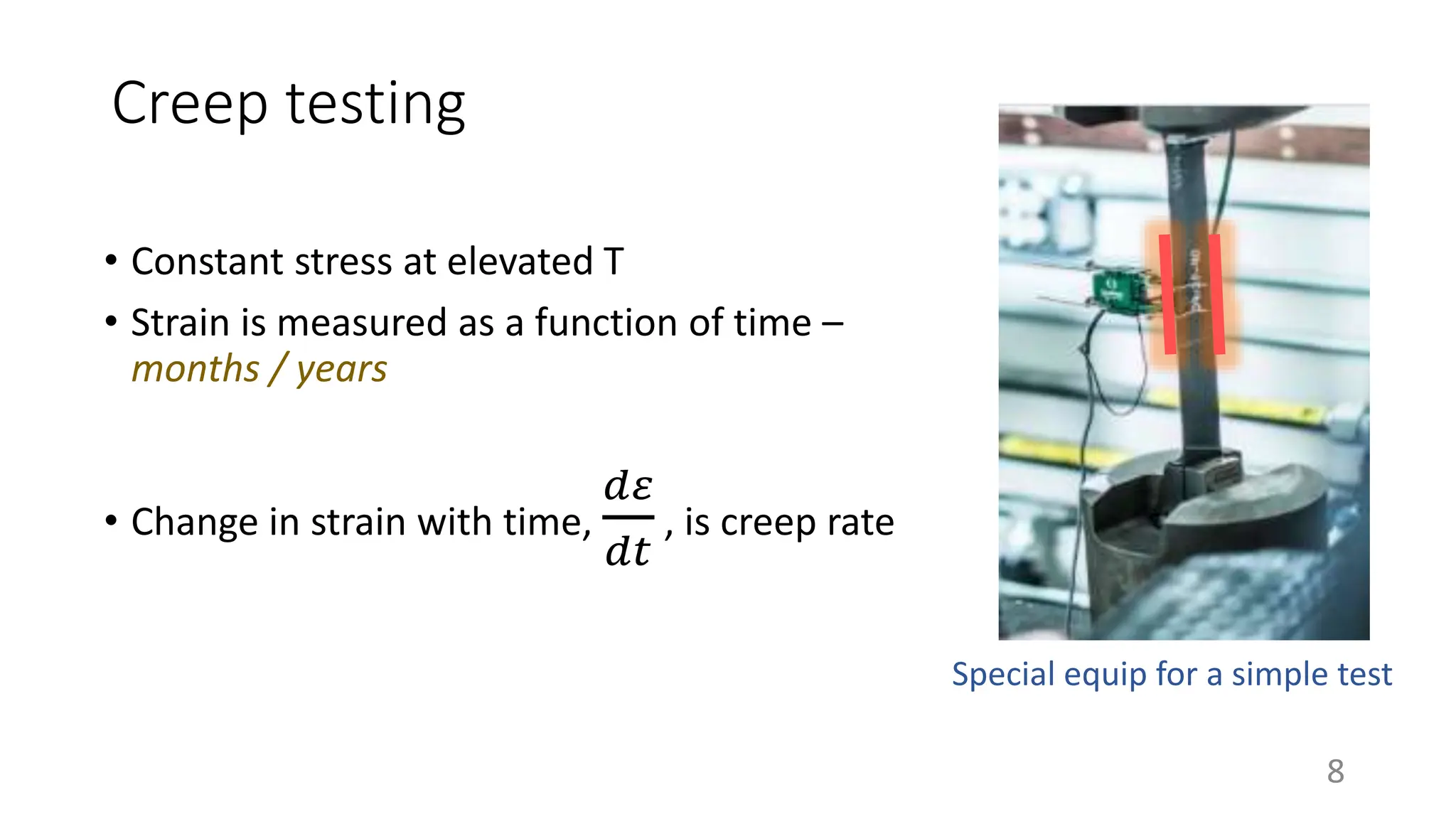
Thermal and mechanical loading can cause 10 times more damage than isothermal fatigue at maximum operating temperatures. During thermo-mechanical fatigue, maximum strain and temperature occur simultaneously during in-phase loading, while compression occurs at highest temperatures and tension at lower temperatures during out-of-phase loading.
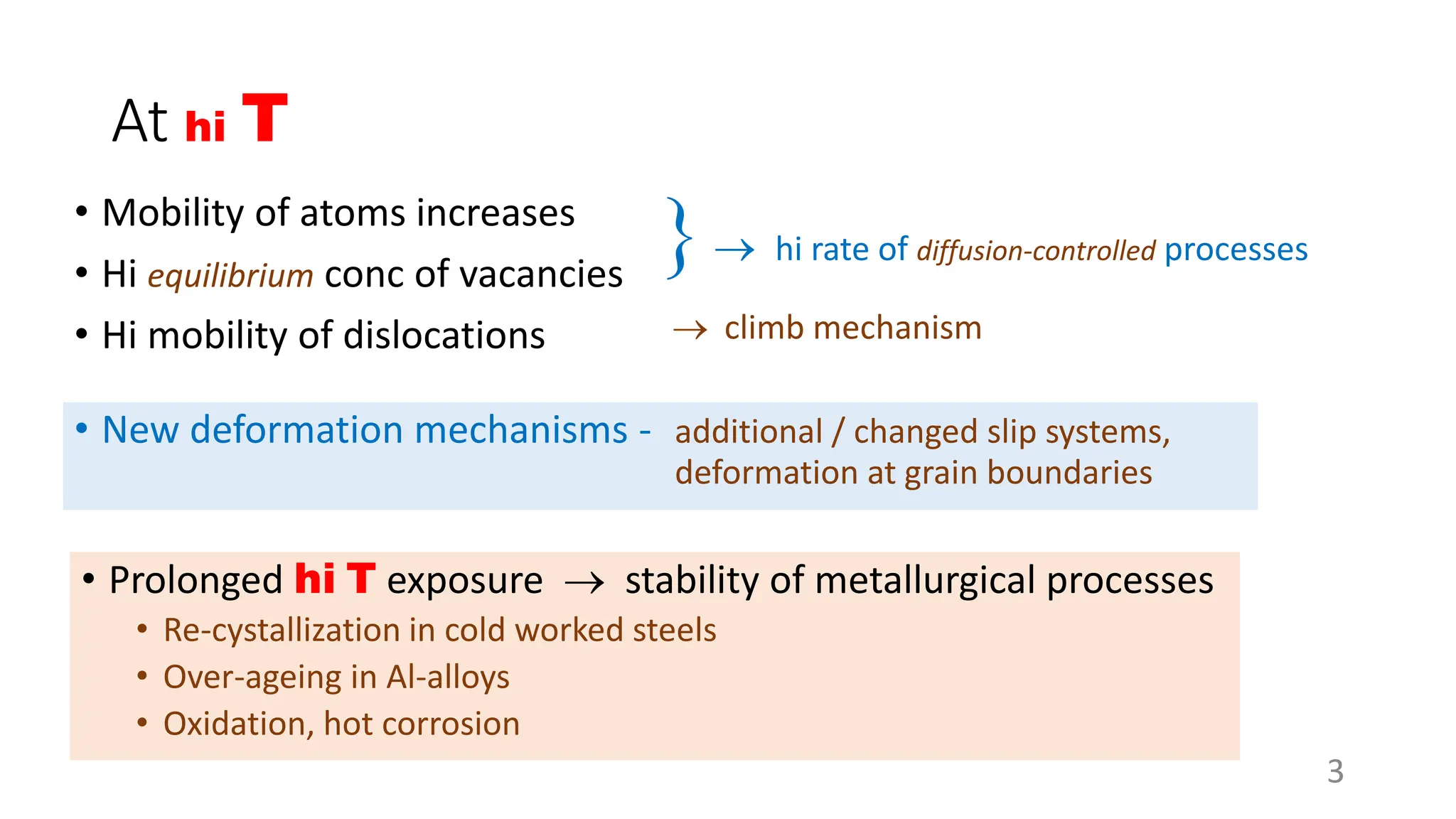
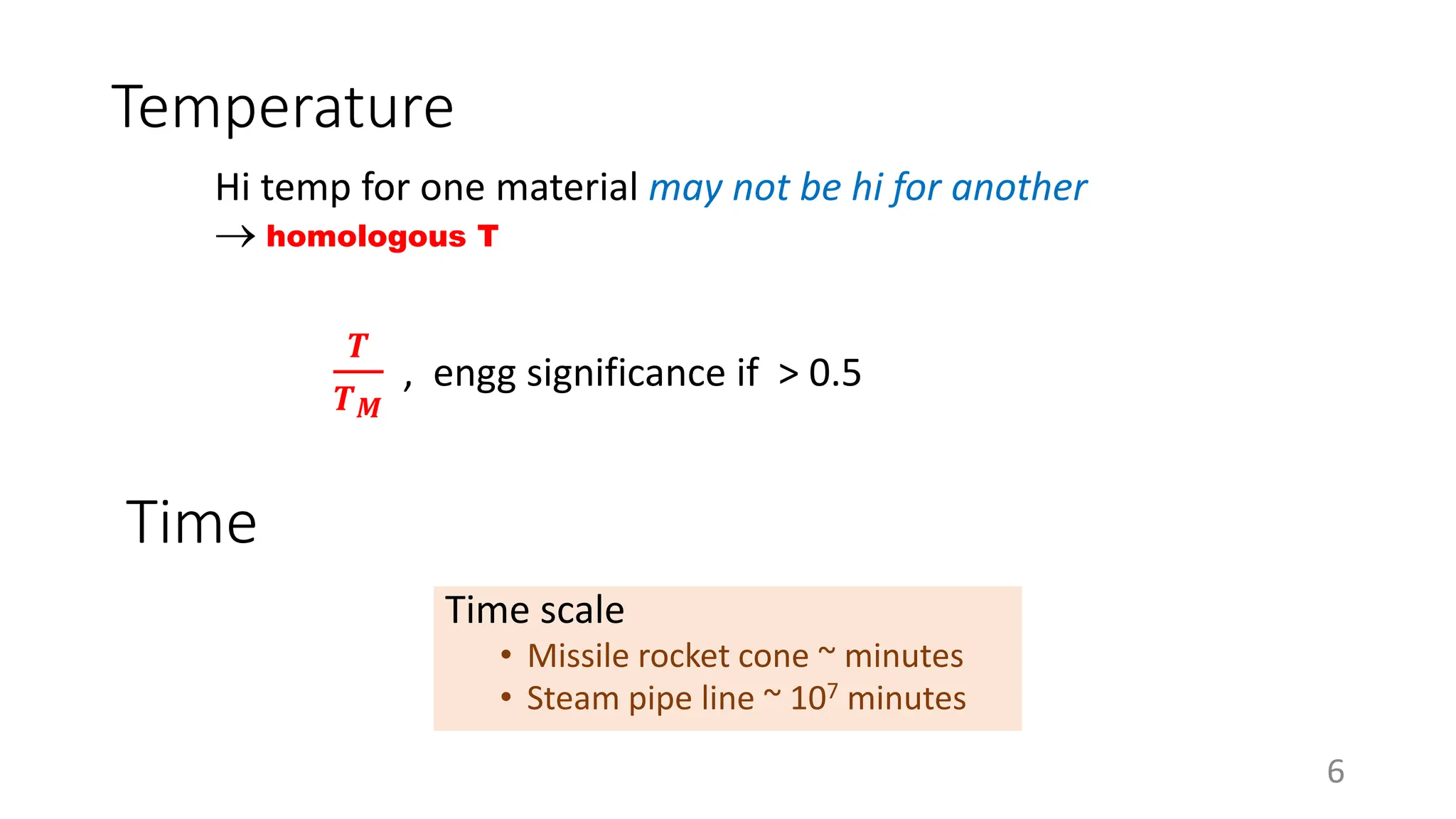
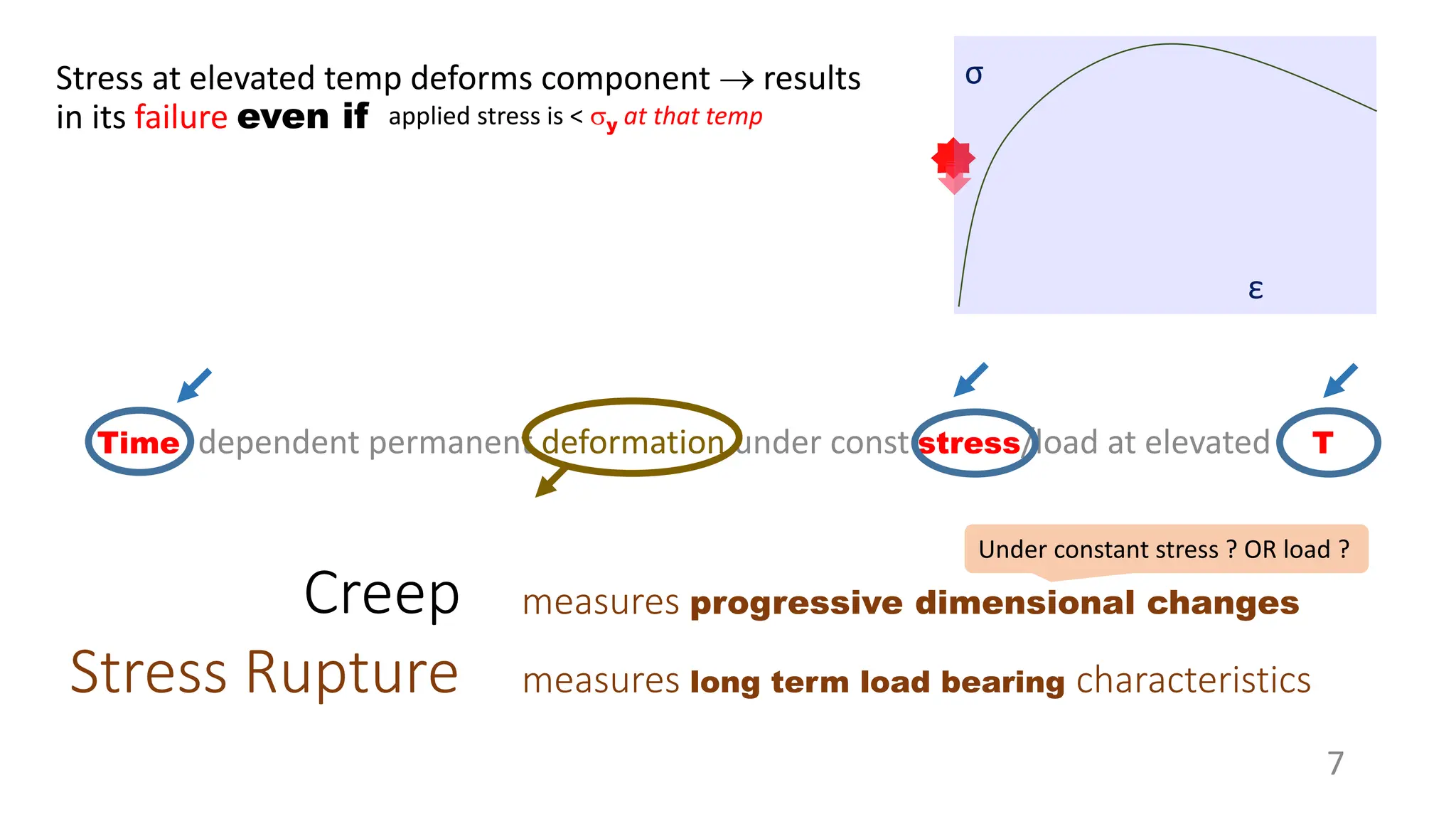
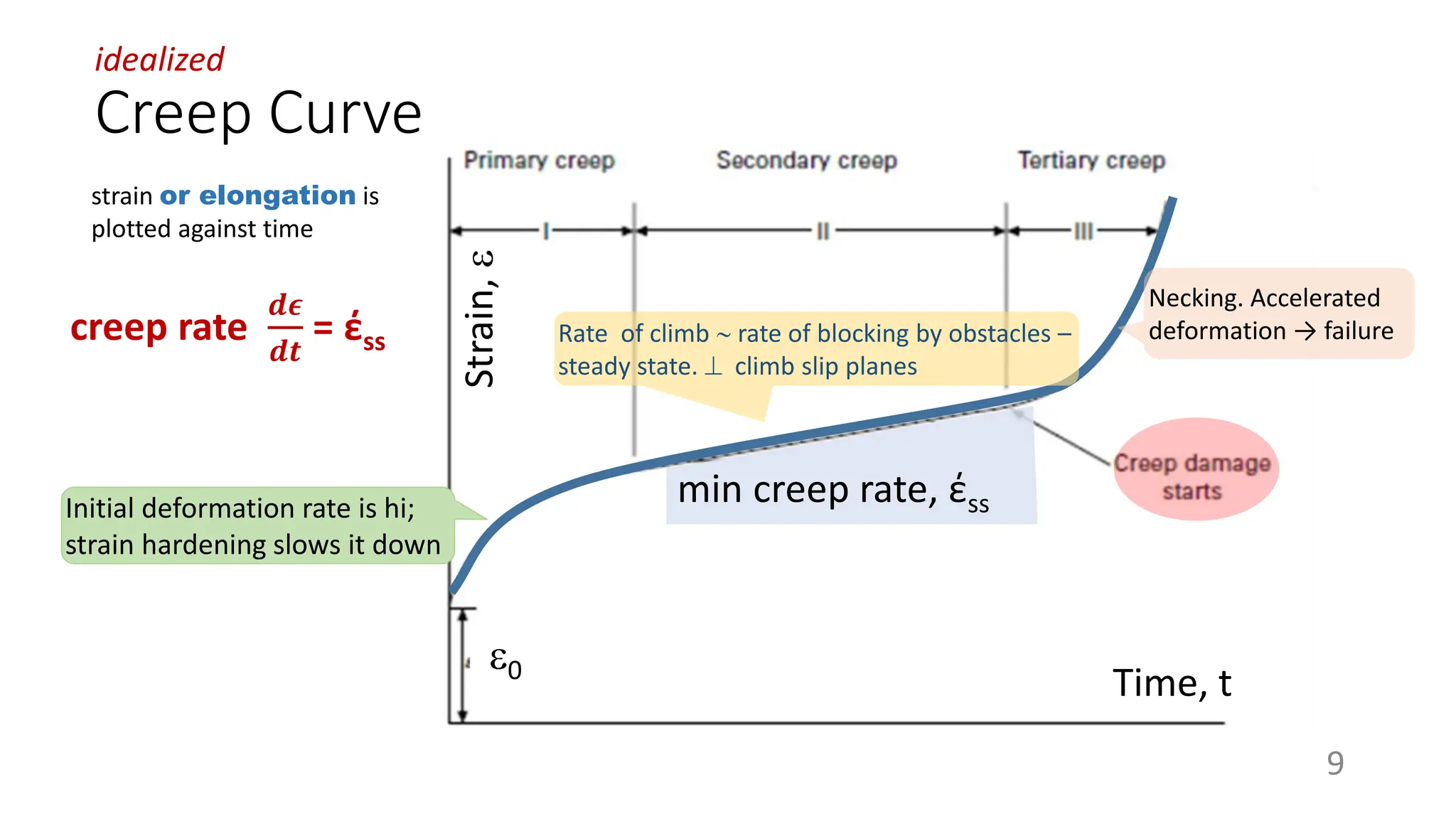
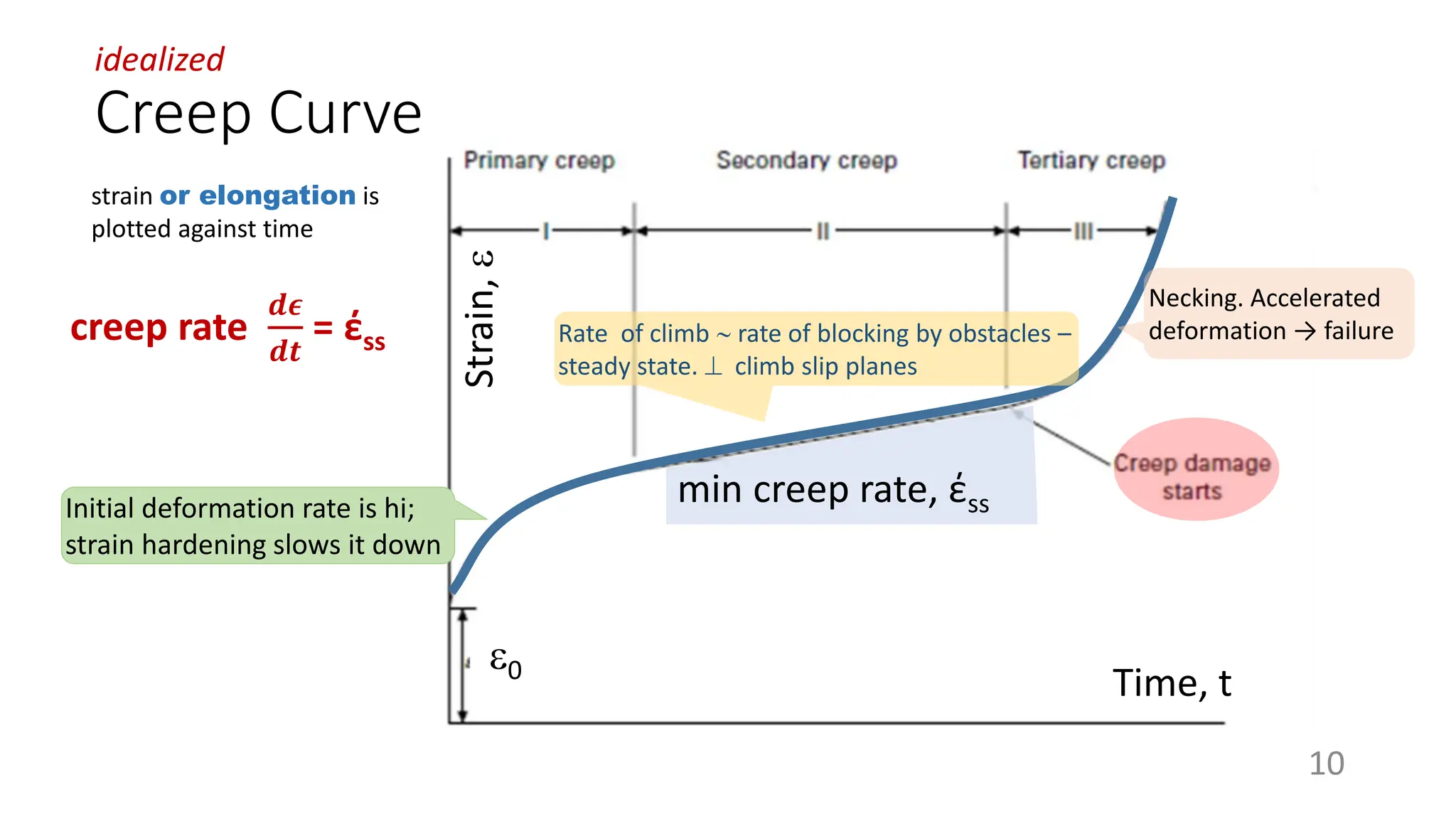
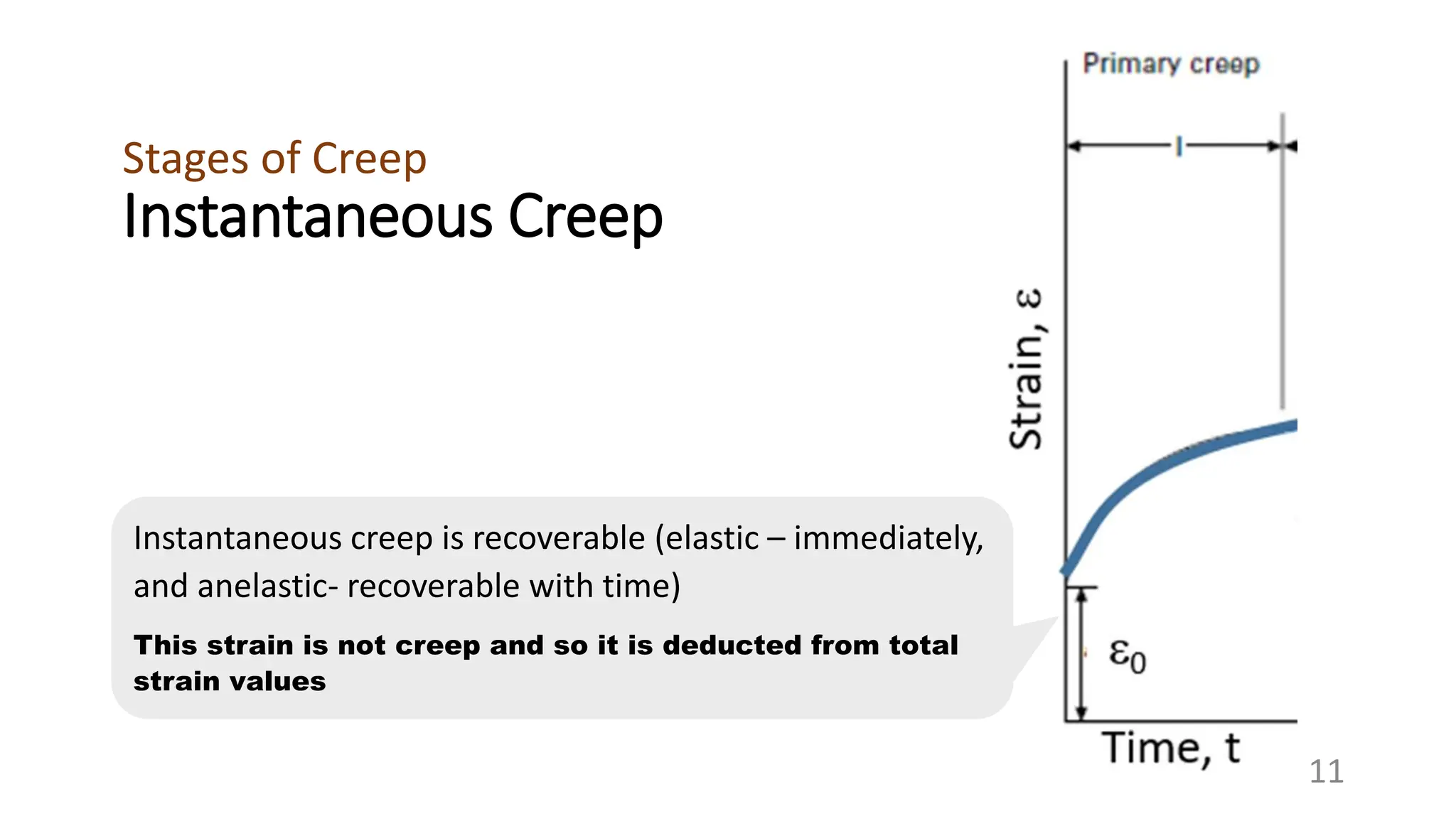
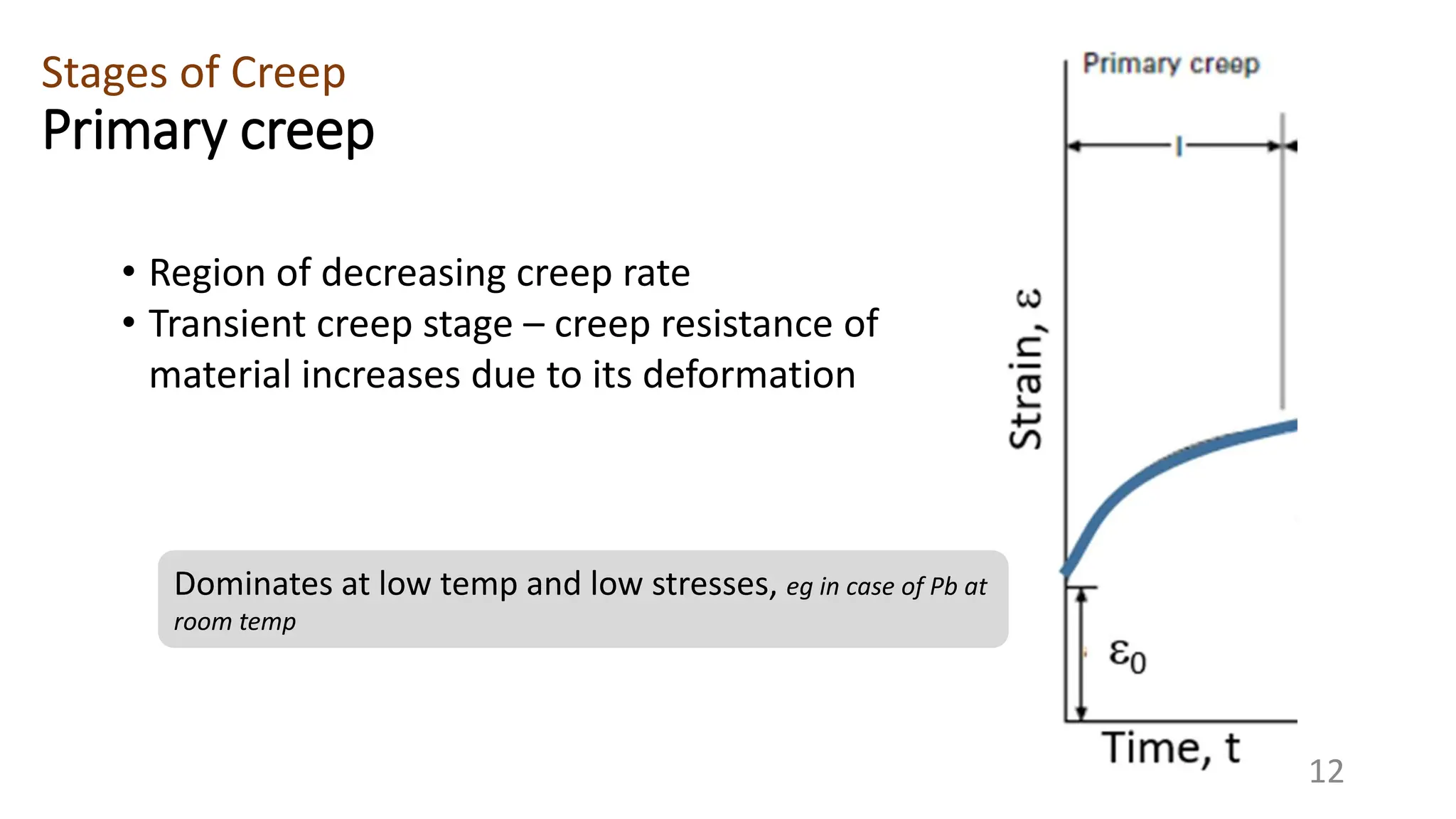
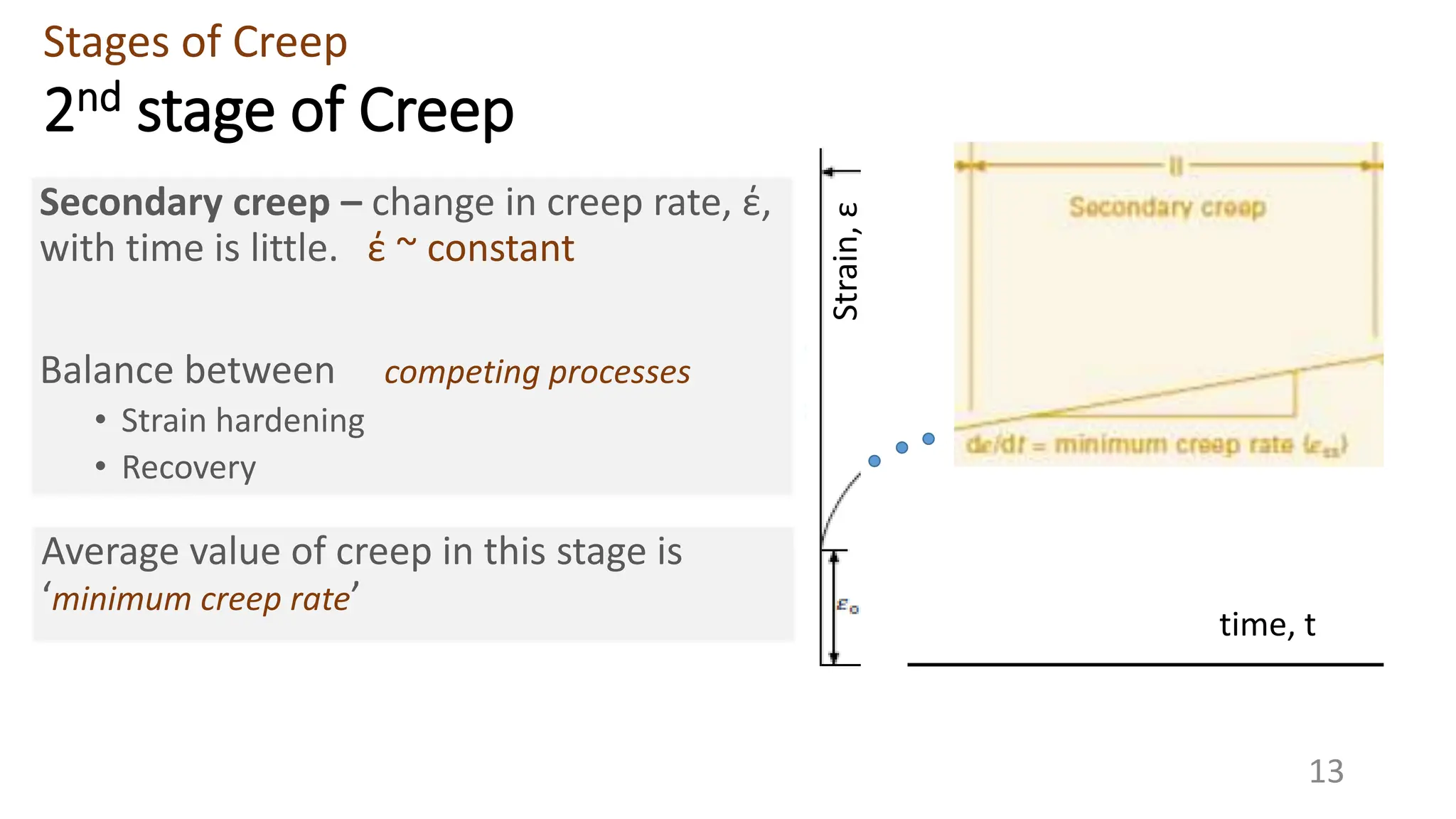
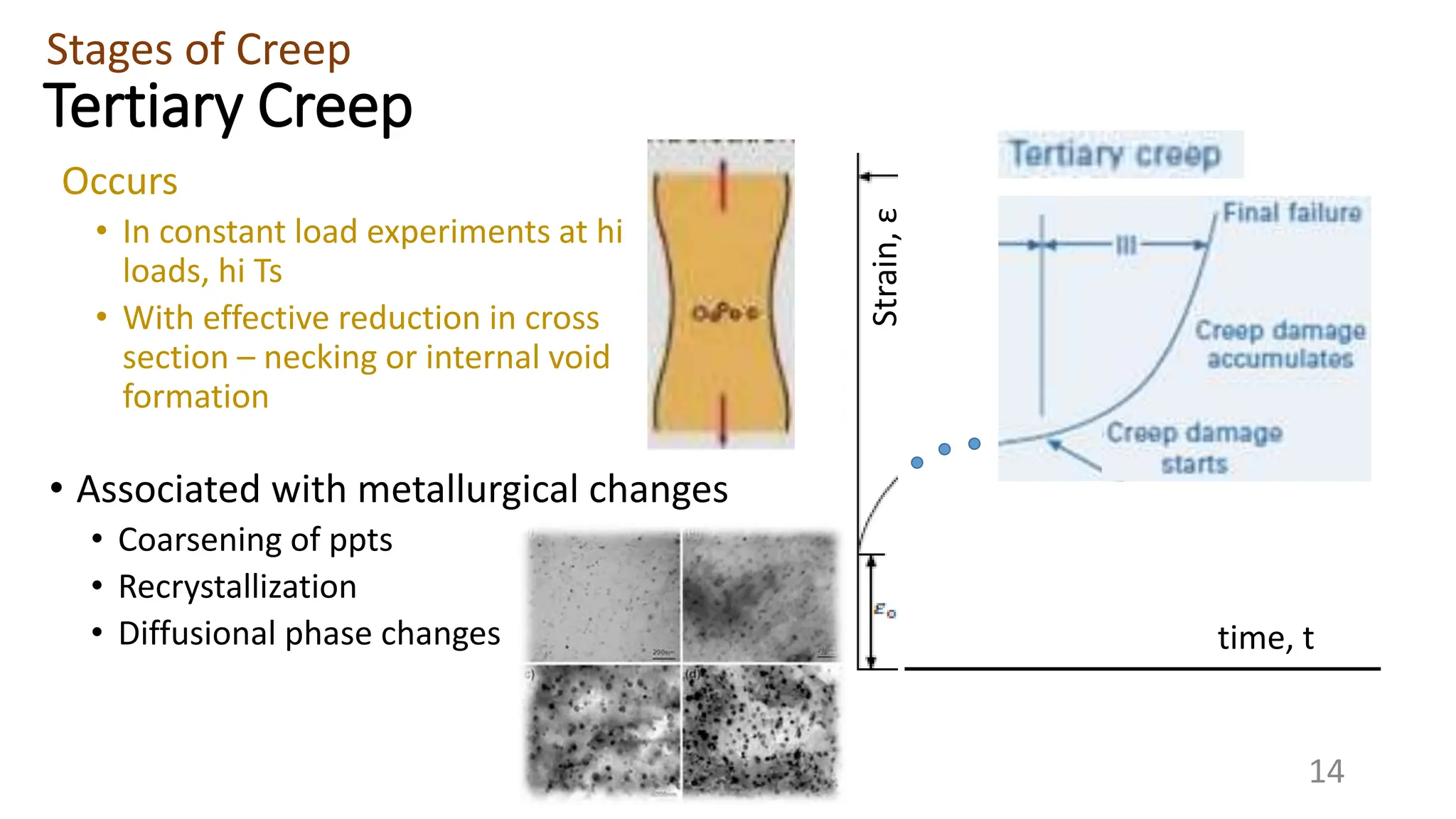
Creep strength deteriorates with increasing temperature as diffusion processes that cause deformation accelerate. Creep is the time-dependent permanent deformation of a material under constant stress or load at elevated temperatures, even if the applied stress is below the yield strength at that temperature. The creep curve shows an initial high creep rate that decreases and reaches a minimum steady-state creep rate during secondary creep. Tertiary creep occurs at high loads and