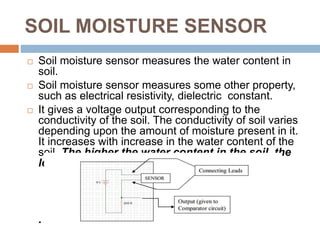
The document discusses the importance of irrigation for agriculture, outlining various types such as surface, drip, and sprinkler irrigation, and the issues associated with these systems. It highlights automation technologies including time-based, volume-based, and sensor-based systems, specifically focusing on soil moisture sensors for effective water management. The conclusion emphasizes the effectiveness of a microcontroller-based drip irrigation system in enhancing productivity, reducing water consumption, and modernizing agricultural practices.