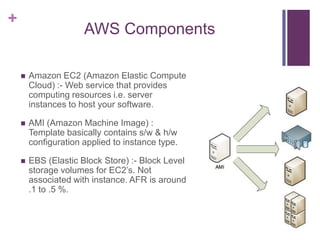
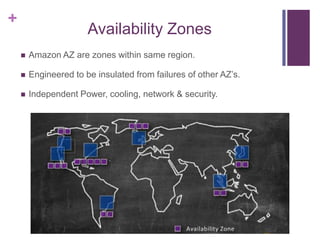
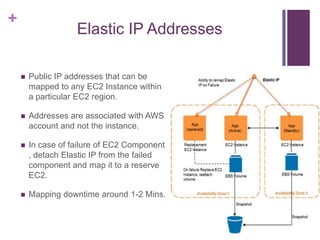
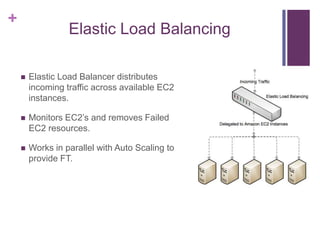
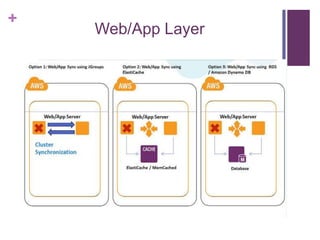
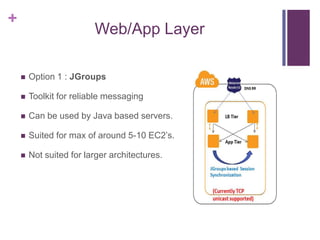
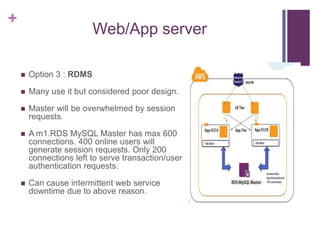
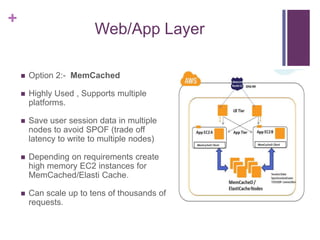
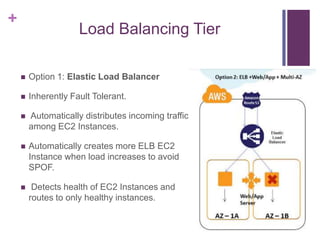
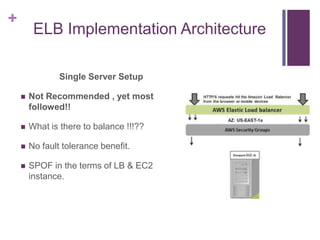
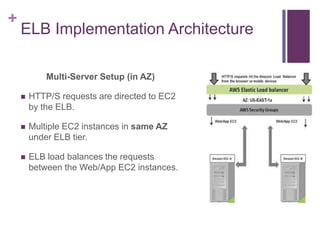
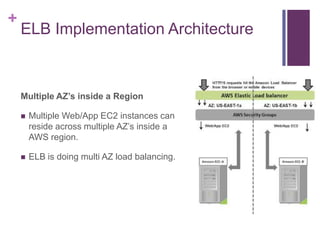
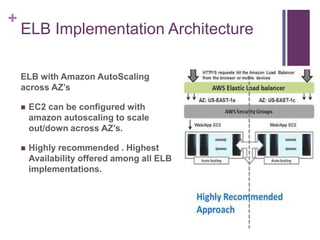
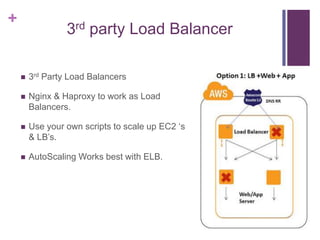
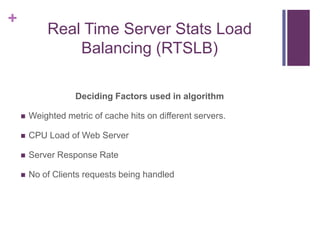
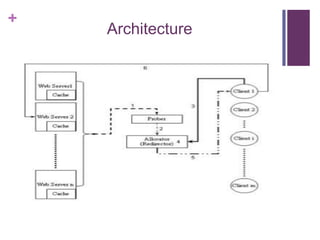
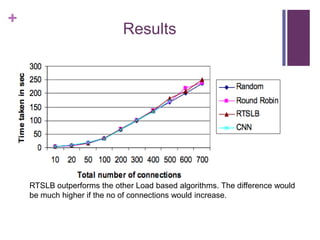
This document discusses designing fault tolerant web services on AWS. It covers motivation for fault tolerance on AWS, inherent fault tolerant AWS components like availability zones and Elastic IPs, and how to implement redundancy using Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing. It then discusses designing high availability at the web/app, load balancing, and database layers, providing options for session synchronization and load balancing. It proposes a new load balancing algorithm that dynamically adapts strategies based on real-time server stats.