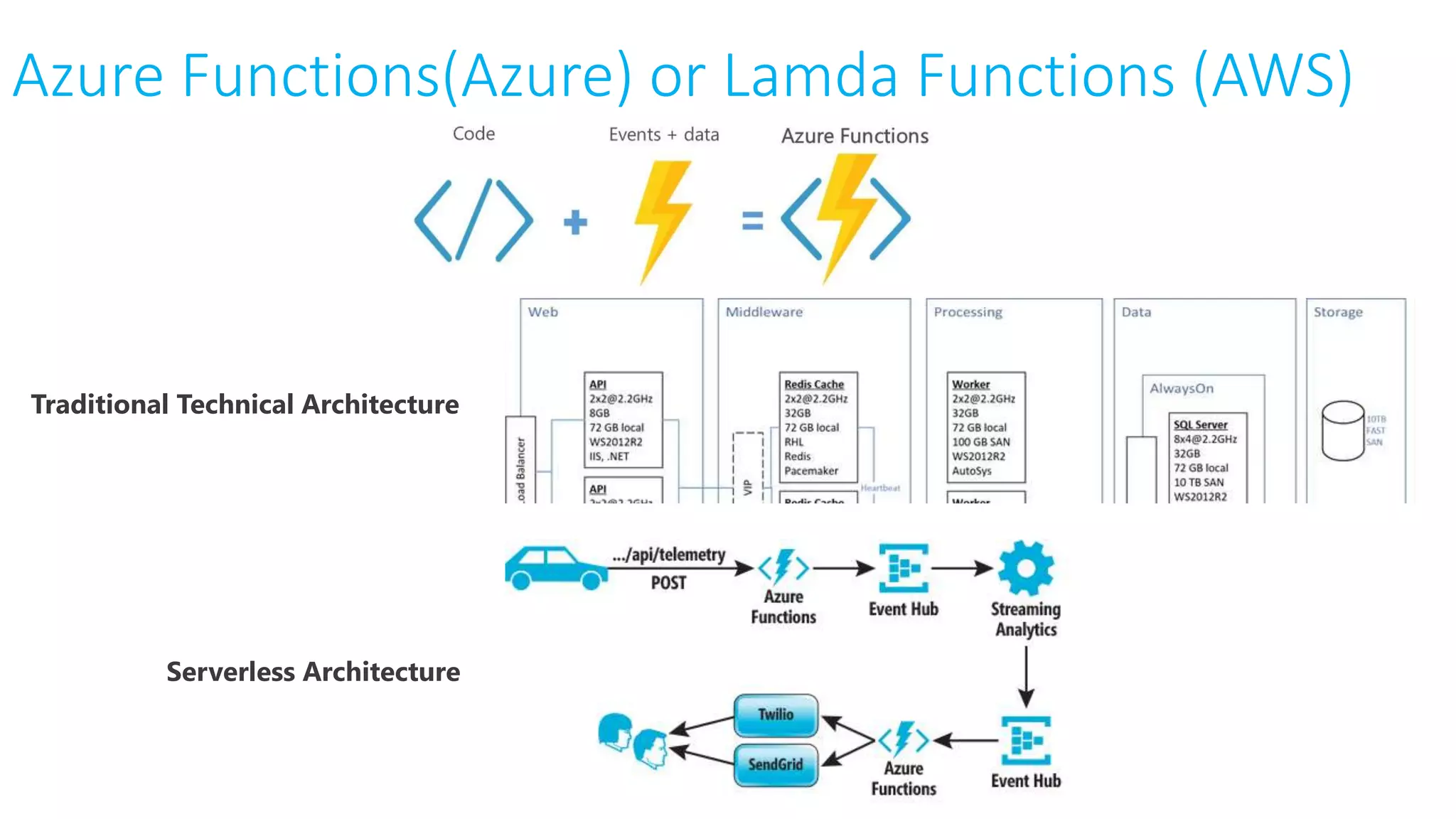
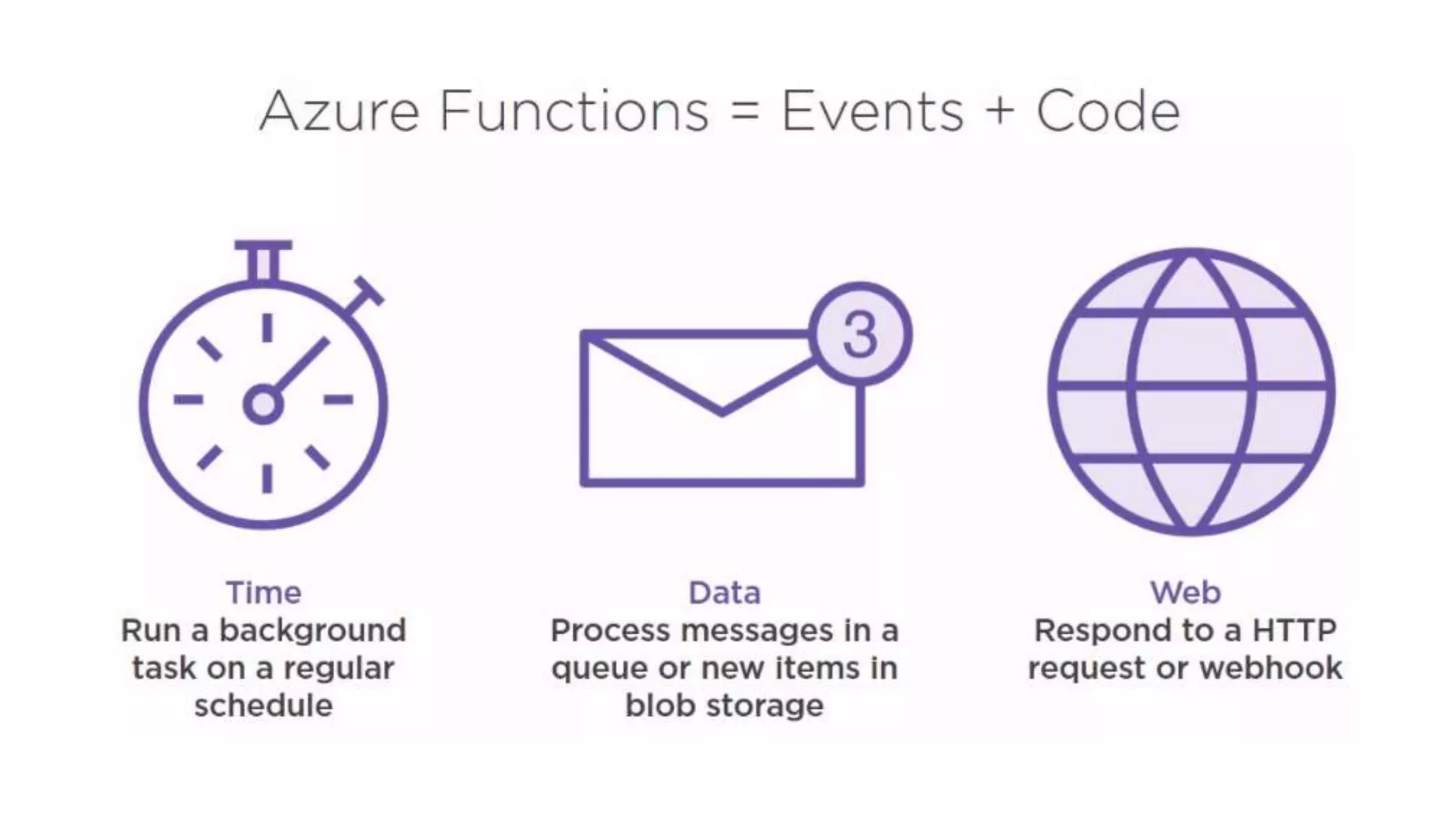
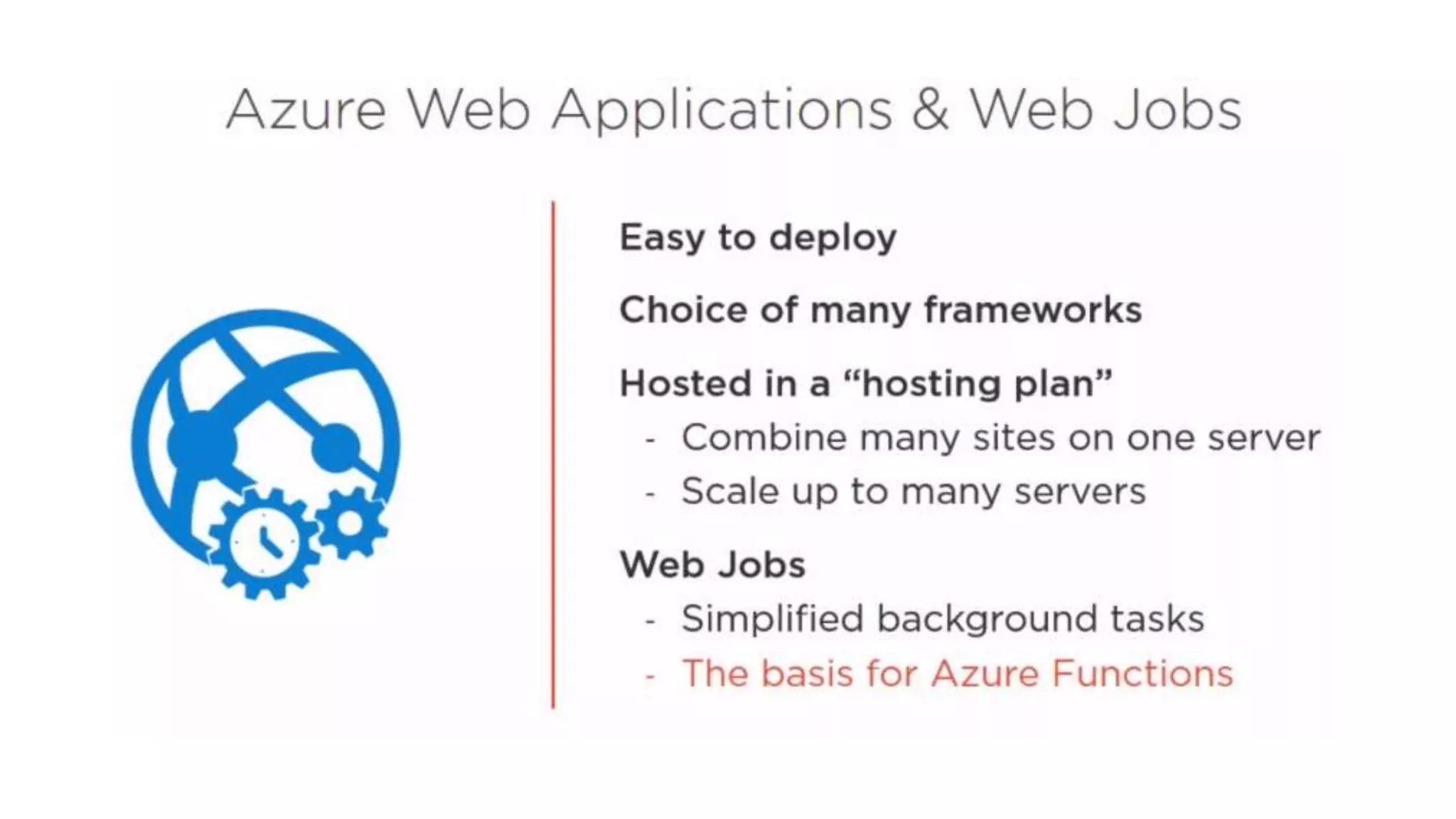
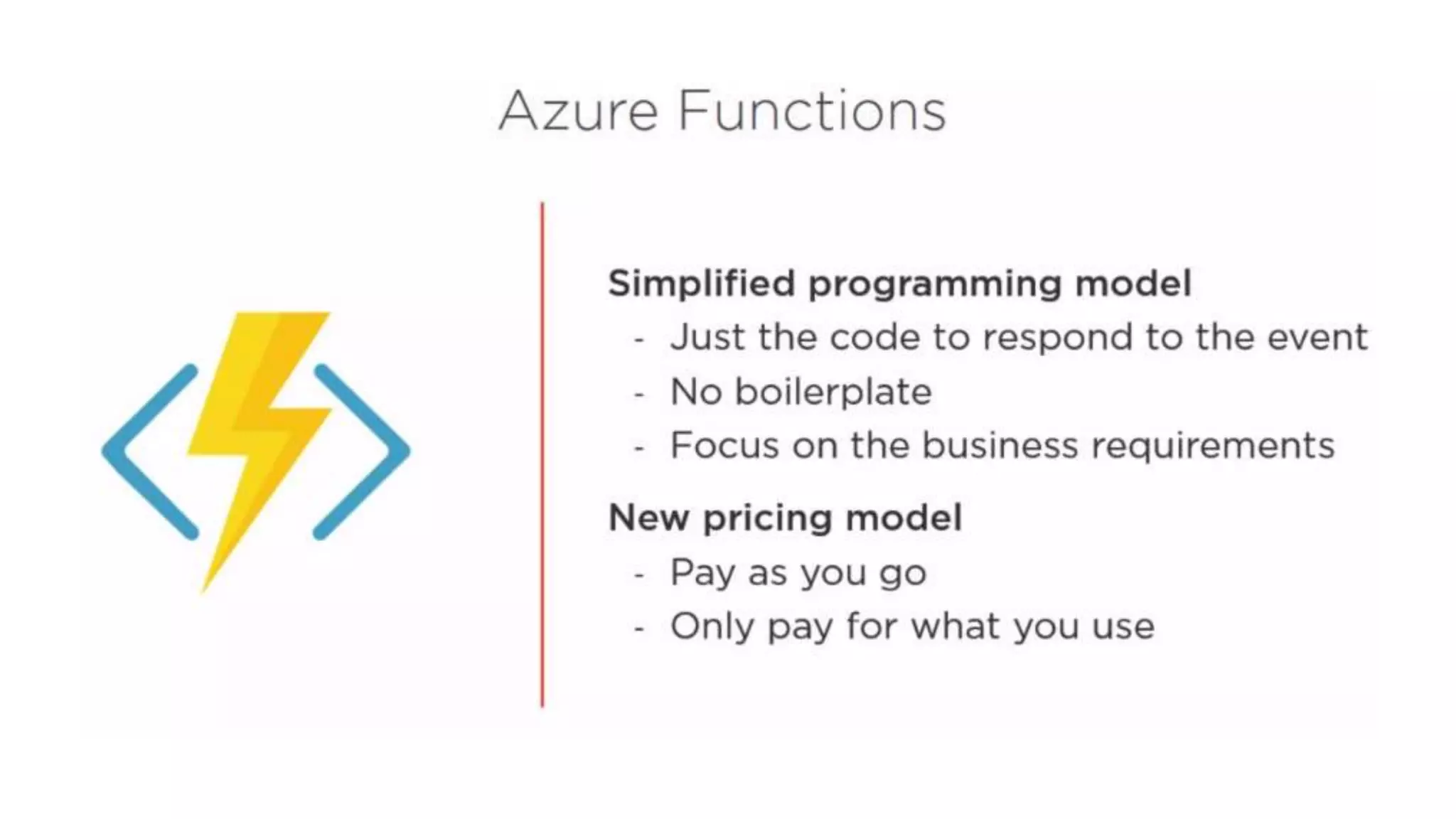
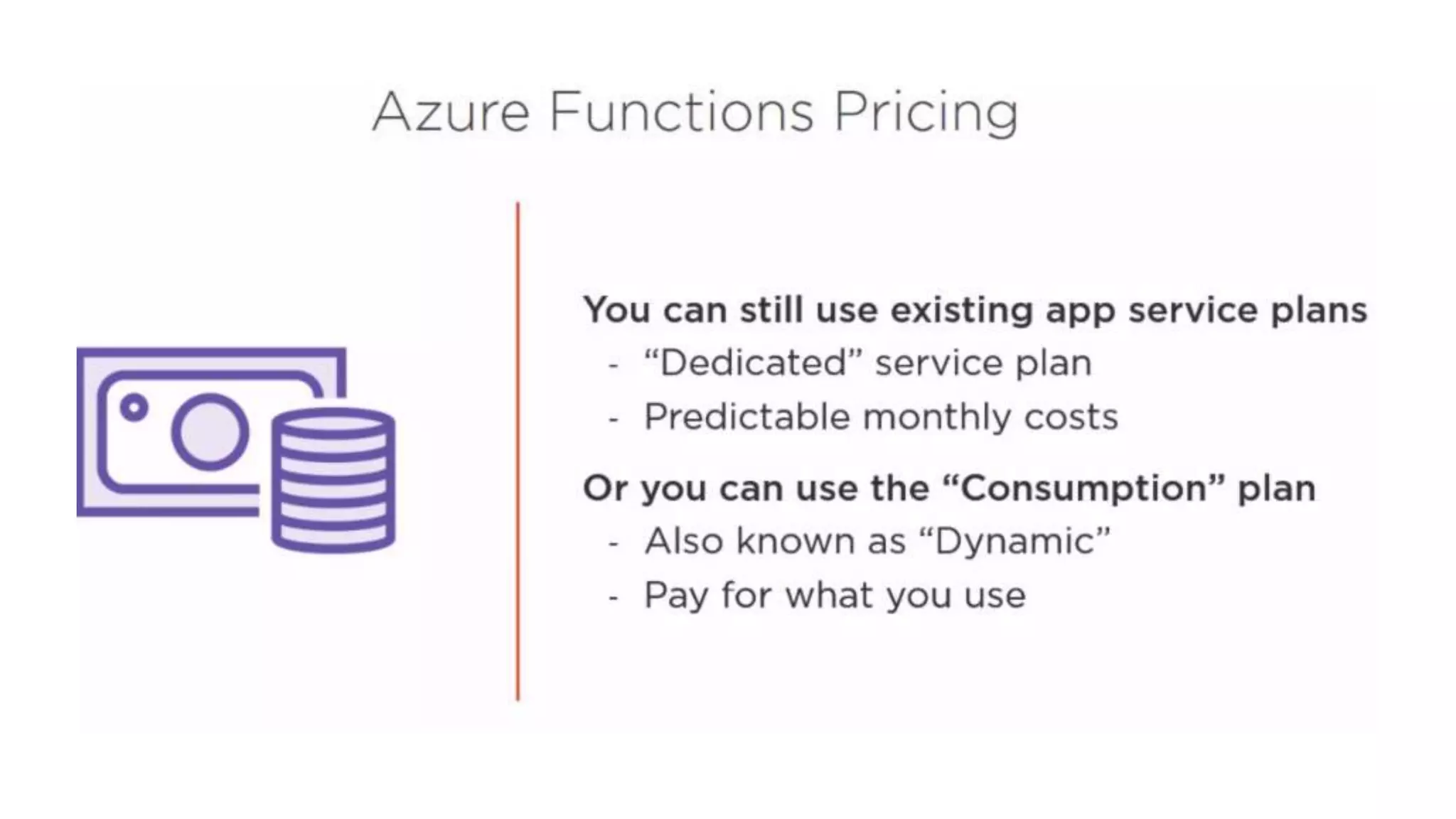
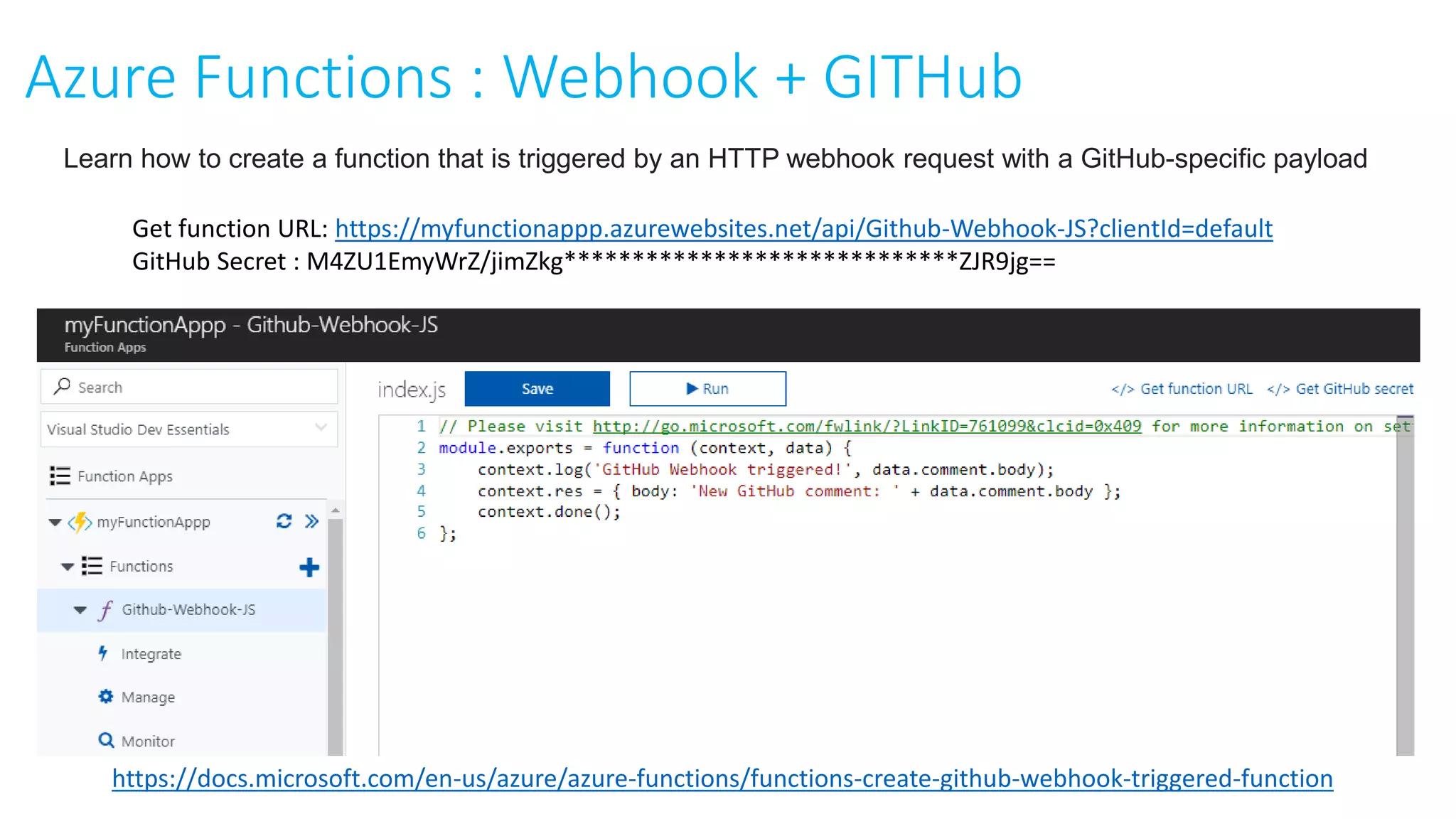
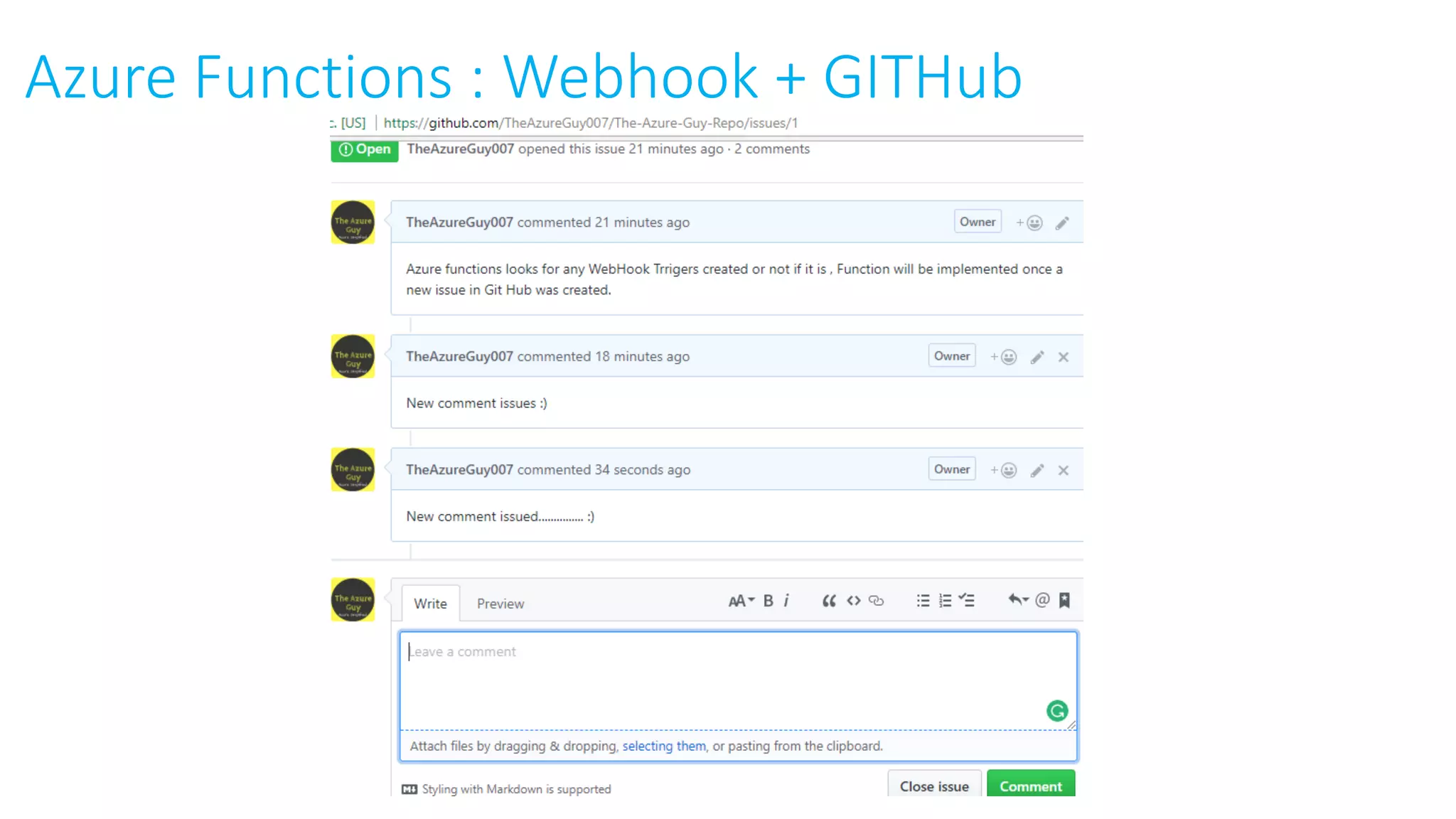
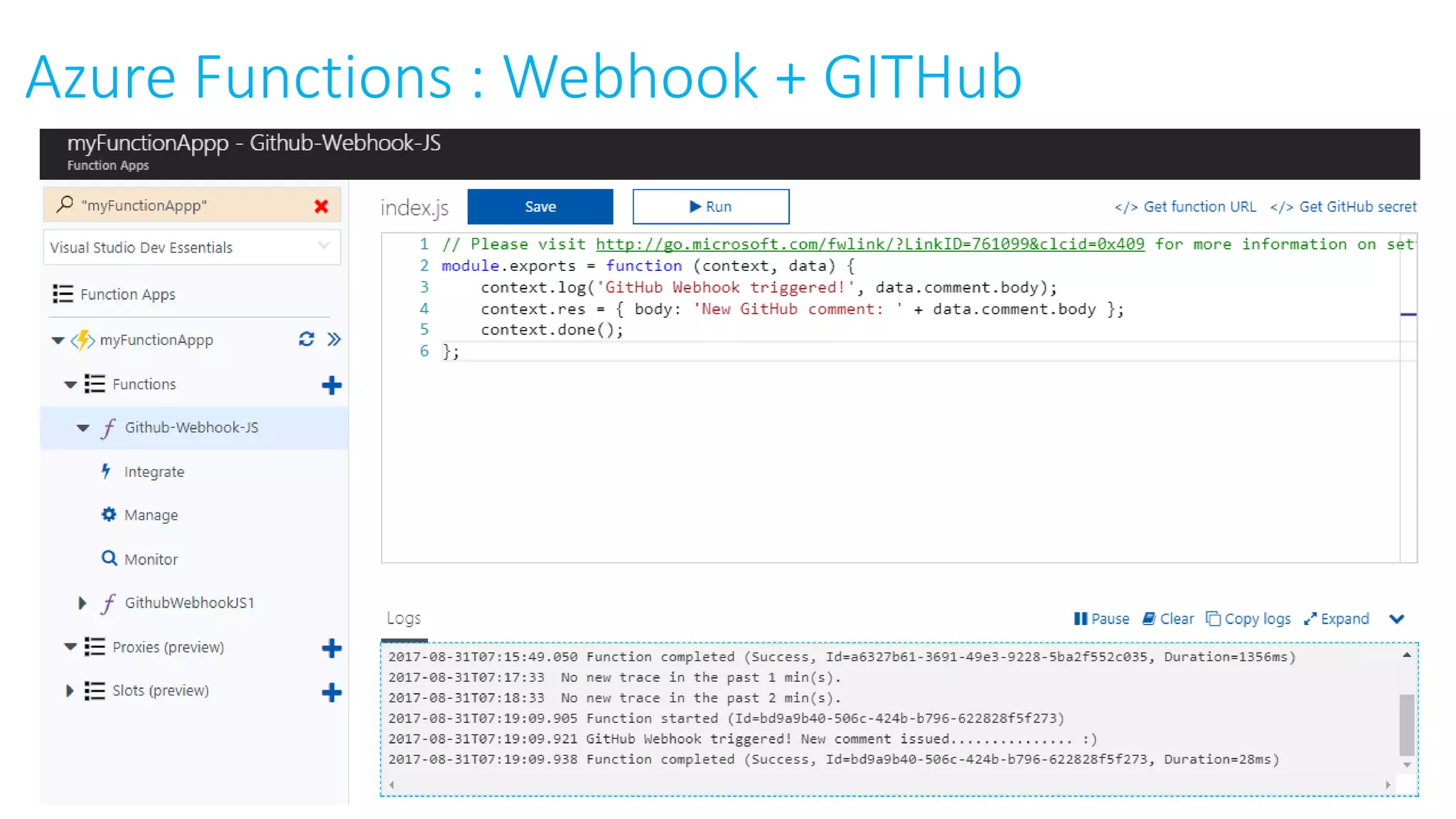
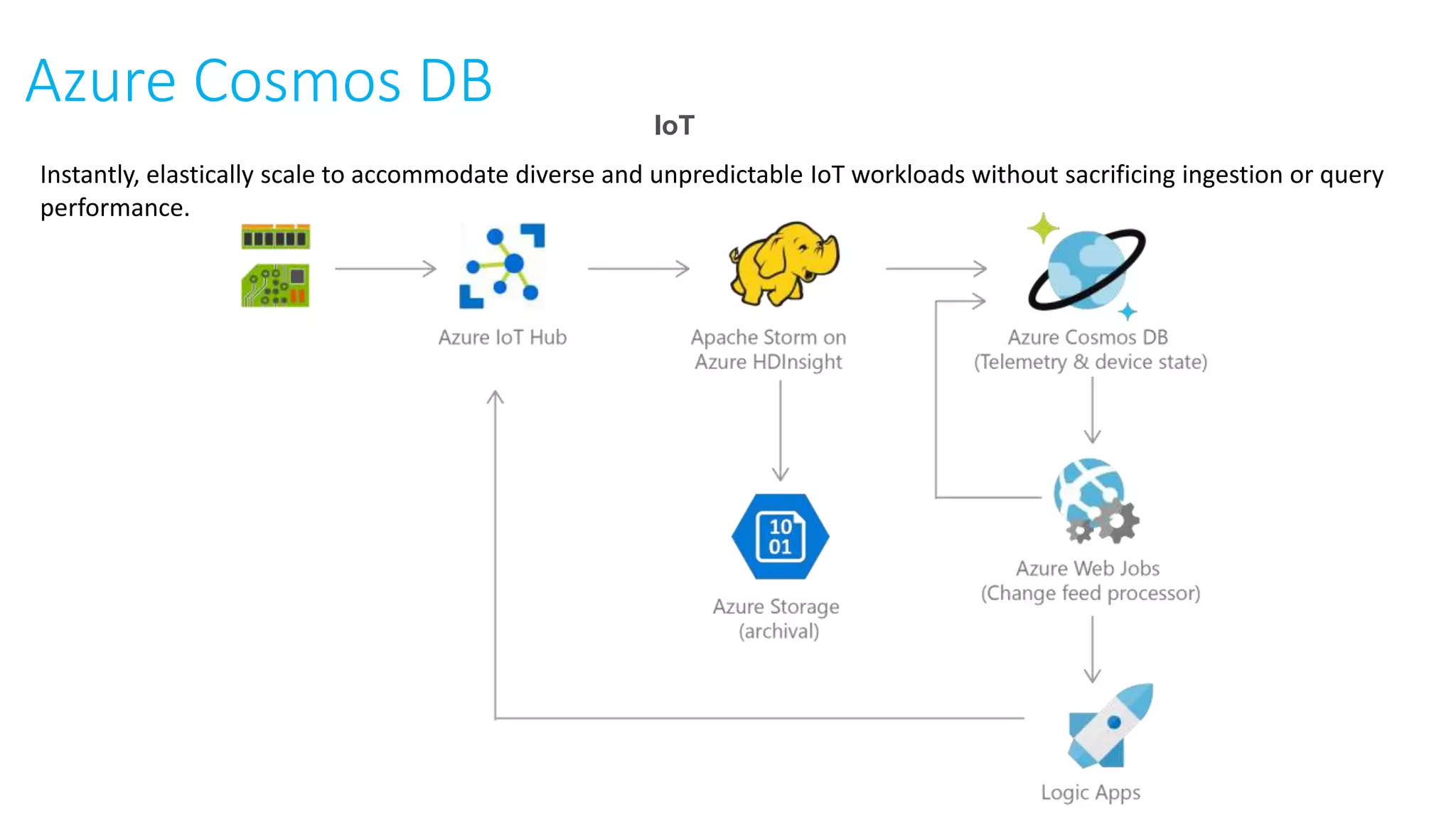
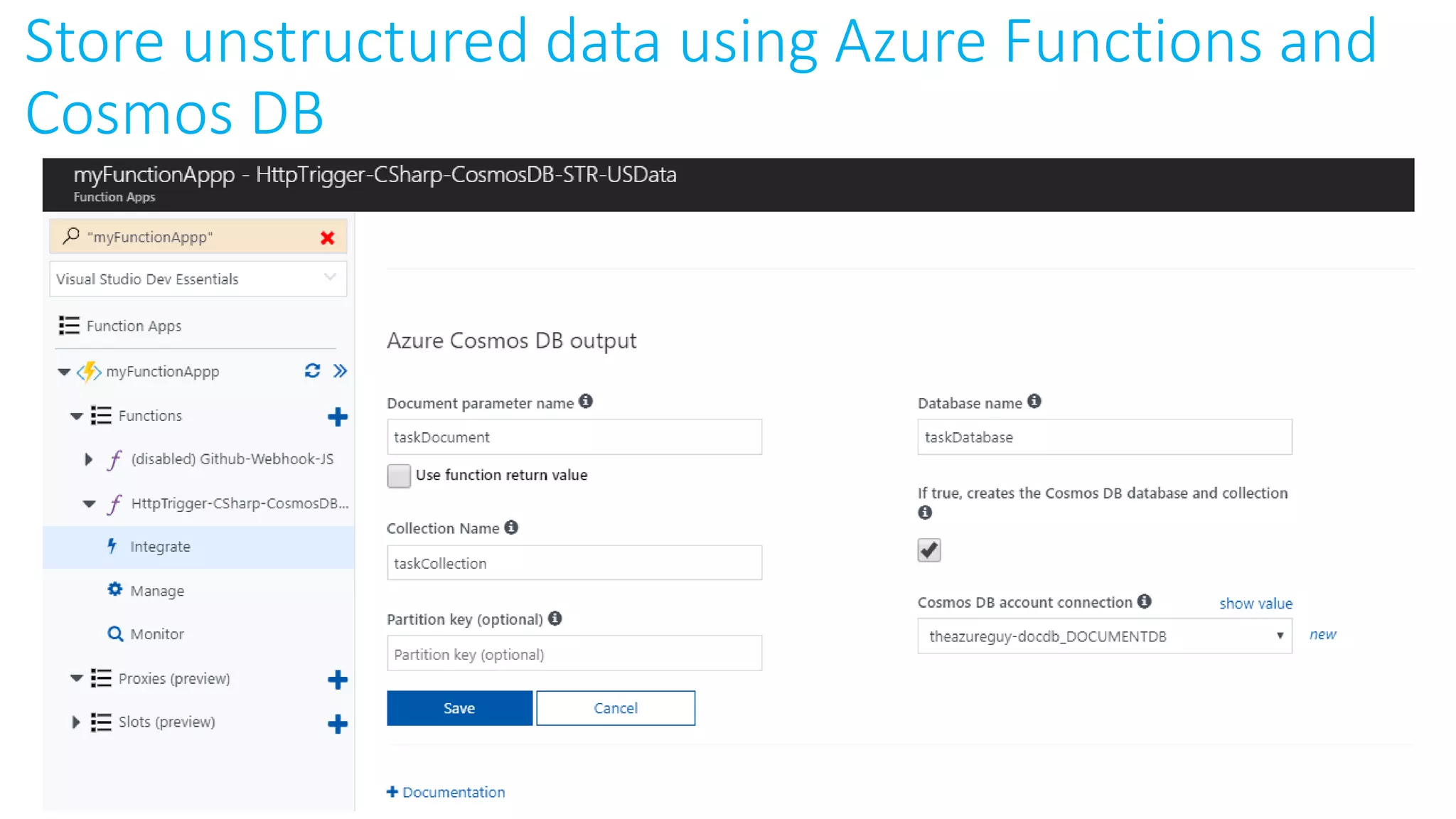
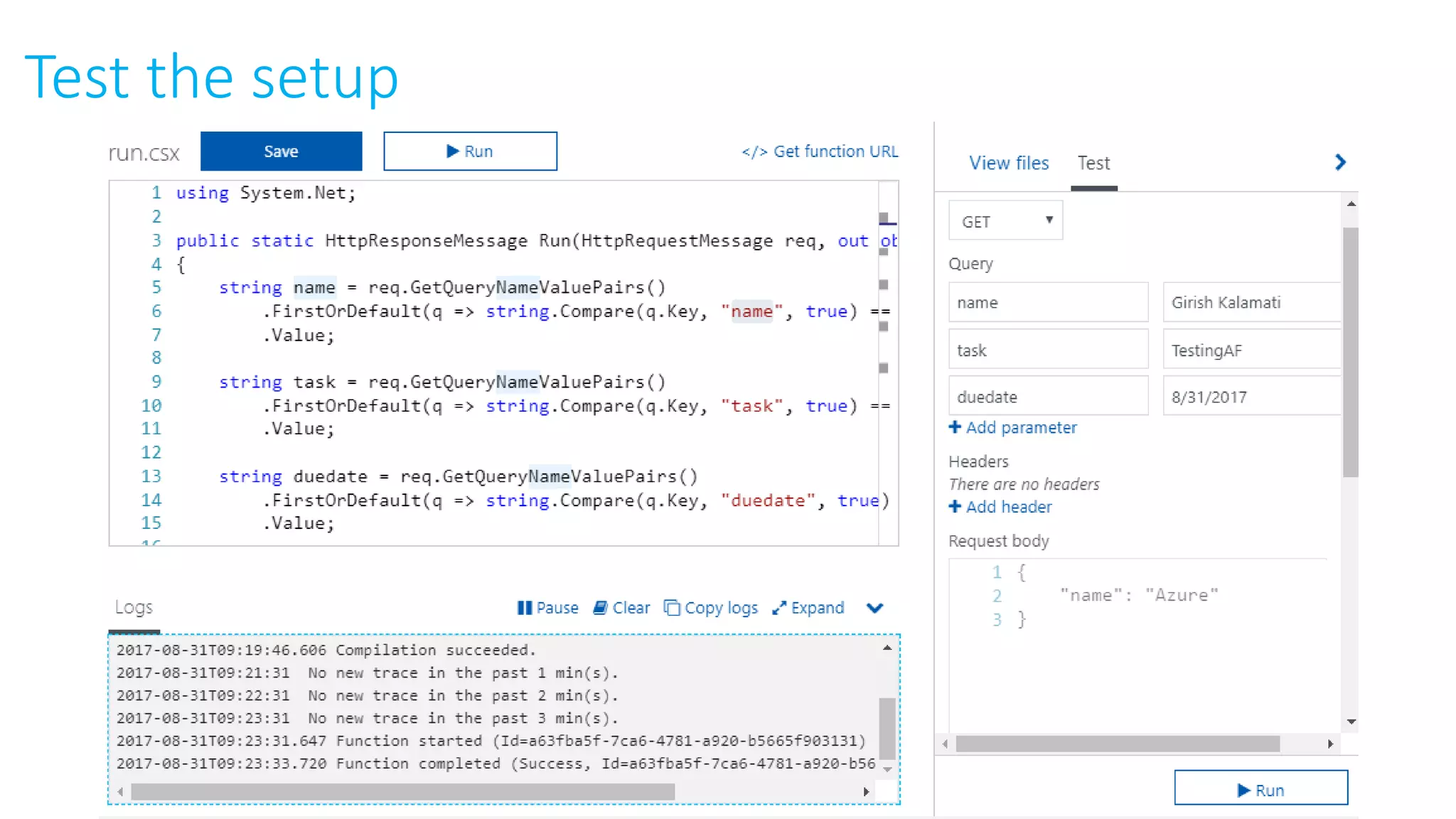
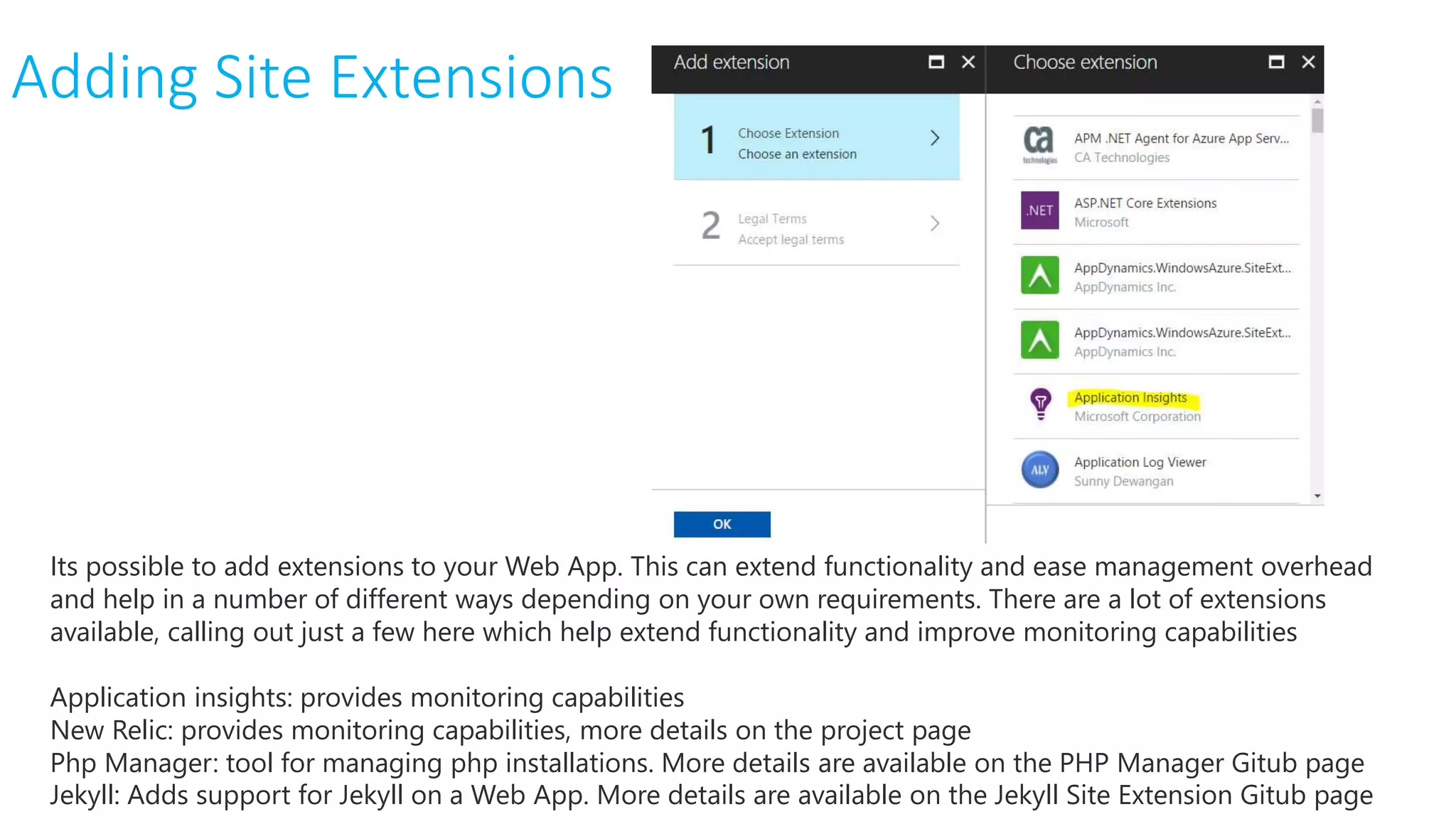
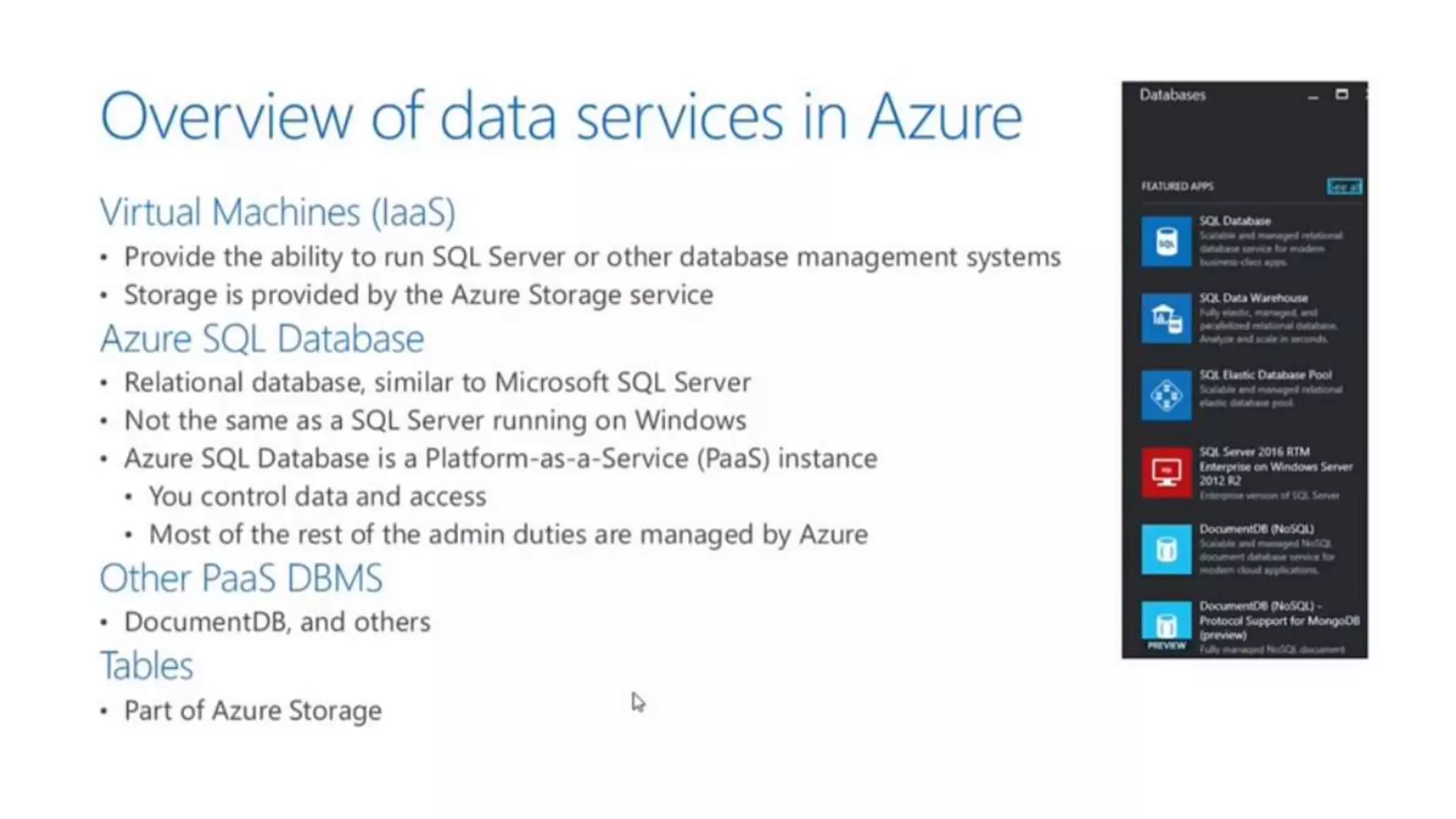
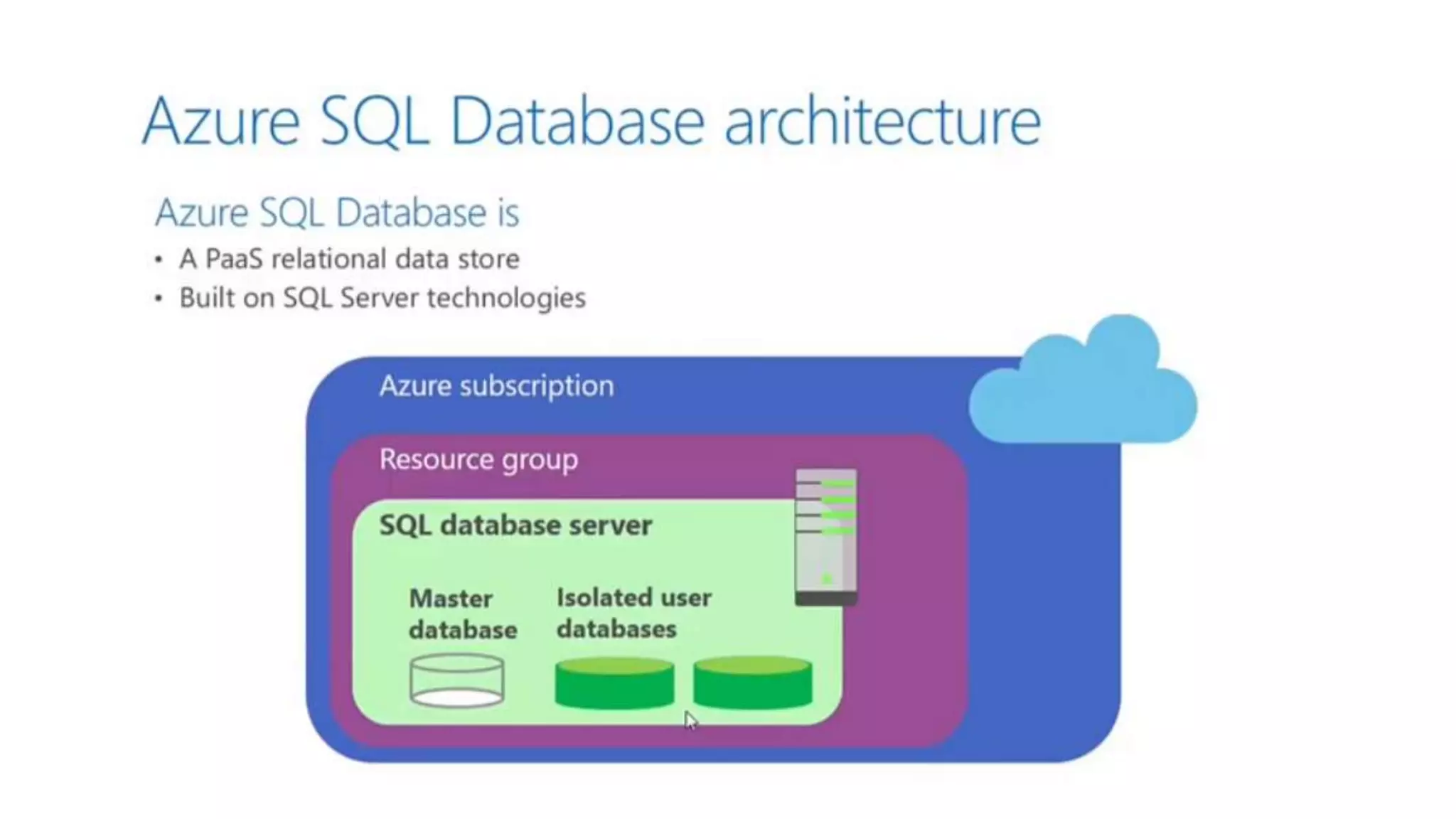
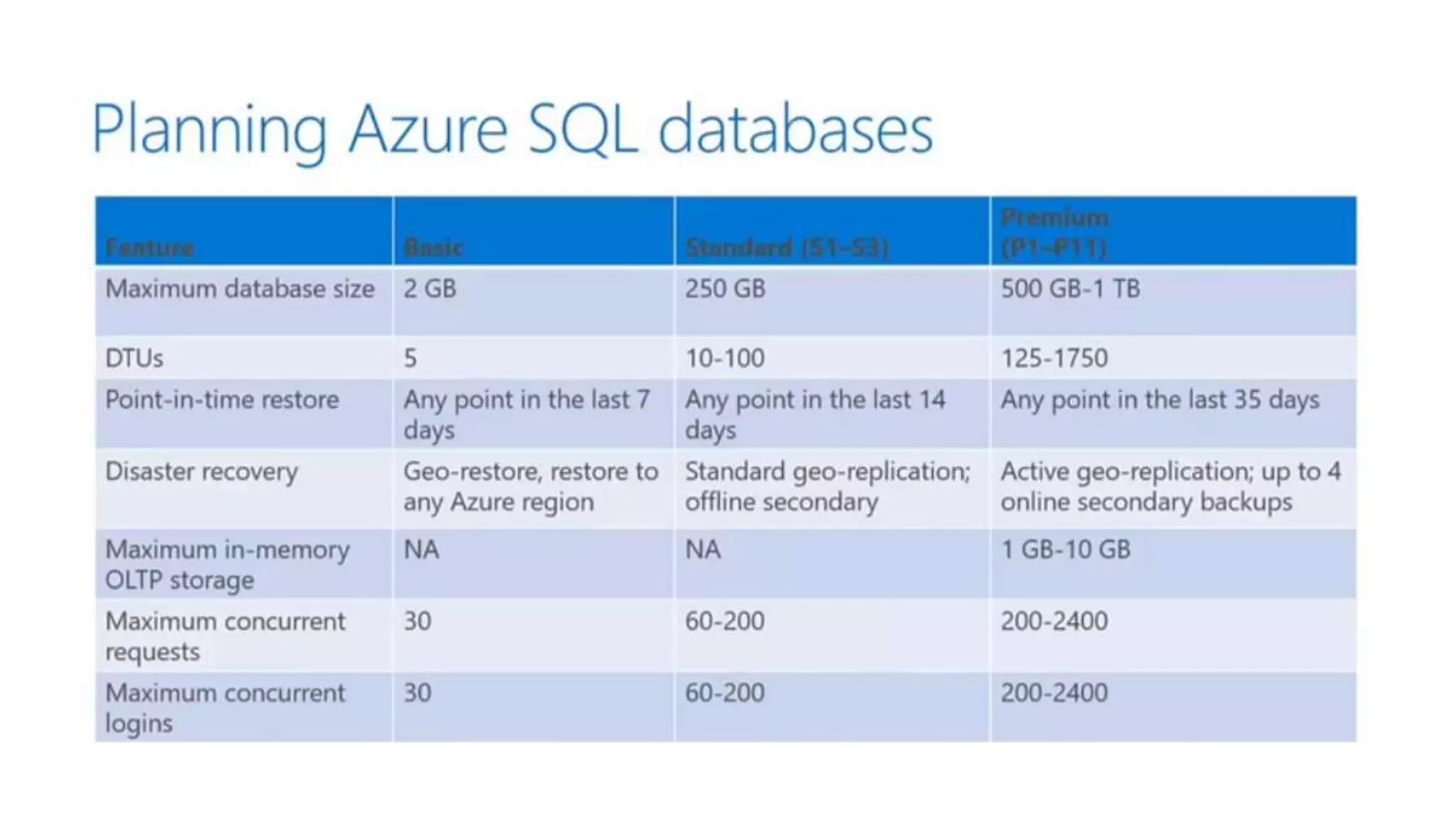
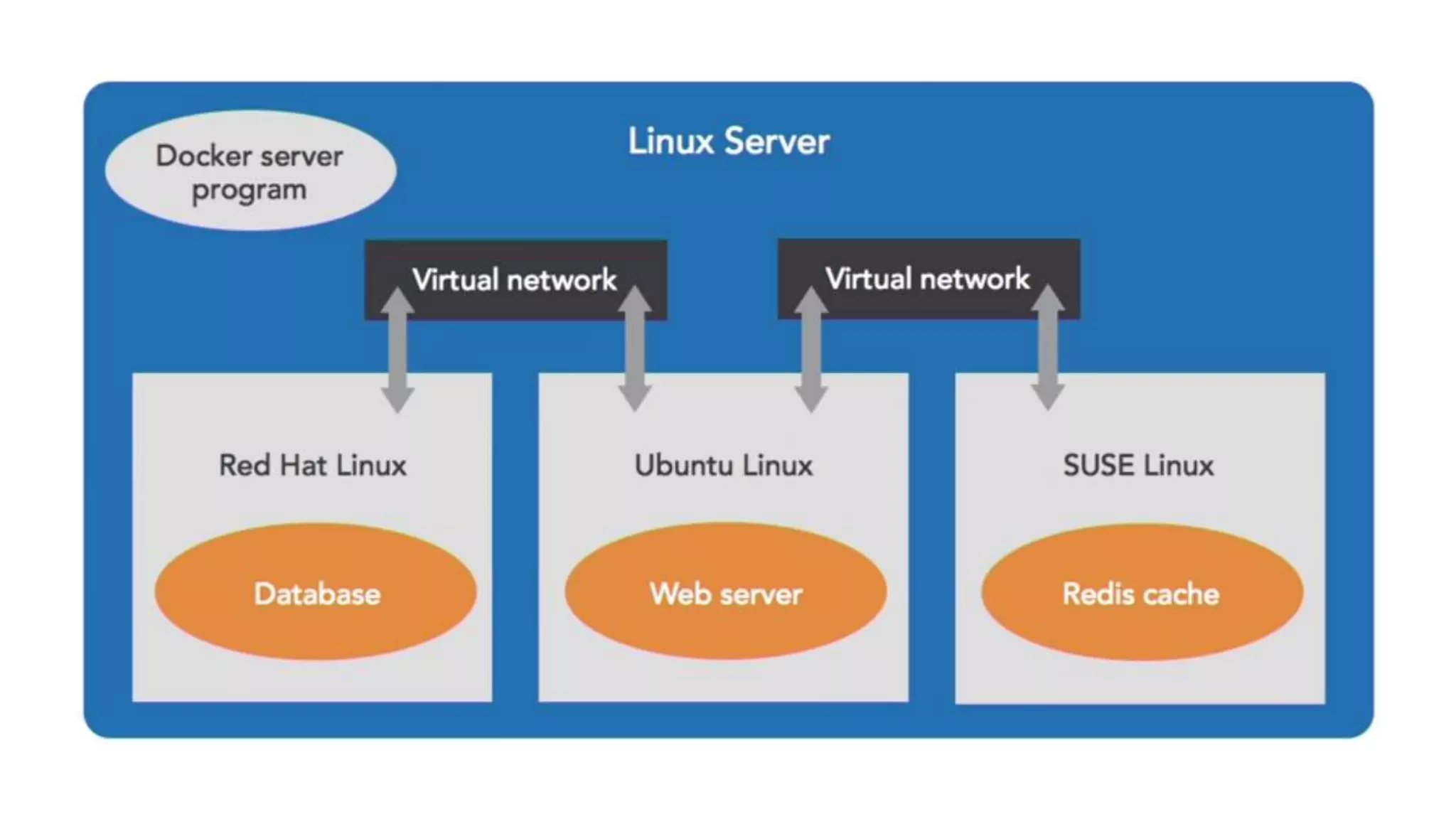
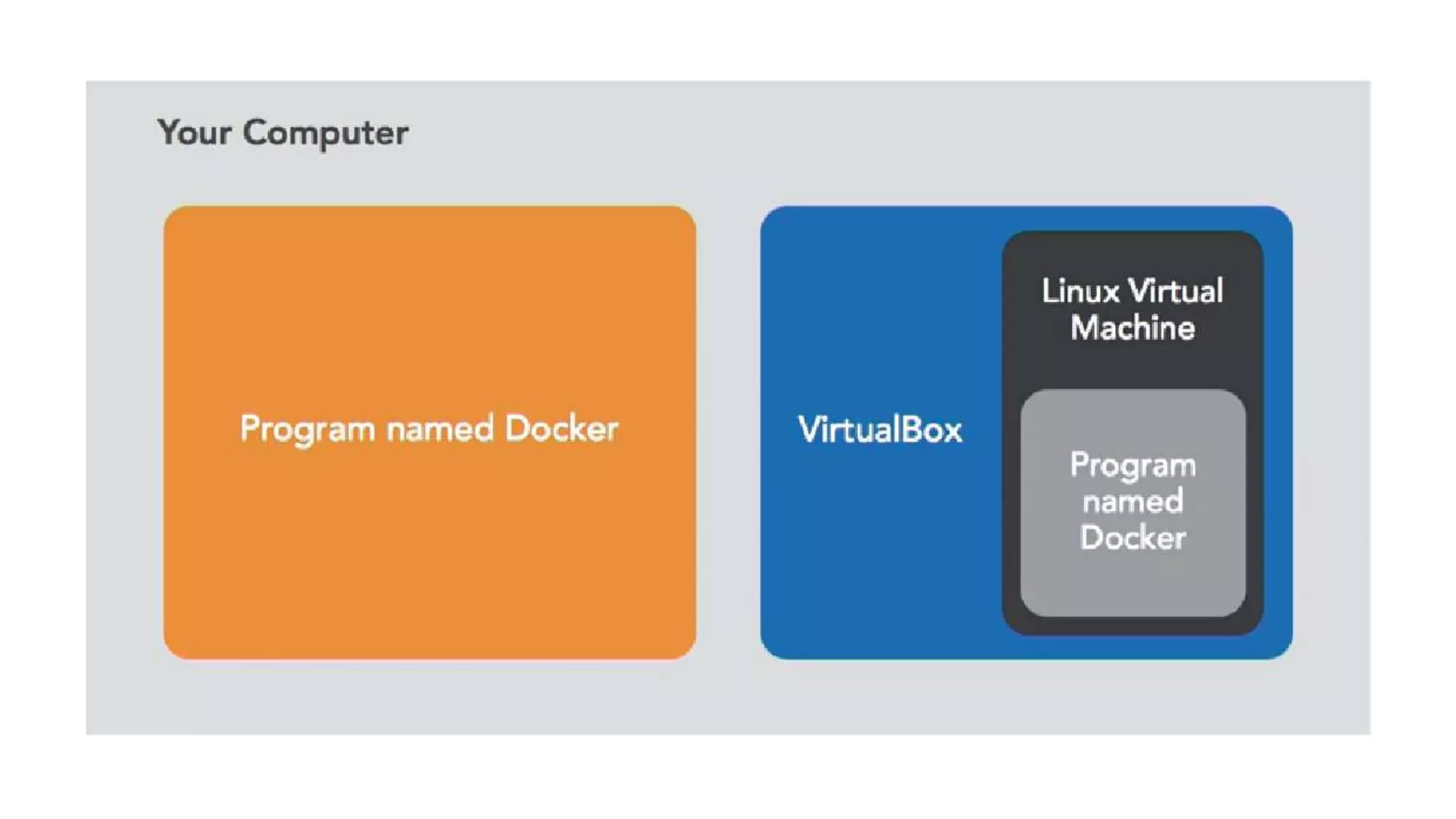
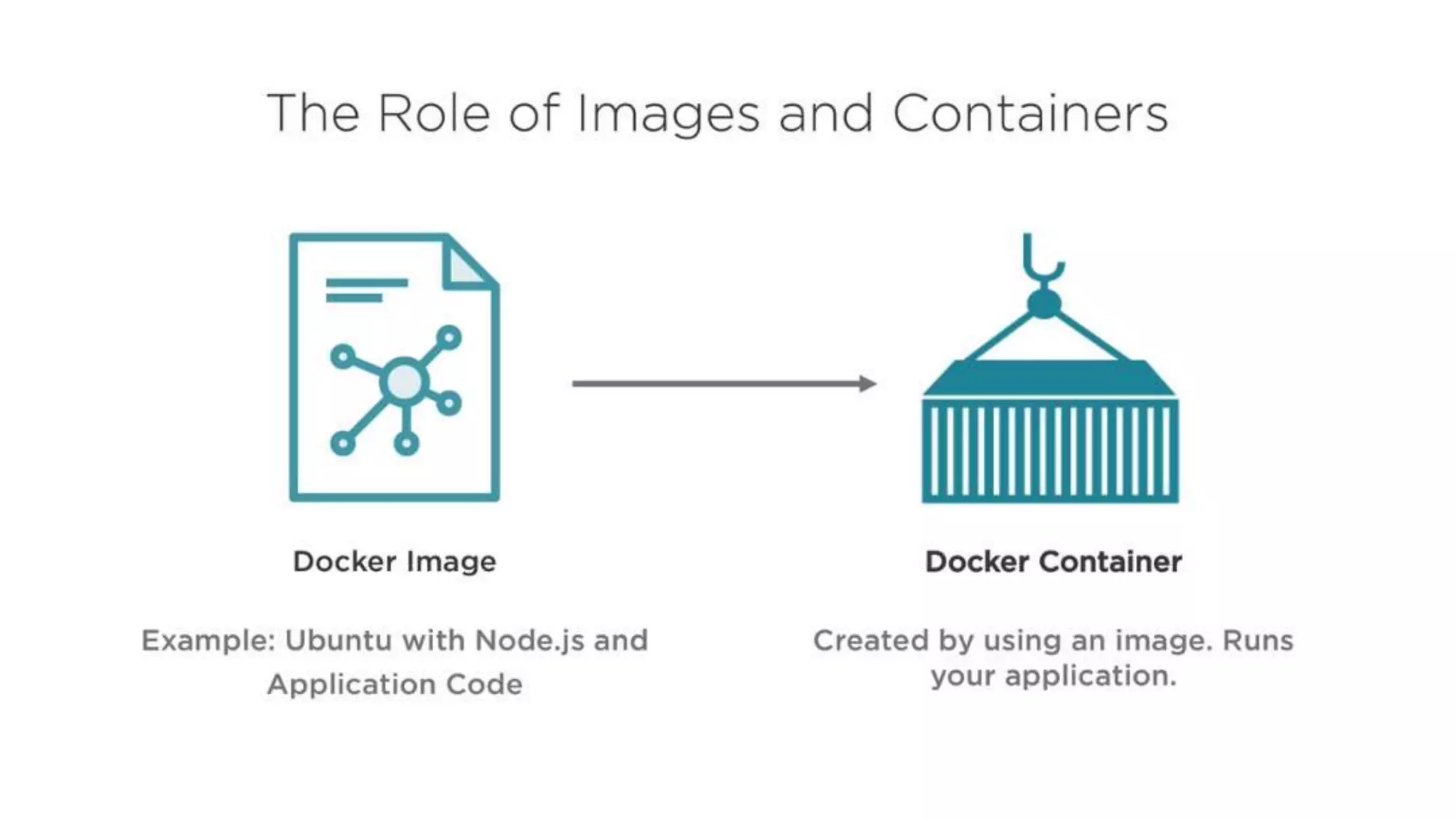
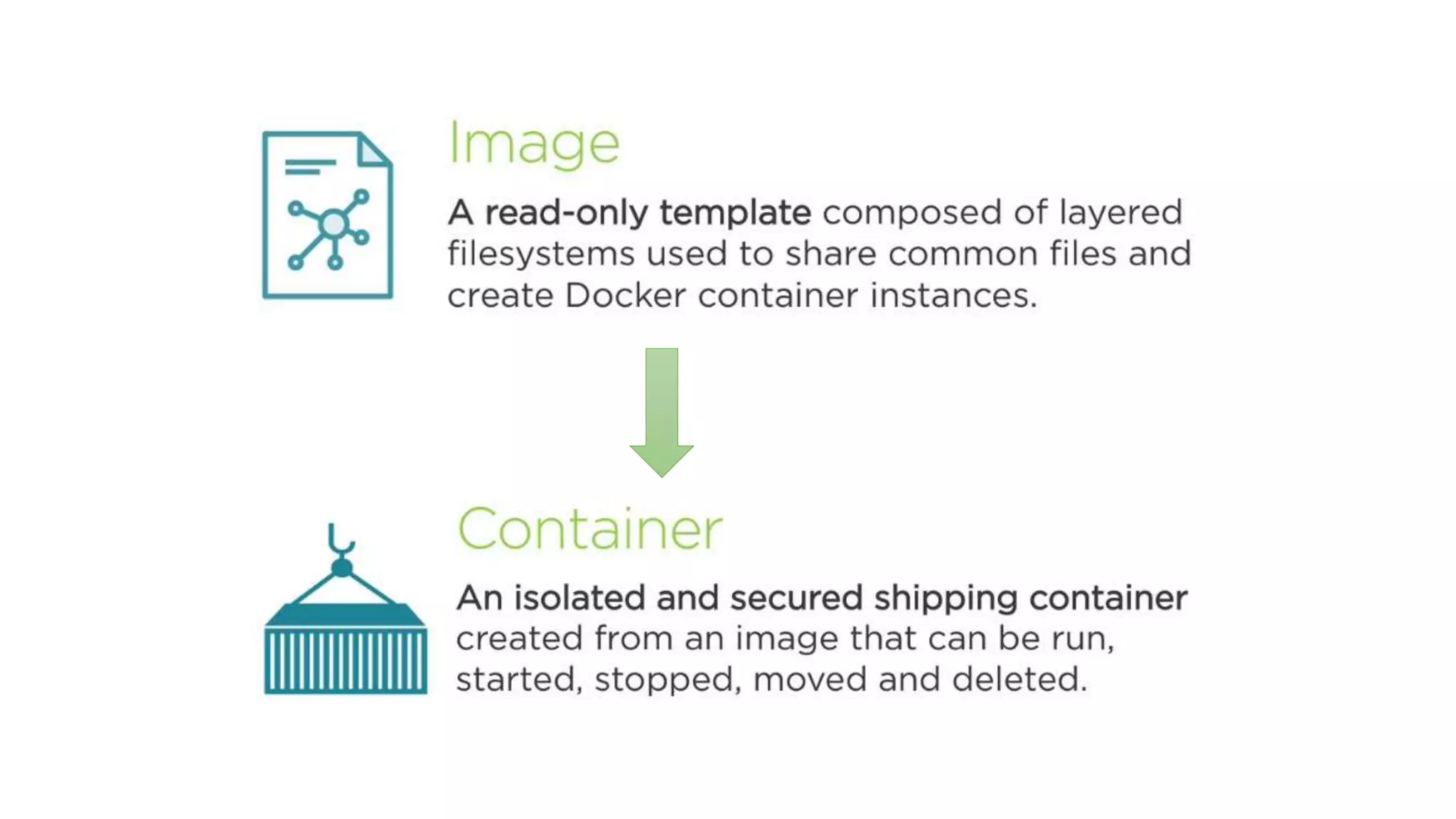
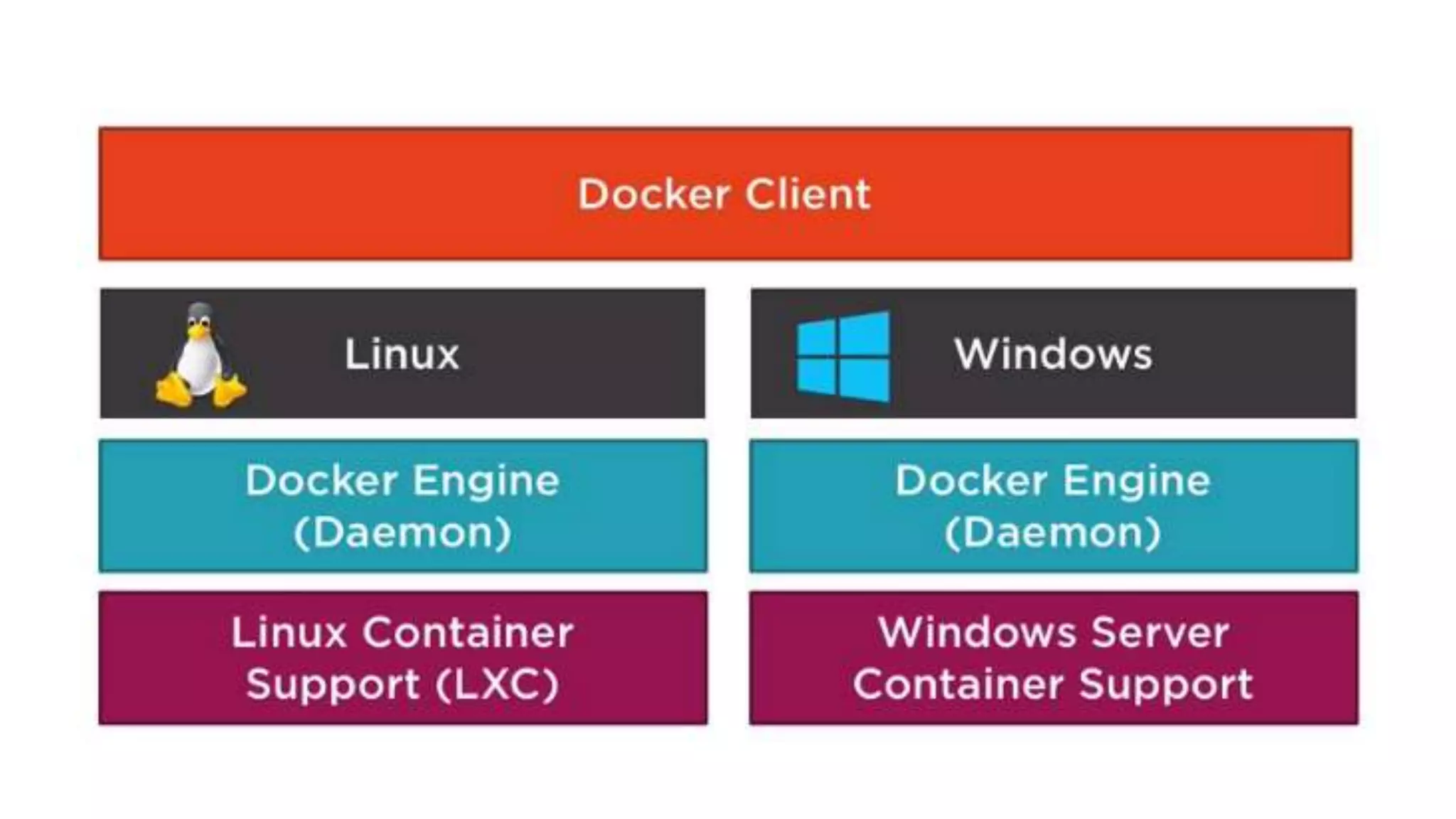
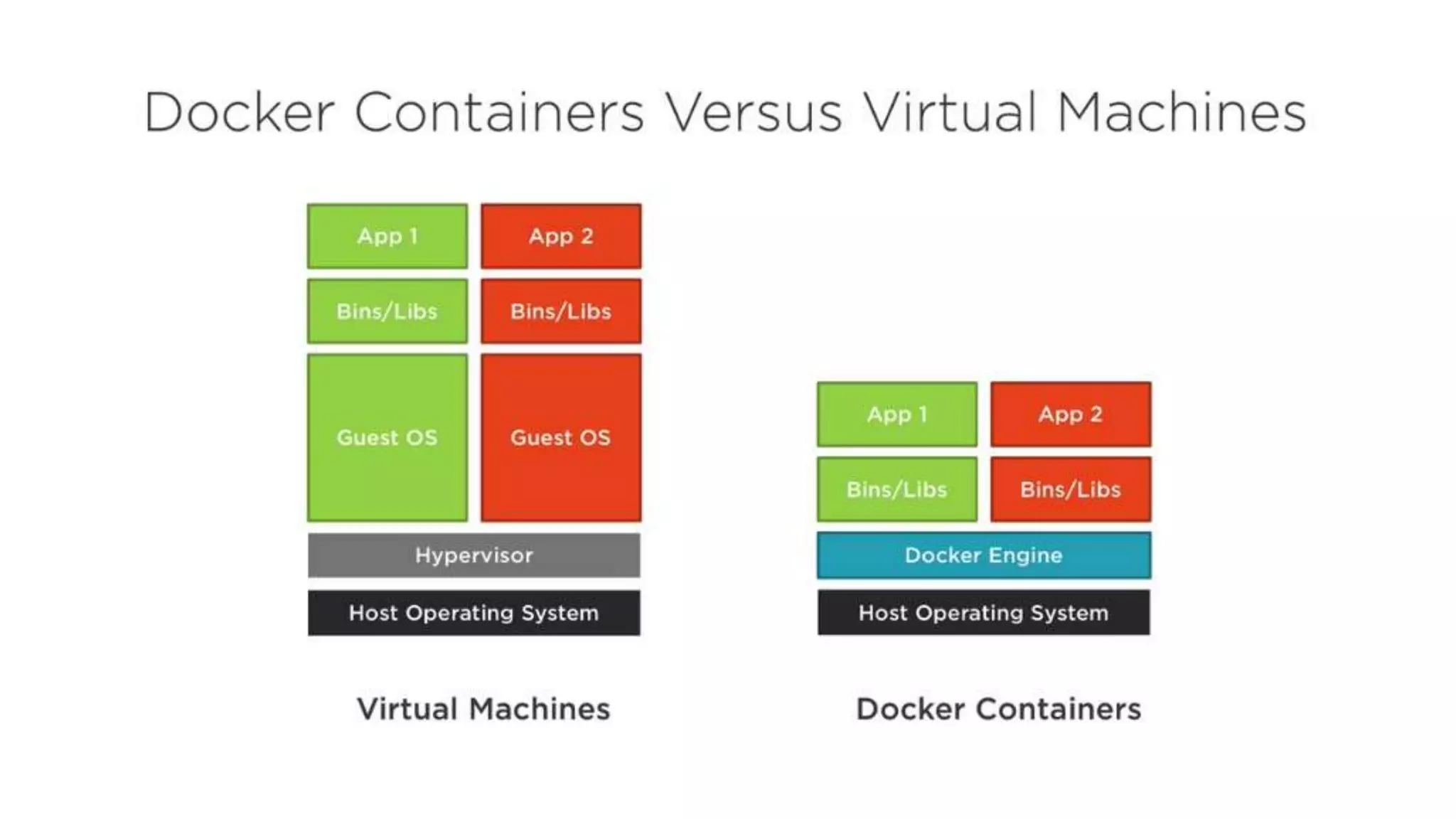
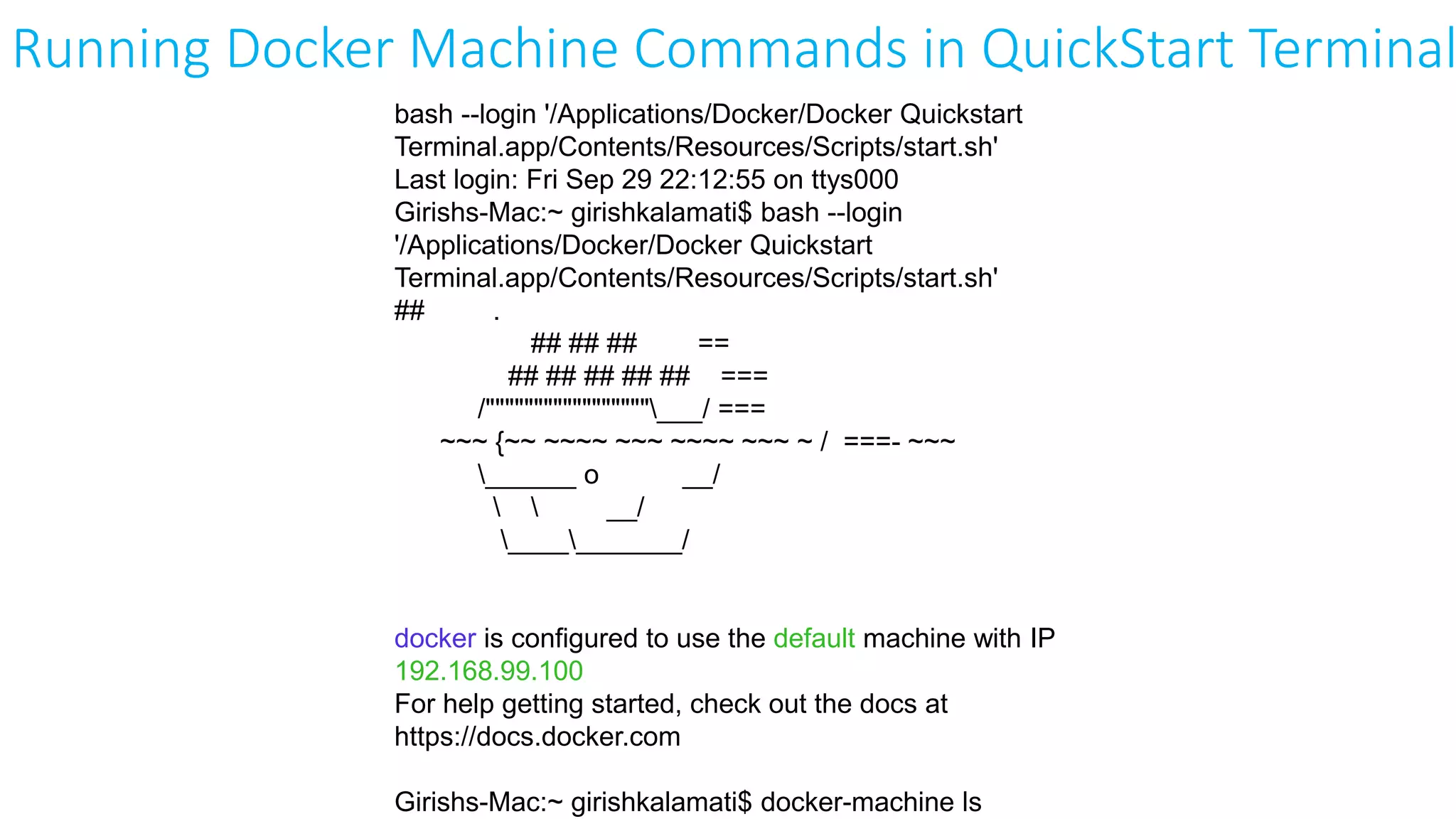
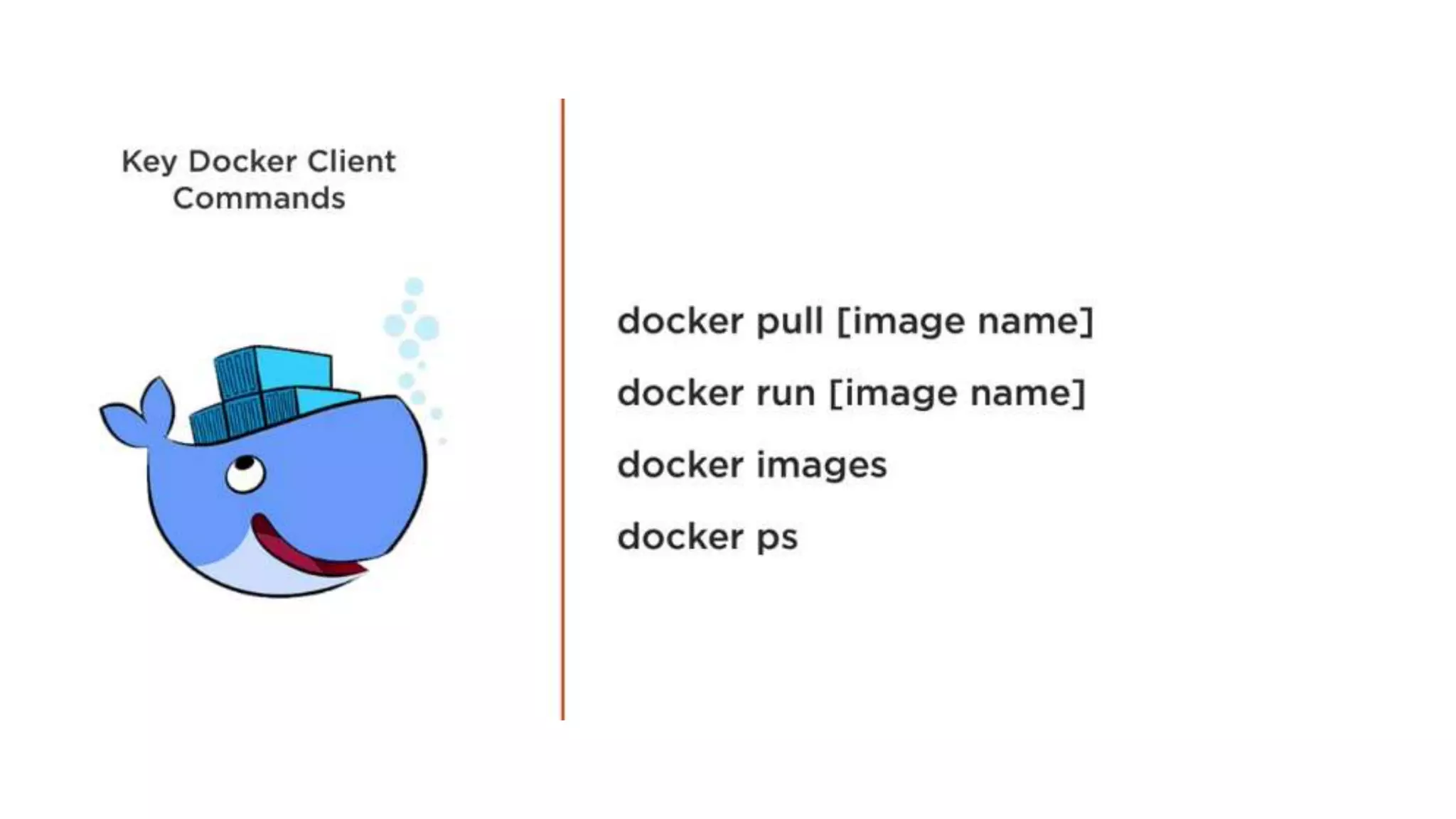
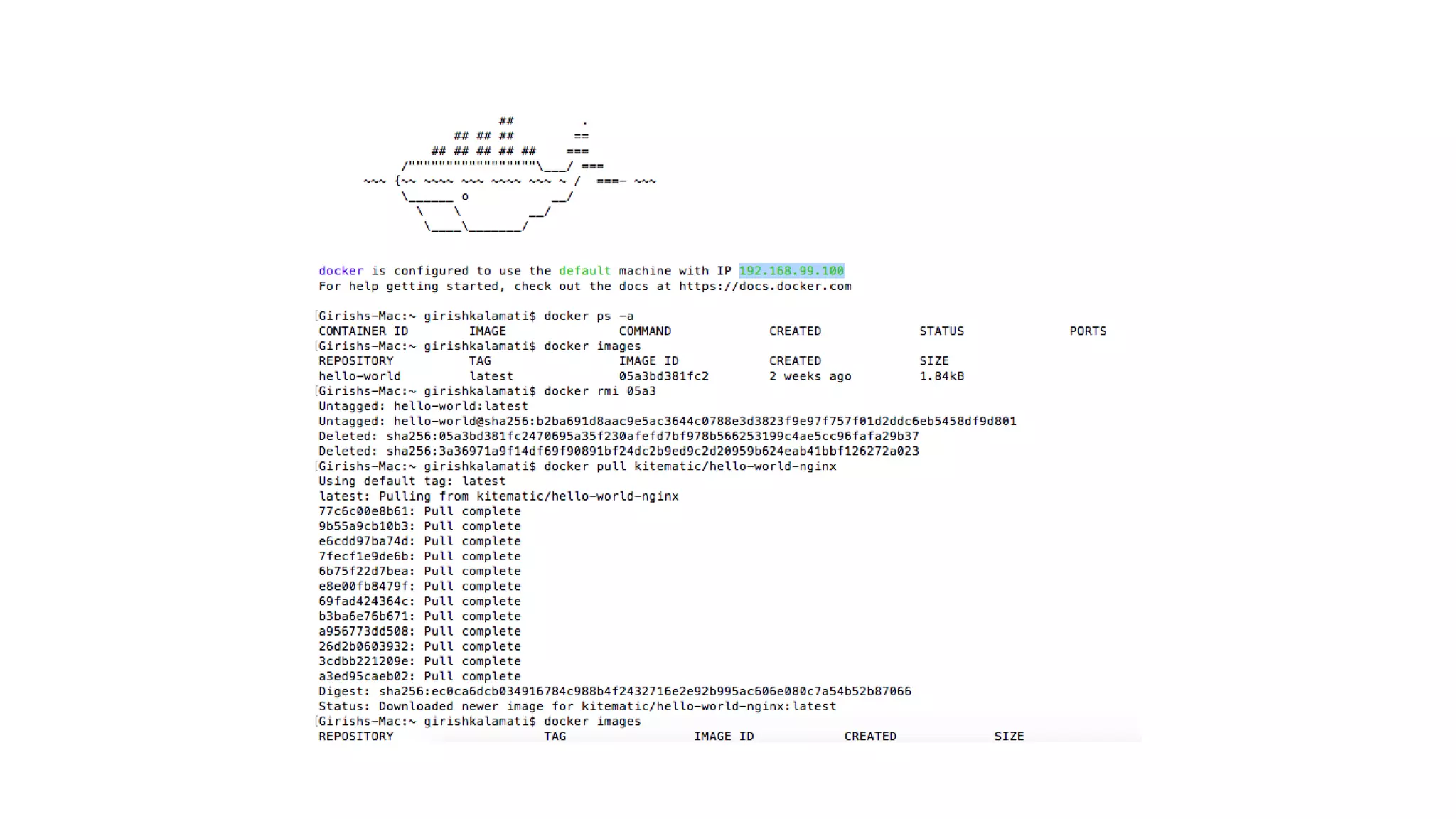
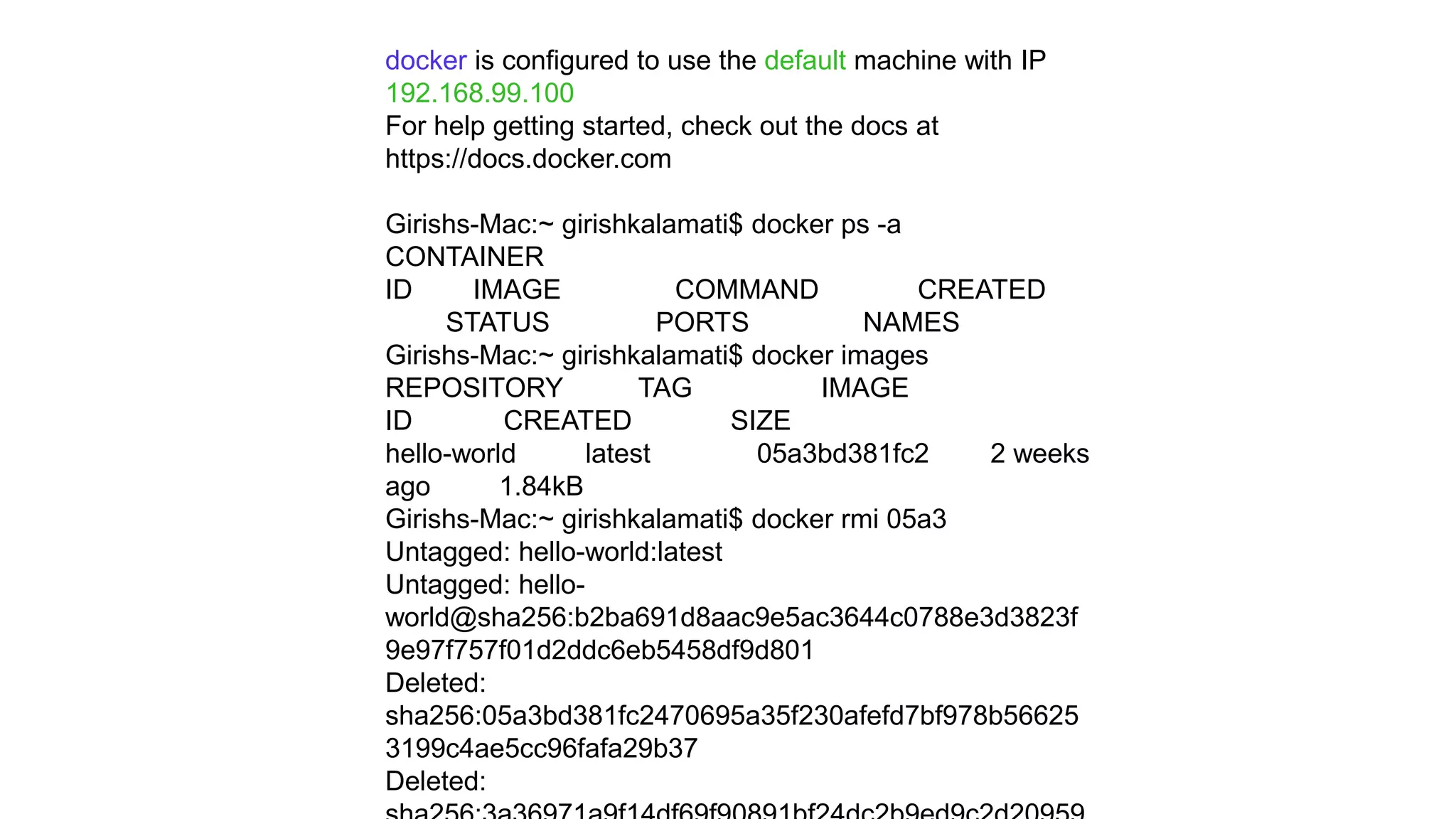
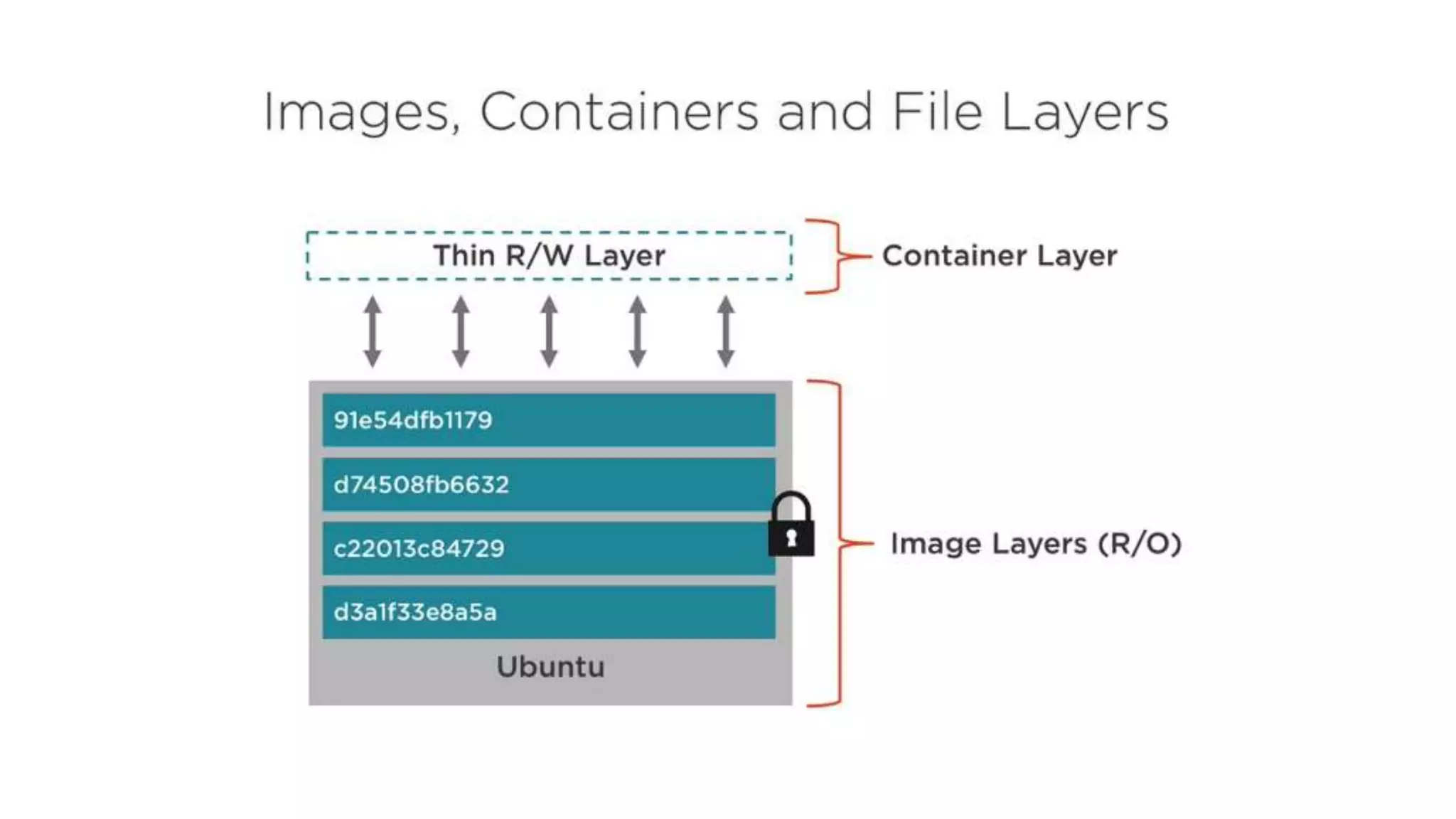
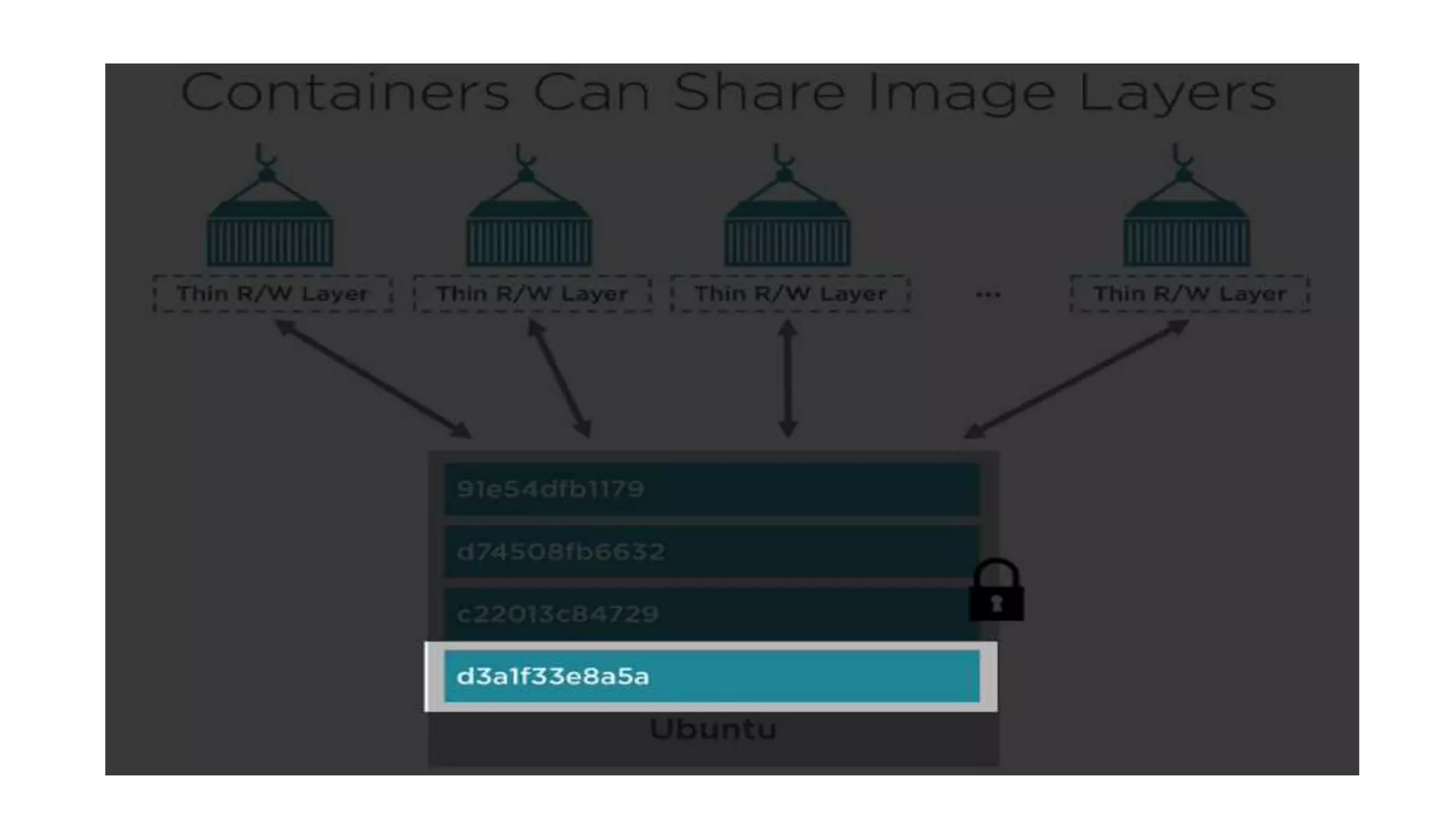
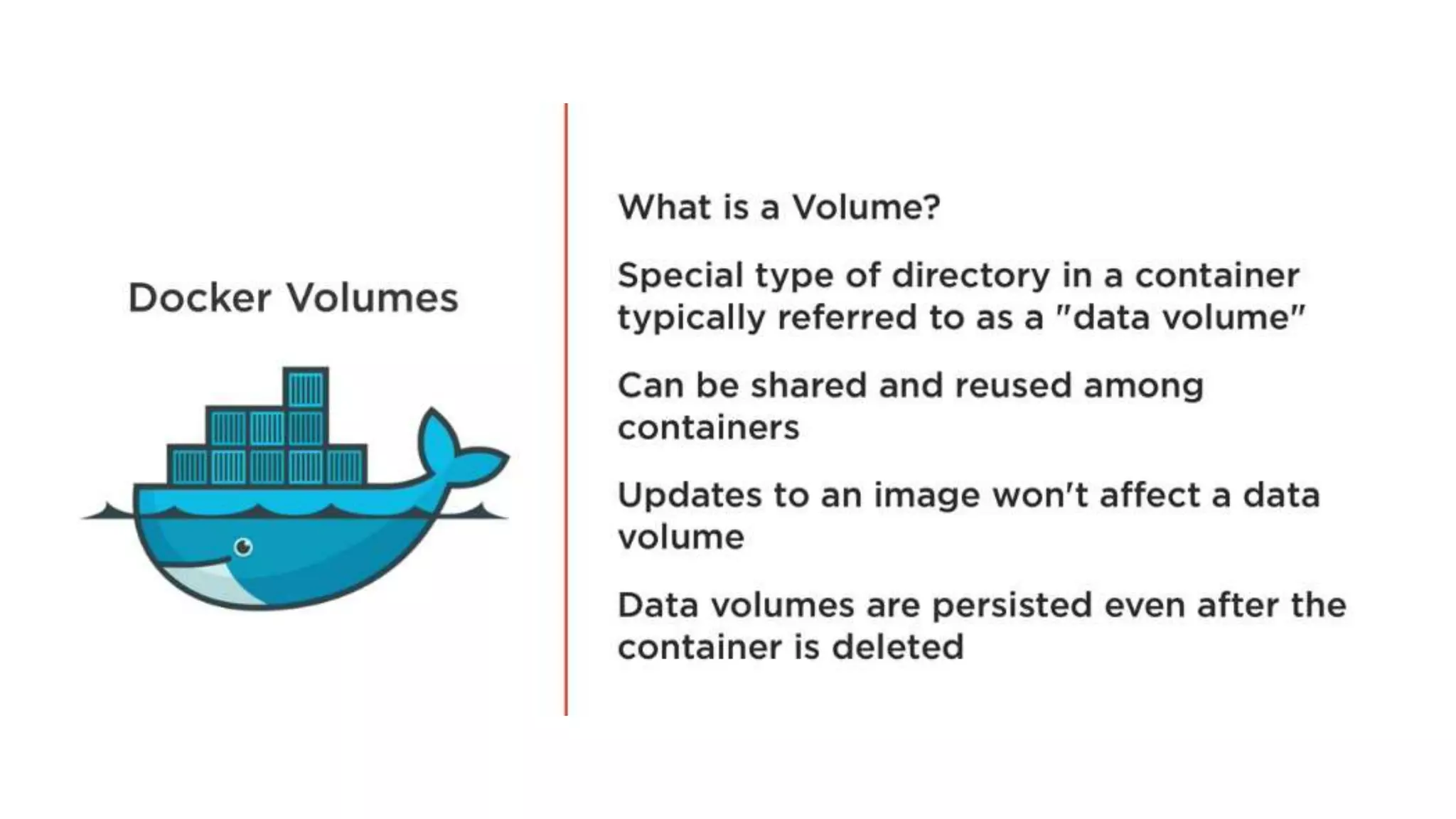
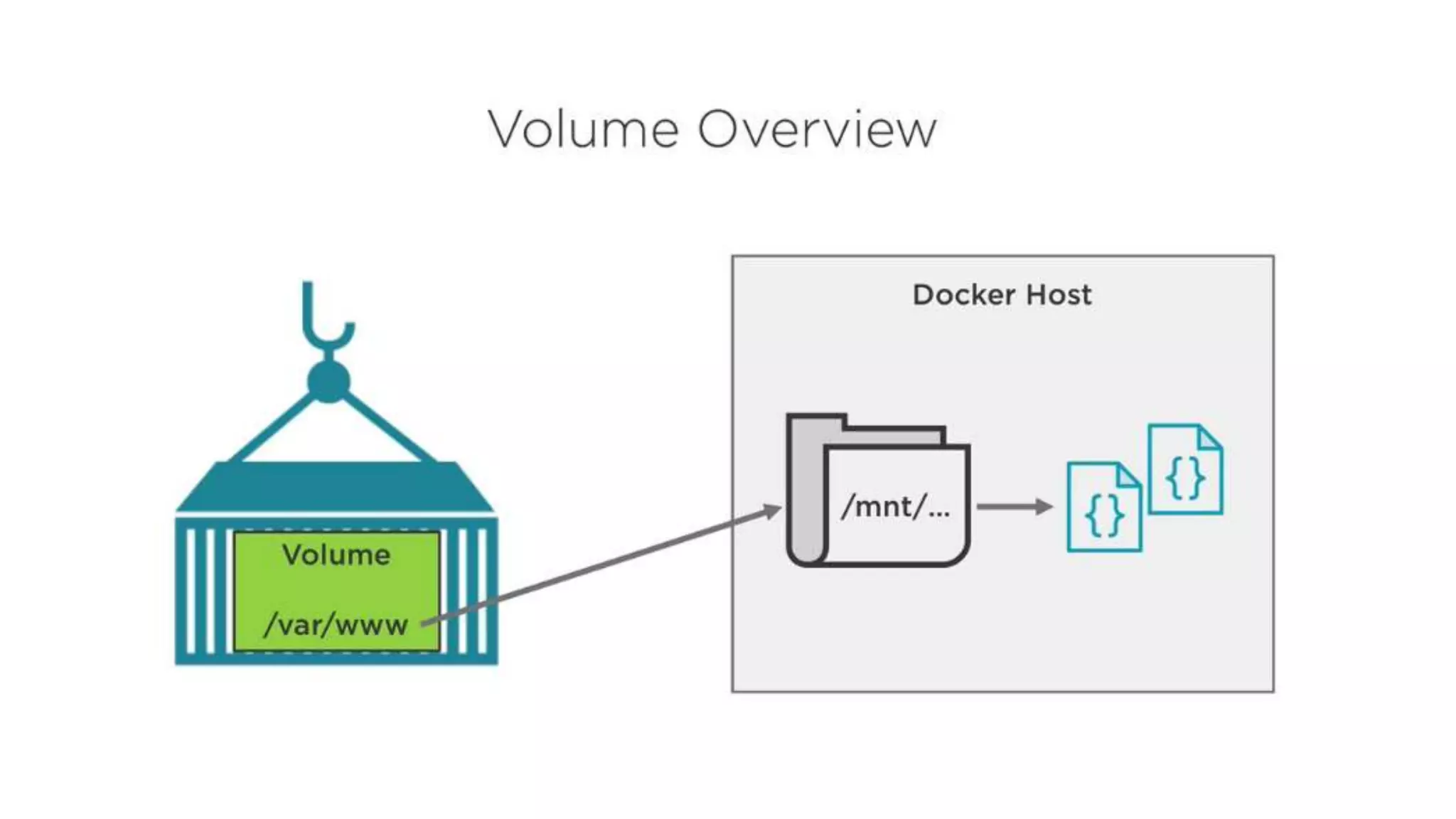
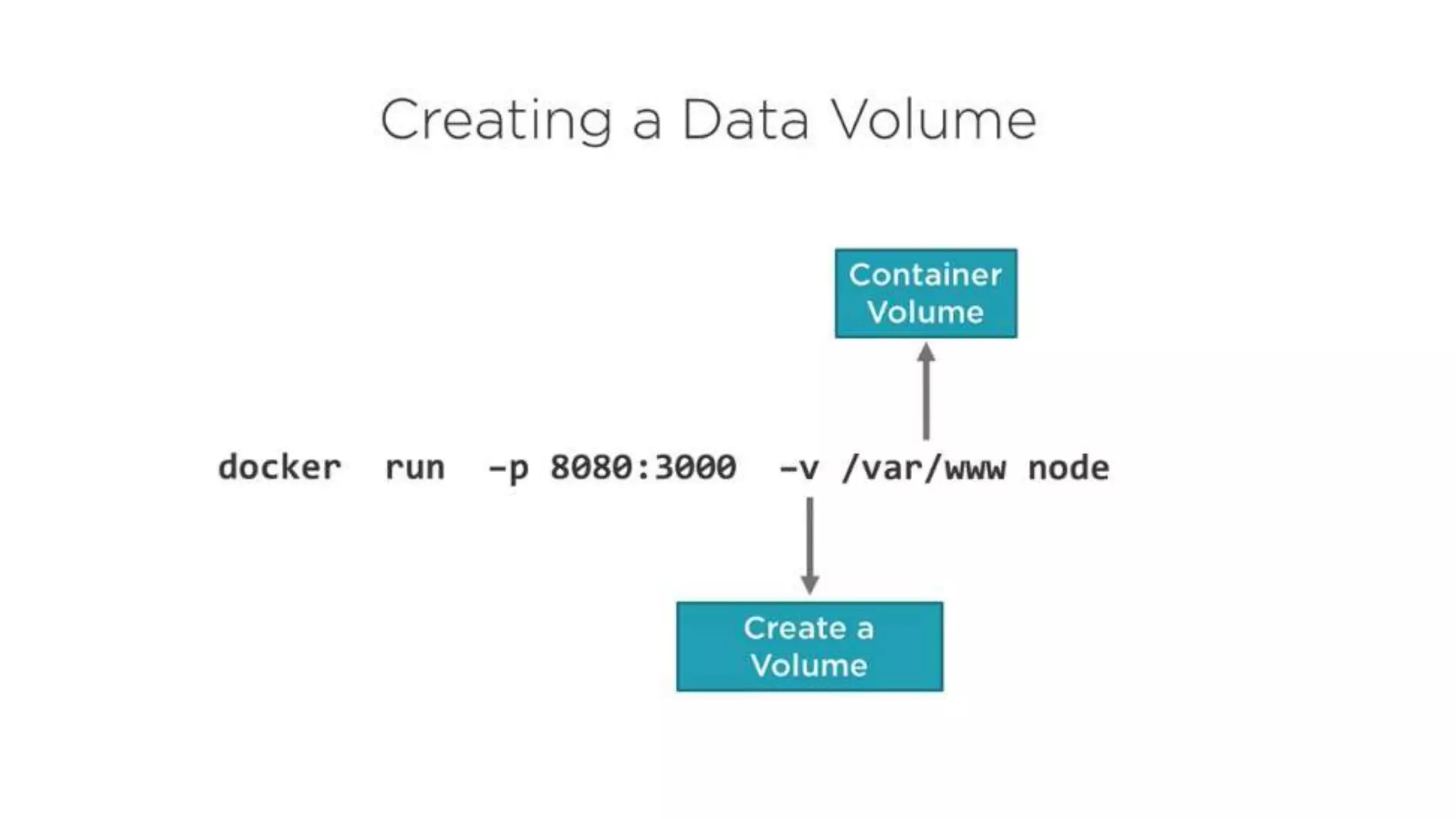
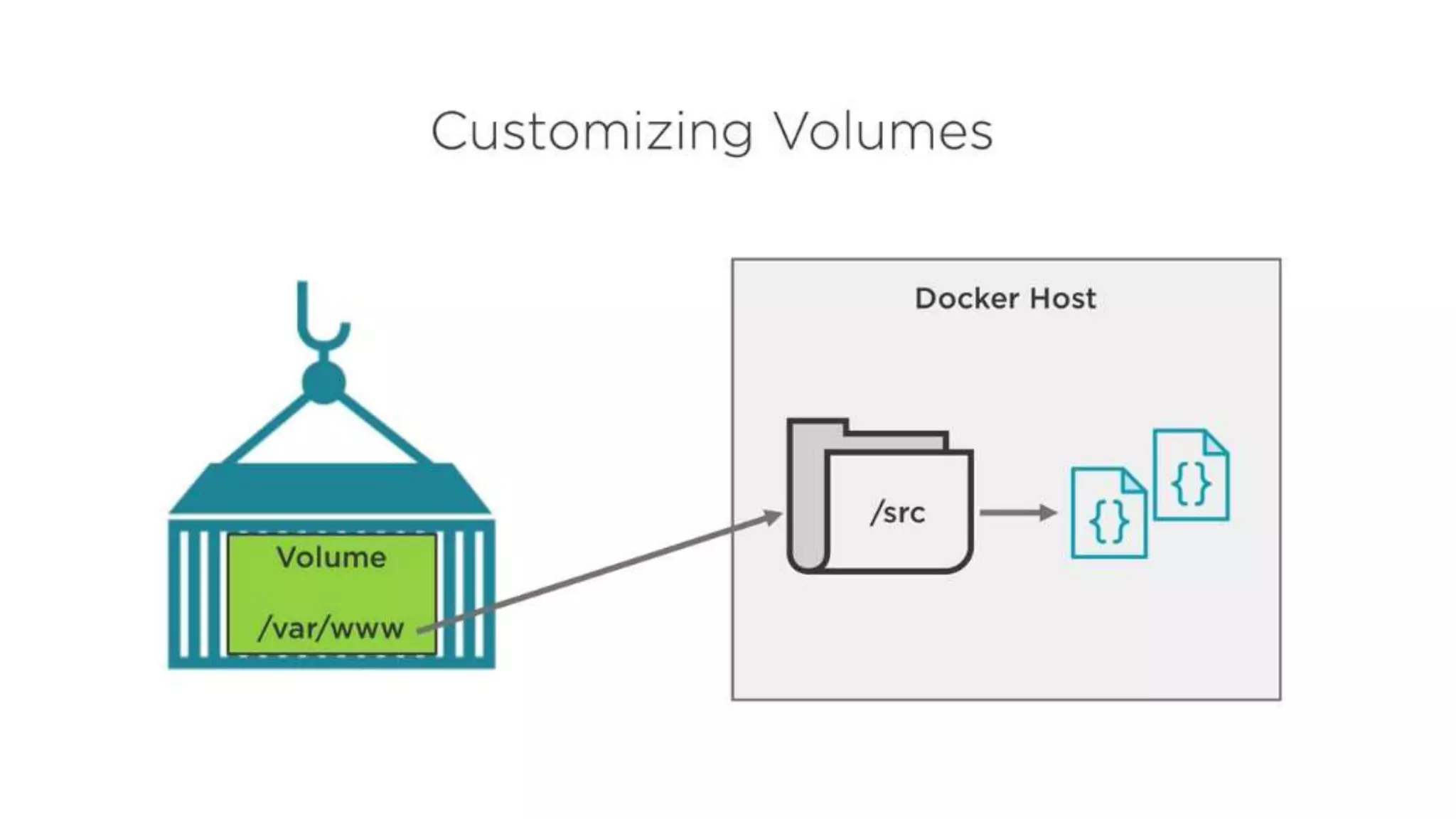
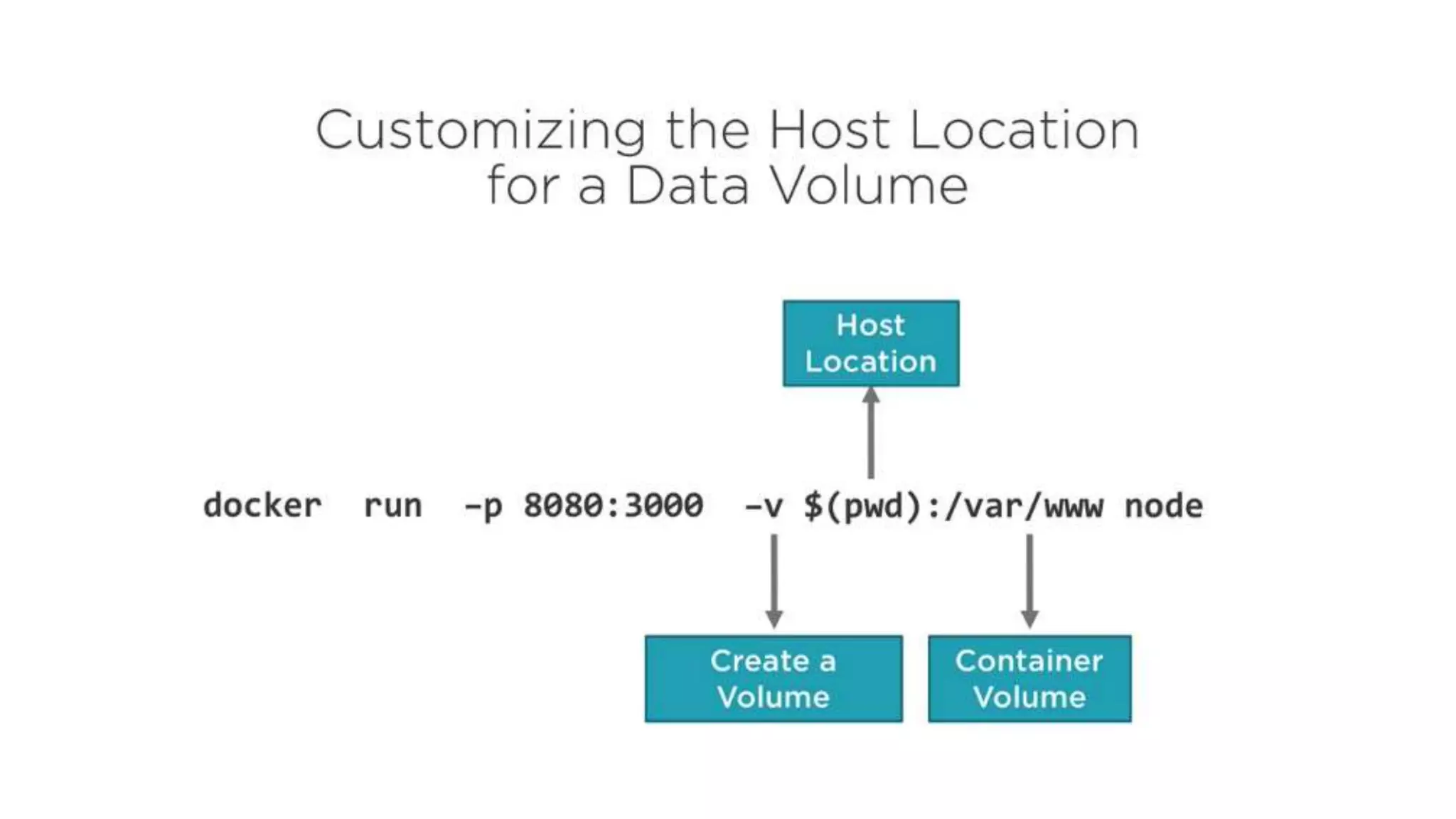
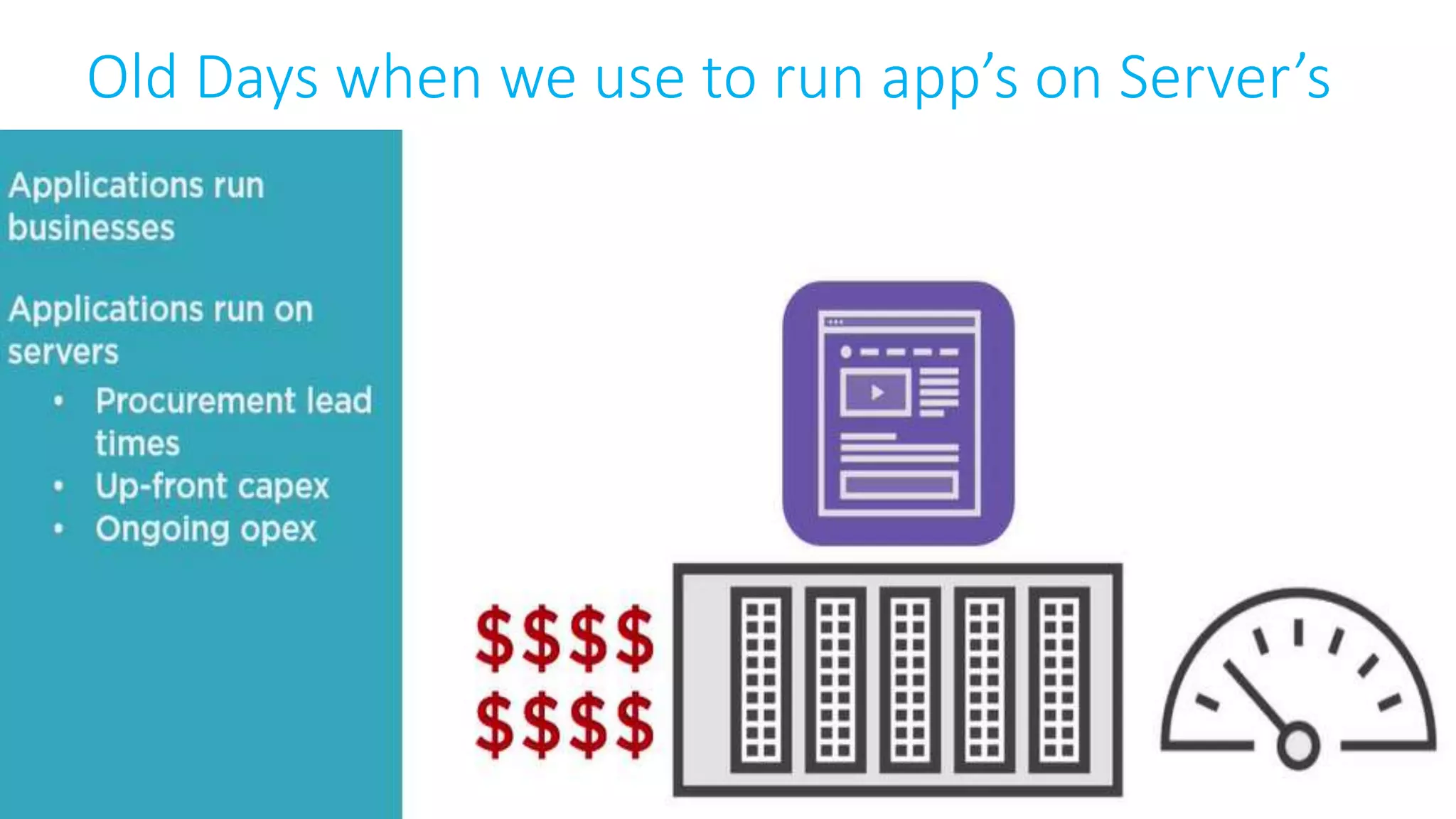
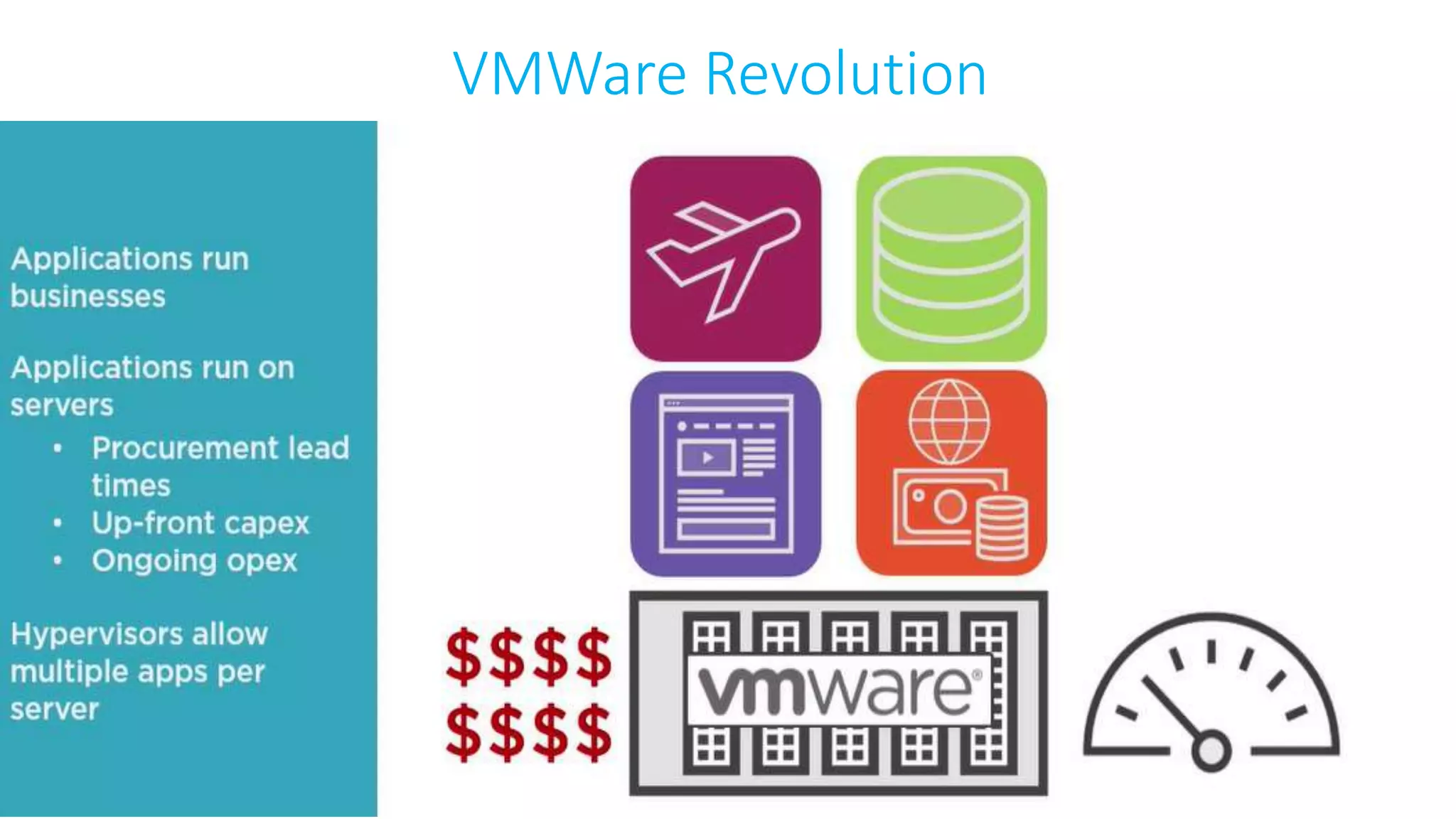
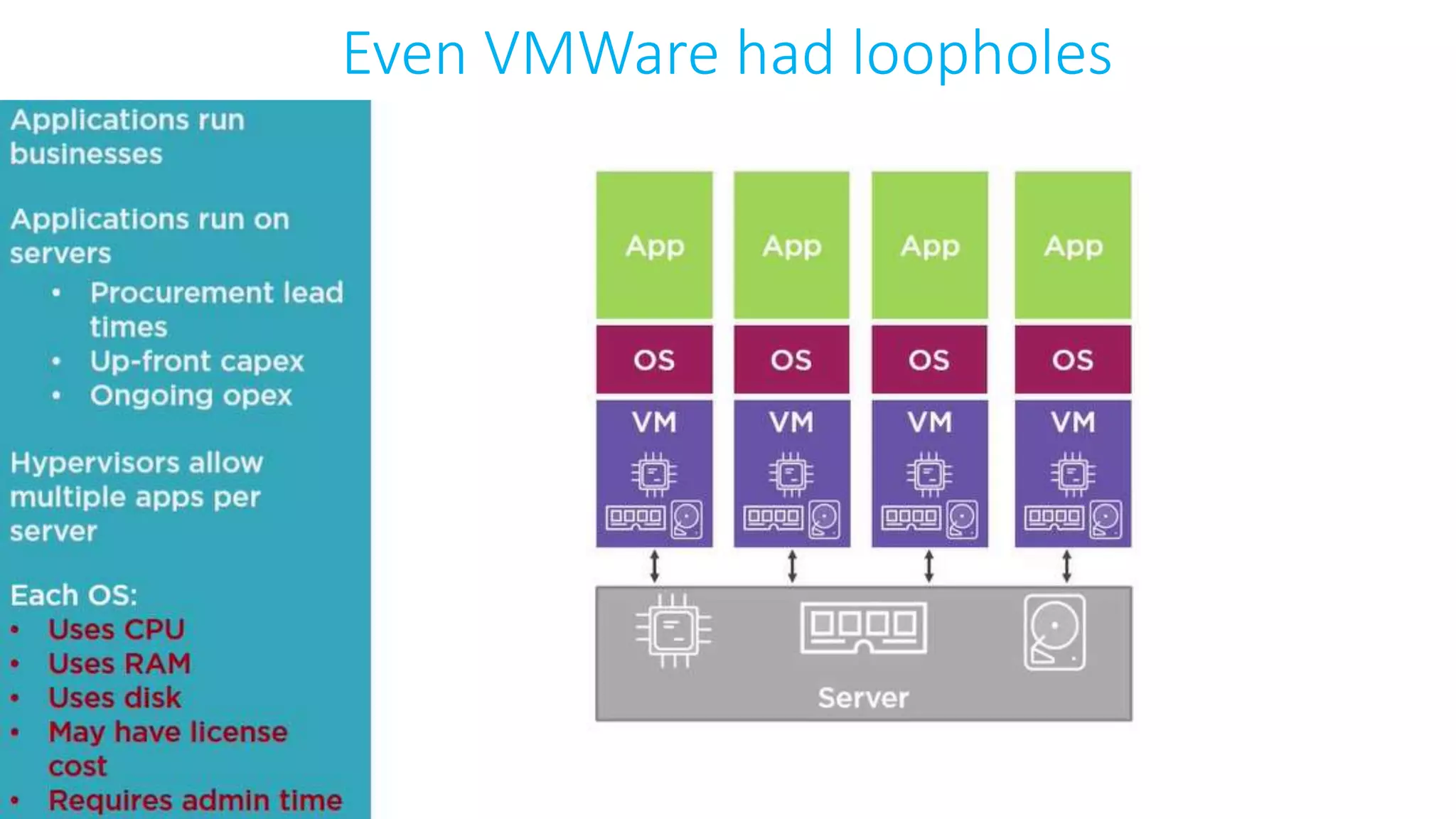
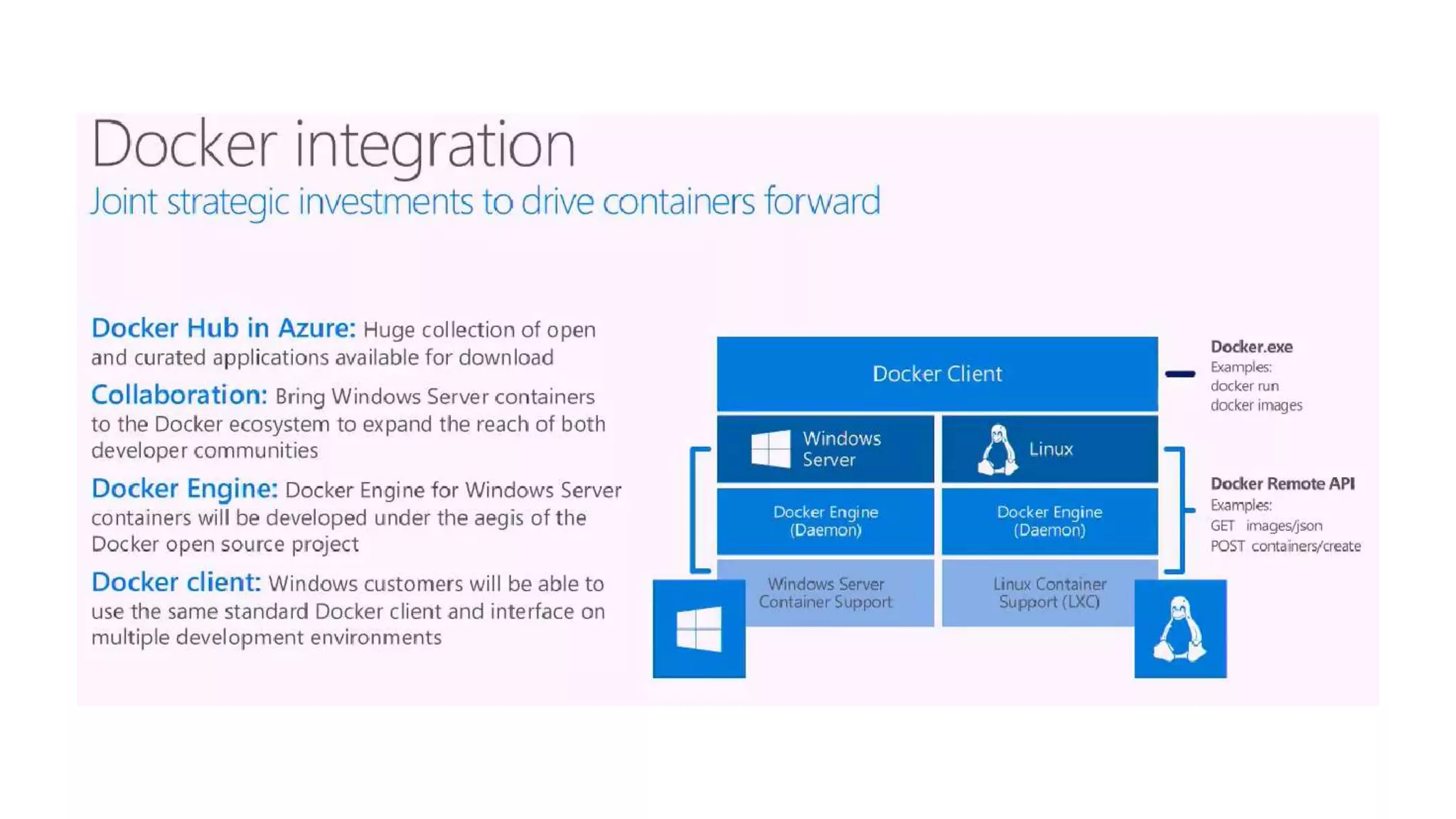
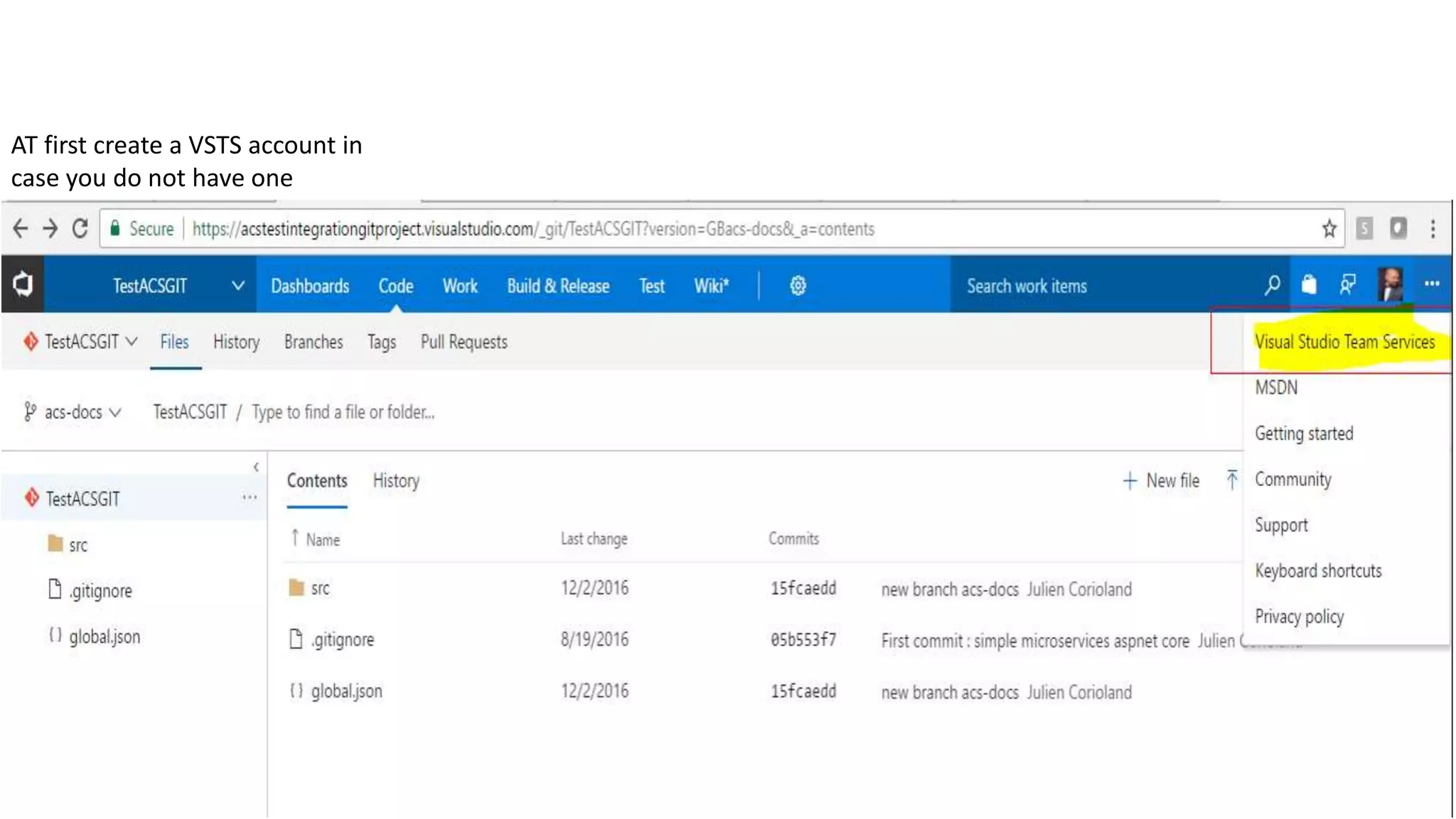
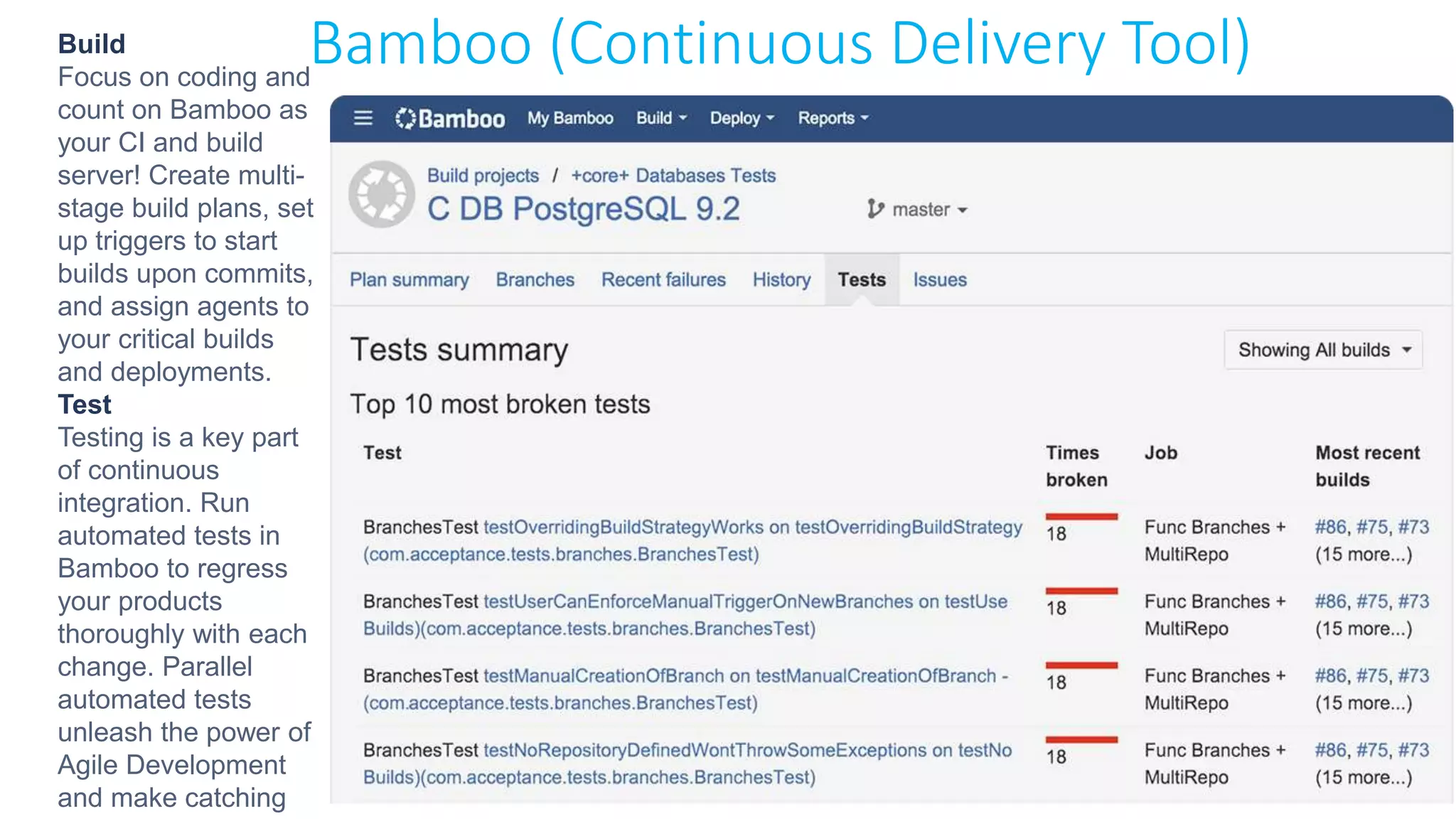
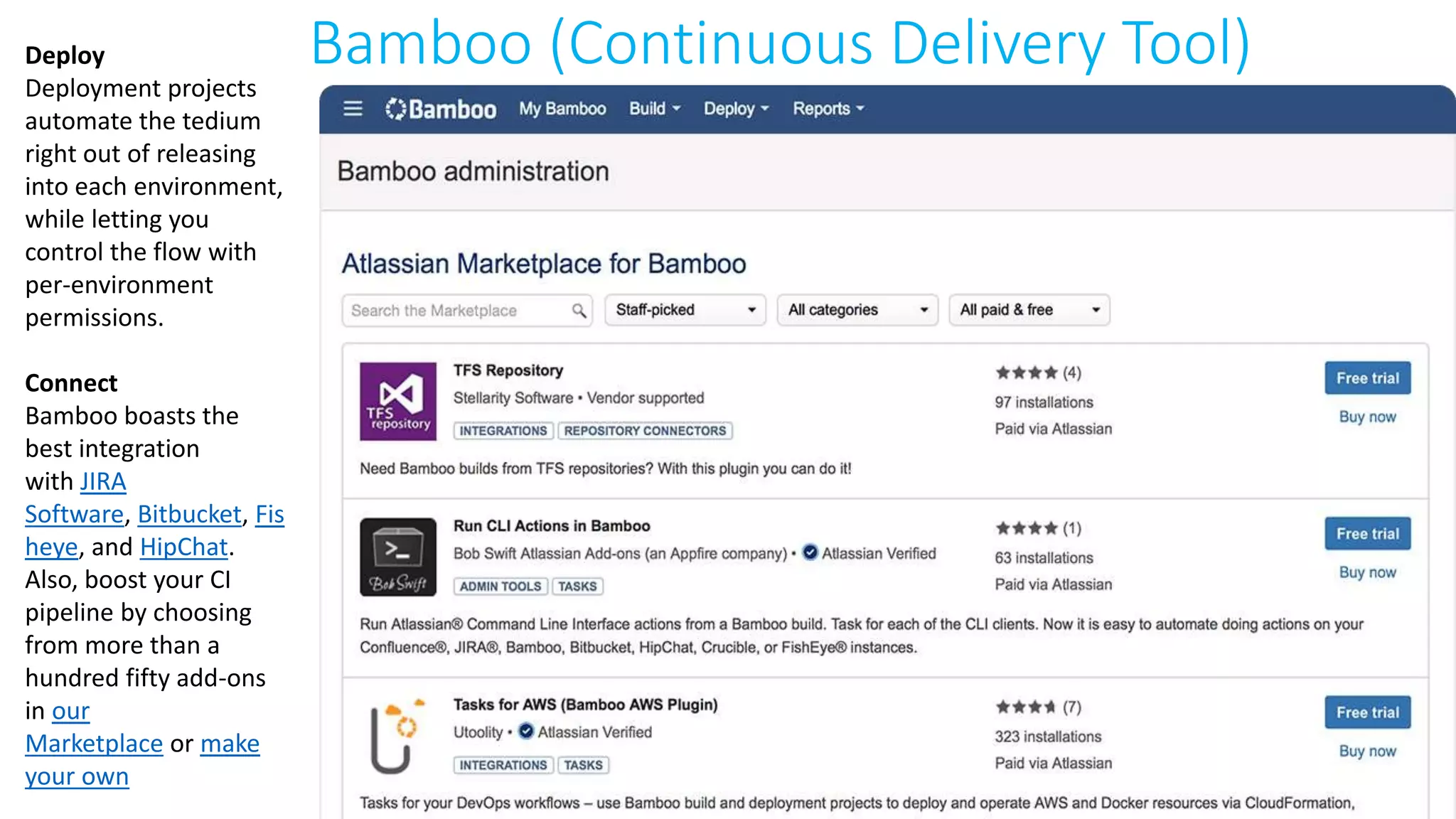
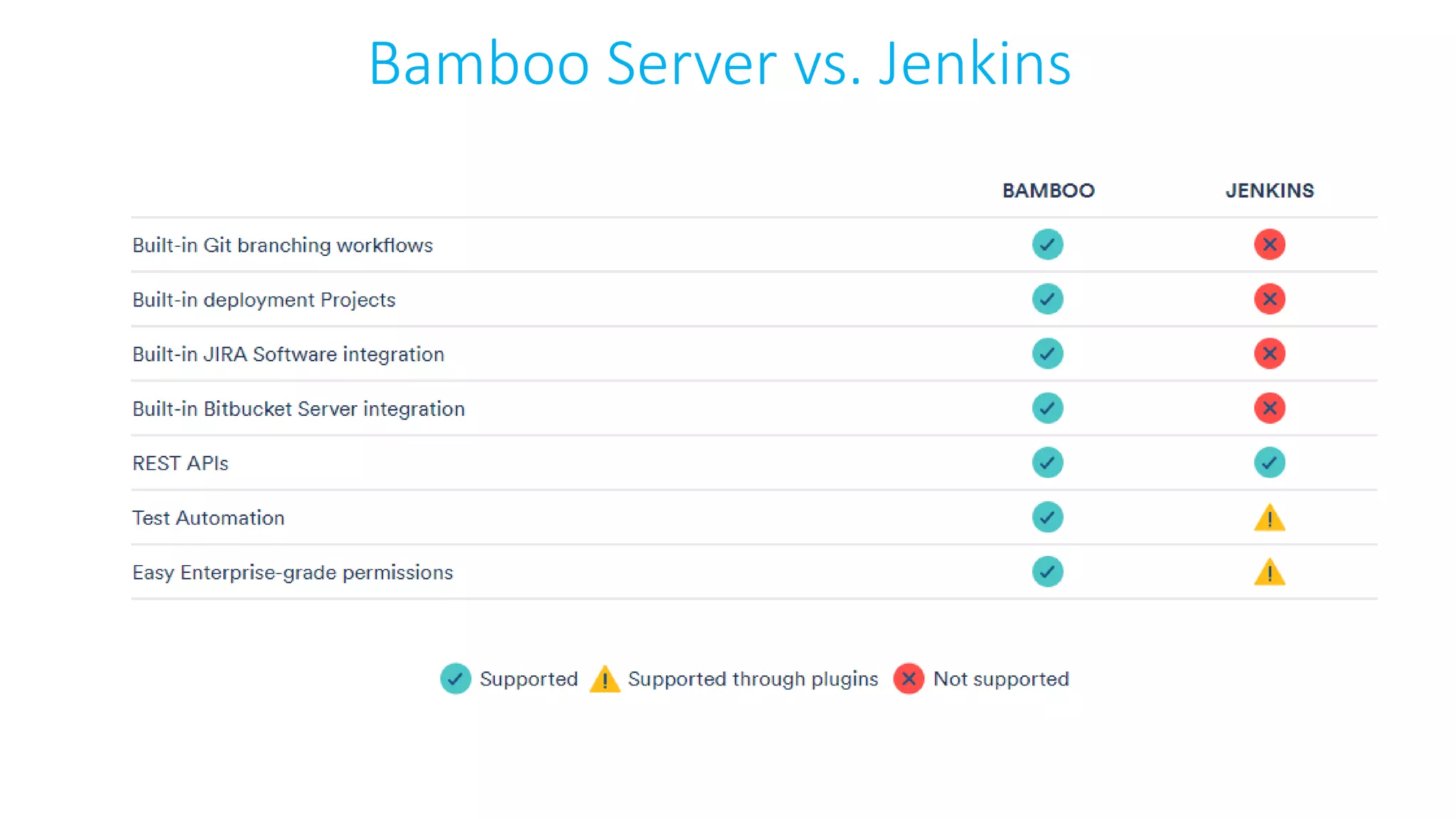
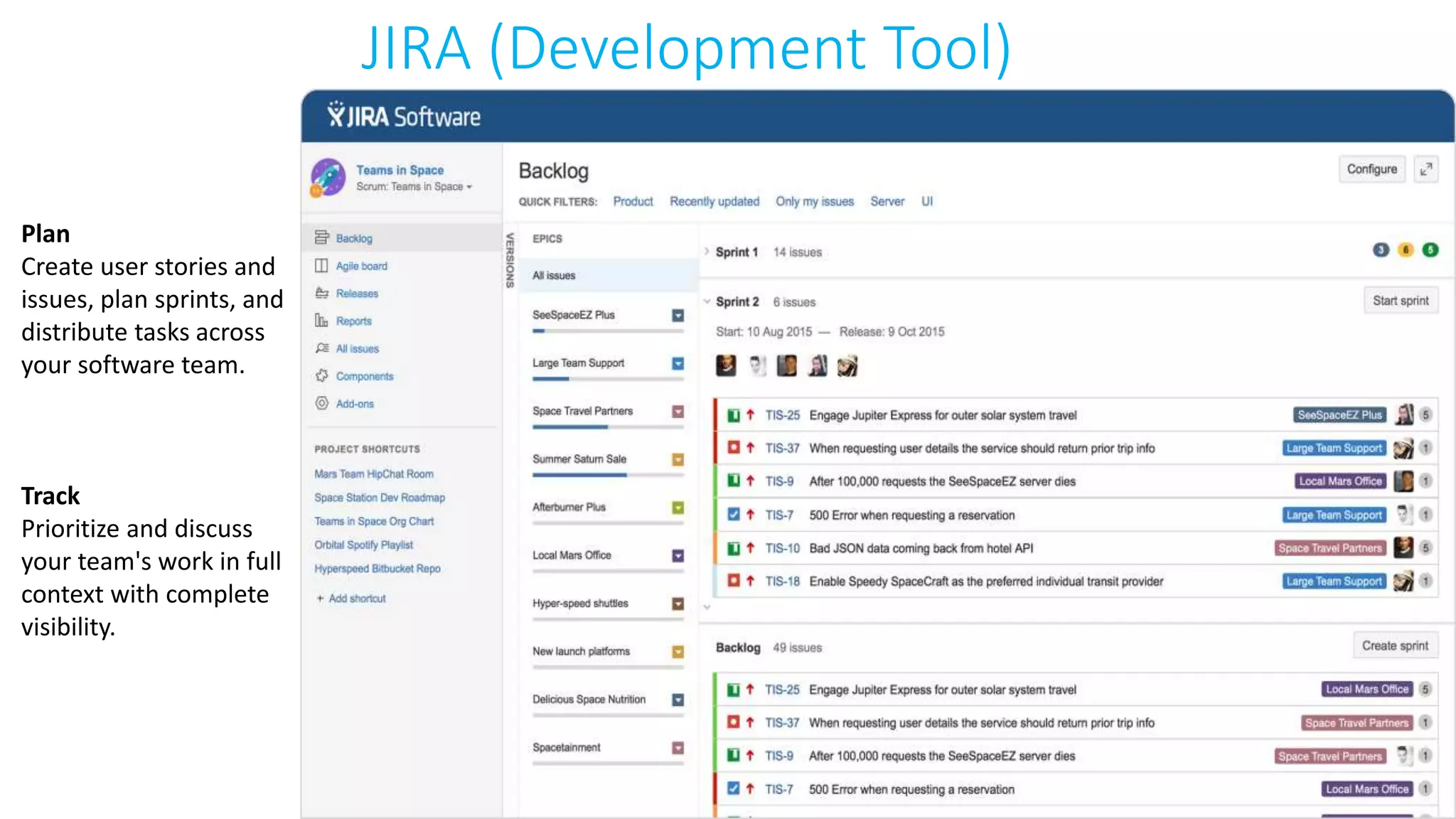
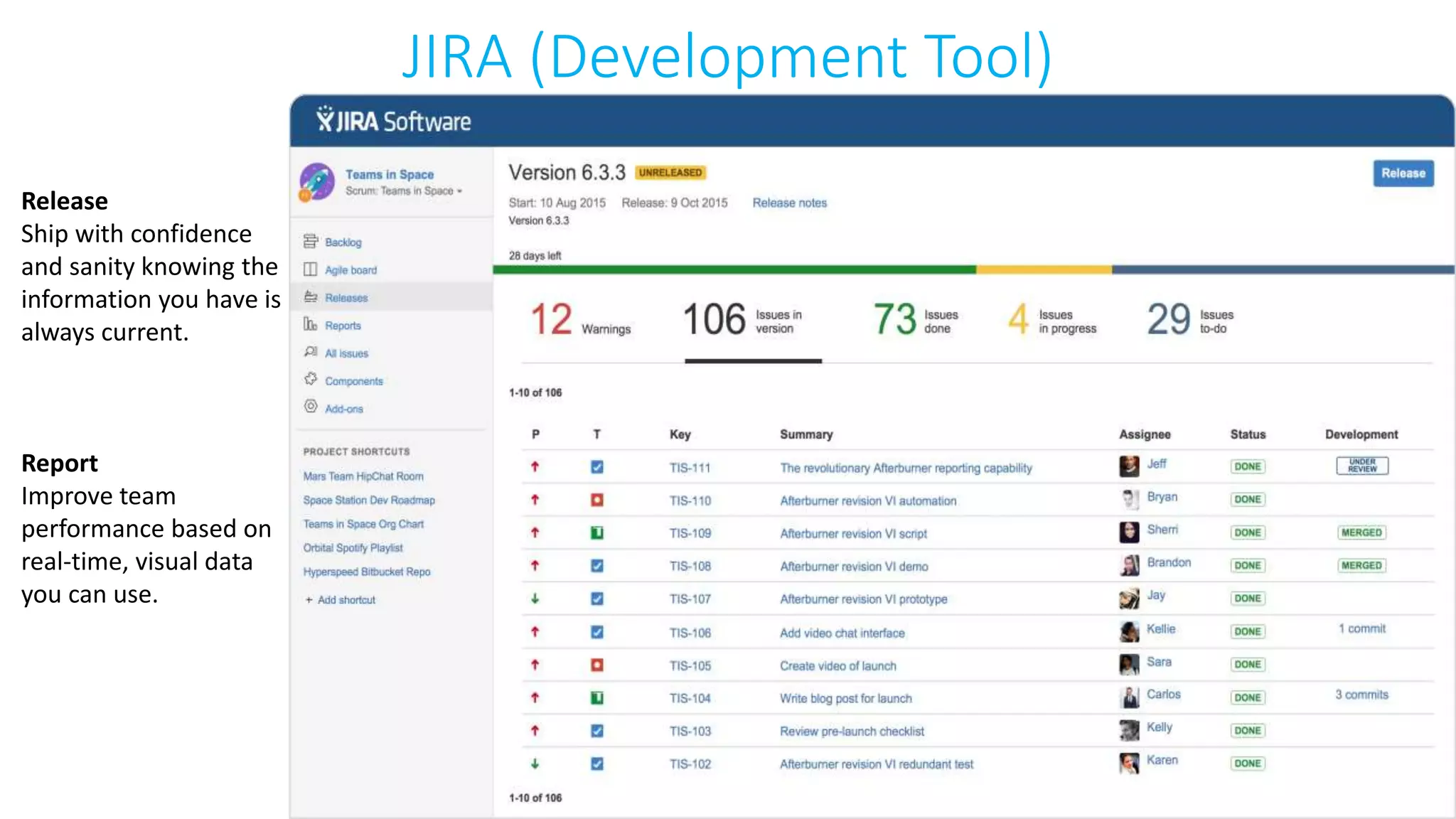
This document provides an extensive overview of Azure services, focusing on serverless architecture, management tools, and deployment options for applications. It highlights the capabilities of Azure Functions, Azure Cosmos DB, and data services, as well as methodologies for migrating SQL databases to Azure. Additionally, it delves into Docker commands and configurations for managing containers and provides guidance on setting up various Azure technologies.