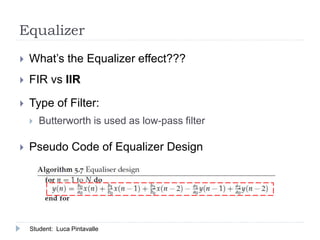
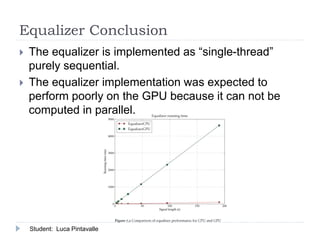
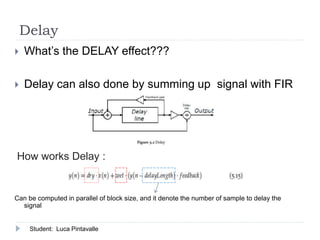
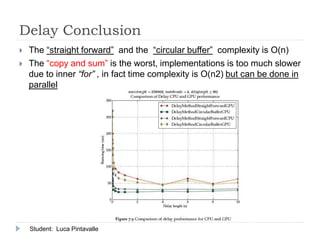
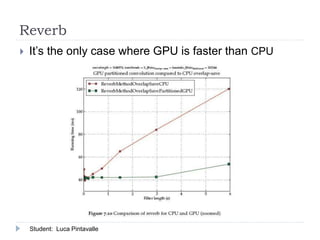
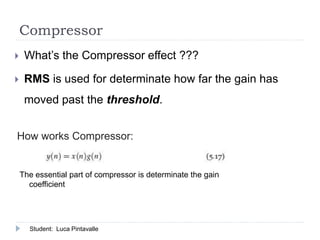
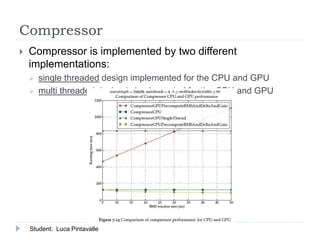
The document presents an analysis of audio processing algorithms on GPUs, focusing on equalizers, delays, reverbs, and compressors. It compares the performance of these algorithms on CPU versus GPU, highlighting that only reverberation can take full advantage of parallel computation, making it faster on a GPU. The conclusions indicate the varying levels of parallelism and performance among the algorithms evaluated.