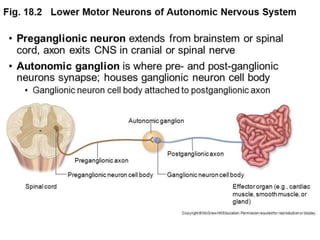
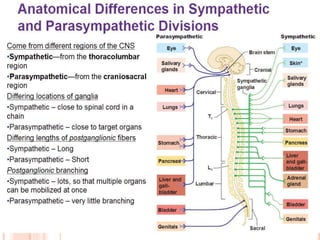
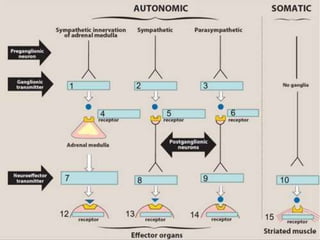
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) receives input from parts of the central nervous system that process and integrate stimuli from the body and environment. It is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic system activates the fight or flight response using norepinephrine and epinephrine as neurotransmitters. The parasympathetic system activates rest and digest functions using acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter to counterbalance the sympathetic system. The ANS regulates involuntary functions through a two-neuron pathway consisting of a preganglionic neuron which releases acetylcholine or norepinephrine at a ganglion, and a postganglionic neuron which travels to the organ and also releases acetylcholine or norepinephrine.