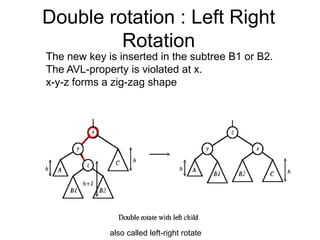
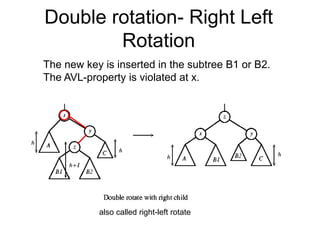
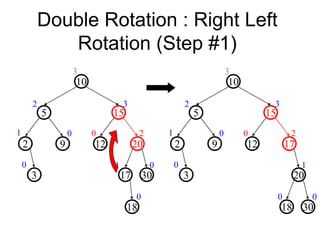
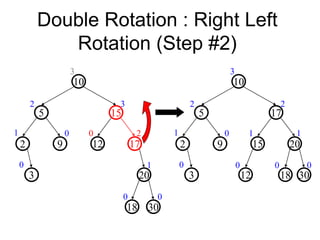
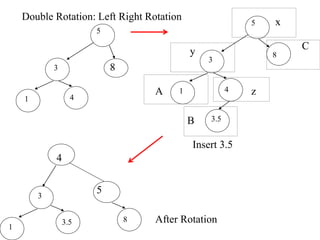
- AVL trees are self-balancing binary search trees where the heights of the two child subtrees of every node differ by at most one.
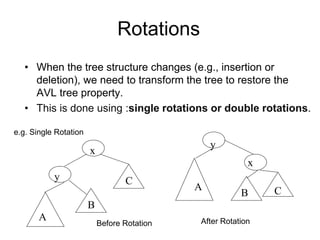
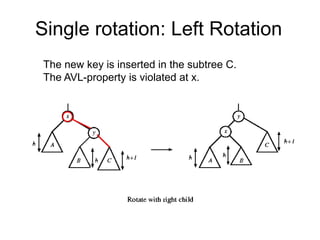
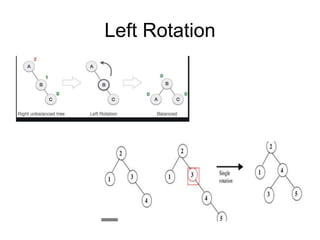
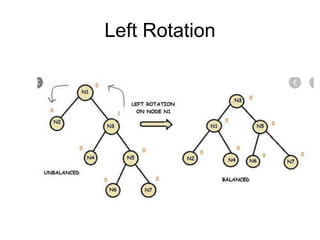
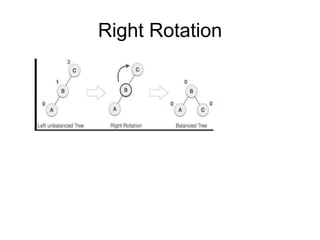
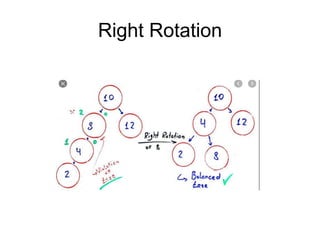
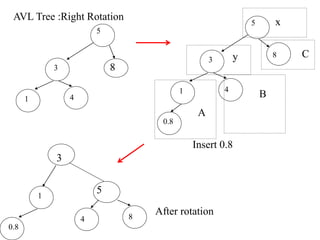
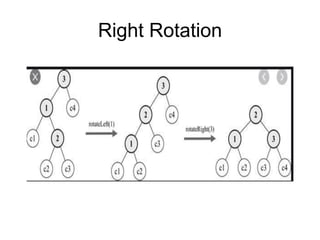
- When a node becomes unbalanced due to an insertion or deletion, rotations are performed to restore the balance property. Single and double rotations are used to rebalance the tree.
- Insertions and deletions in AVL trees take O(log n) time due to rebalancing, compared to O(n) time for unbalanced binary search trees. Rotations are used to restore the balance property during updates.