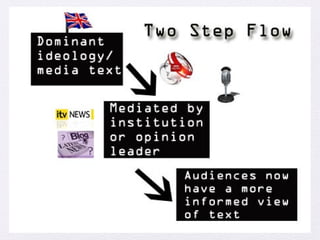
The document discusses several theories of audience response to media:
1) The hypodermic needle model views audiences as passive, simply absorbing messages from media like injections. However, audiences respond individually based on opinions and experiences.
2) The two-step flow theory proposes people are more influenced discussing media with others, whose opinions then shape views. "Opinion leaders" particularly sway others.
3) Uses and gratifications theory argues individuals actively use media to fulfill different needs like information, identity, social interaction, and entertainment. Critics note a lack of choice in some exposures.
4) Reception theory outlines preferred, negotiated, and oppositional readings - the intended, modified, and alternative messages audiences take from media