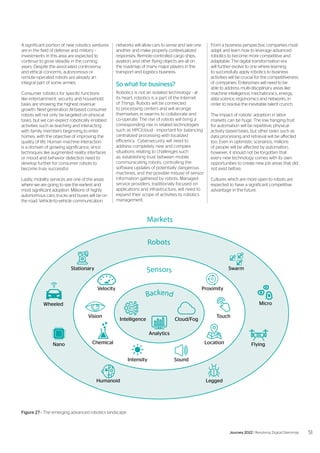
The document discusses digital dilemmas that businesses will face over the next few years as digital technologies continue to evolve rapidly. It notes that the digital and physical worlds are becoming increasingly interconnected, raising questions about how technology impacts humanity. Successful businesses will resolve these dilemmas by balancing insights from technology with inertia from society and potential inequalities, and considering ethical ideals. The future will require a focus on human-centric values and continuous innovation through collaborative ecosystems and workforce flexibility.