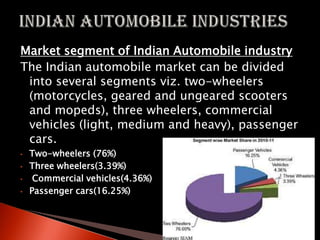
This document provides an overview of the global and Indian automobile industries. It discusses key statistics such as the largest producers and Indian market segments. The top 3 Indian companies are listed as Maruti Suzuki, Hyundai, and Tata Motors. Government policies to promote the industry are outlined. A PESTEL analysis identifies relevant political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors. Finally, Porter's Five Forces model is applied to analyze competitive rivalry, threat of substitutes, supplier power, buyer power, and threat of new entry.