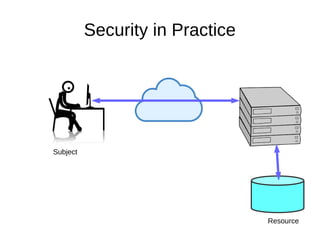
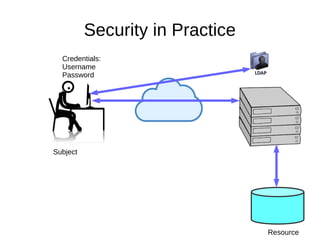
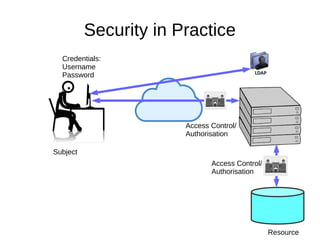
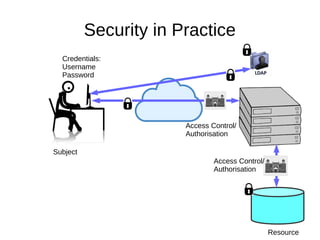
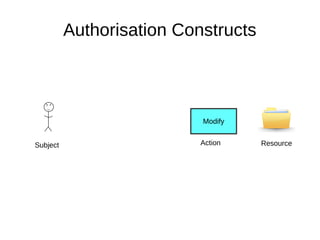
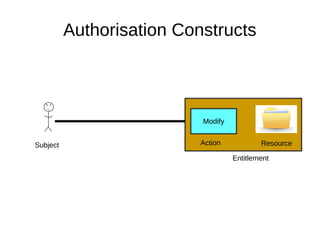
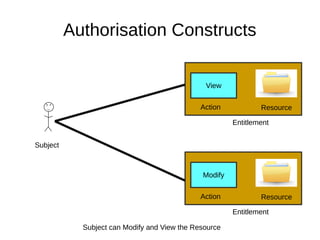
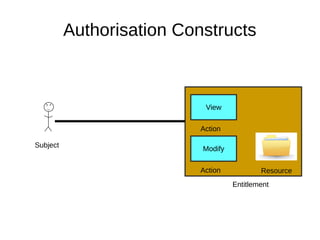
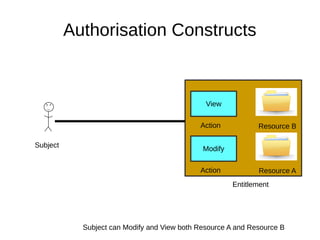
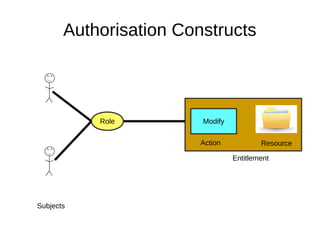
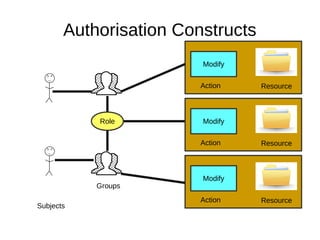
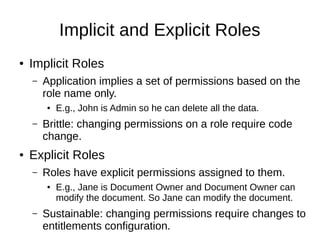
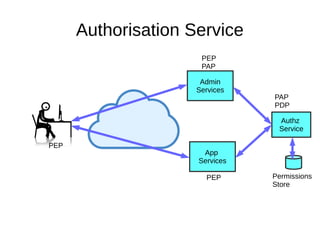
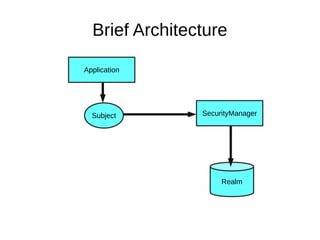
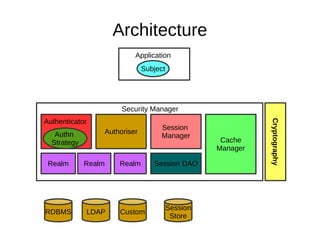
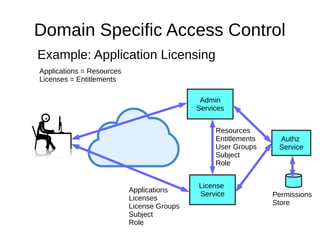
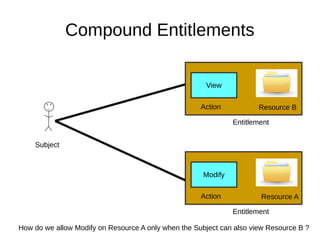
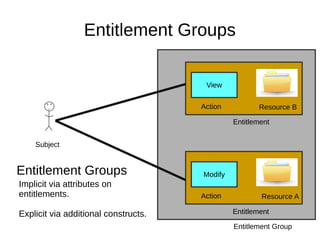
The document discusses the essentials of information security, focusing on concepts such as authentication, authorization, and encryption. It explains the mechanisms for defining entitlements, access control policies, and the various components involved in enforcing these policies, emphasizing the difference between implicit and explicit roles in authorization. Additionally, it covers types of access control like RBAC and ABAC, and suggests a hybrid approach for effective management of permissions.