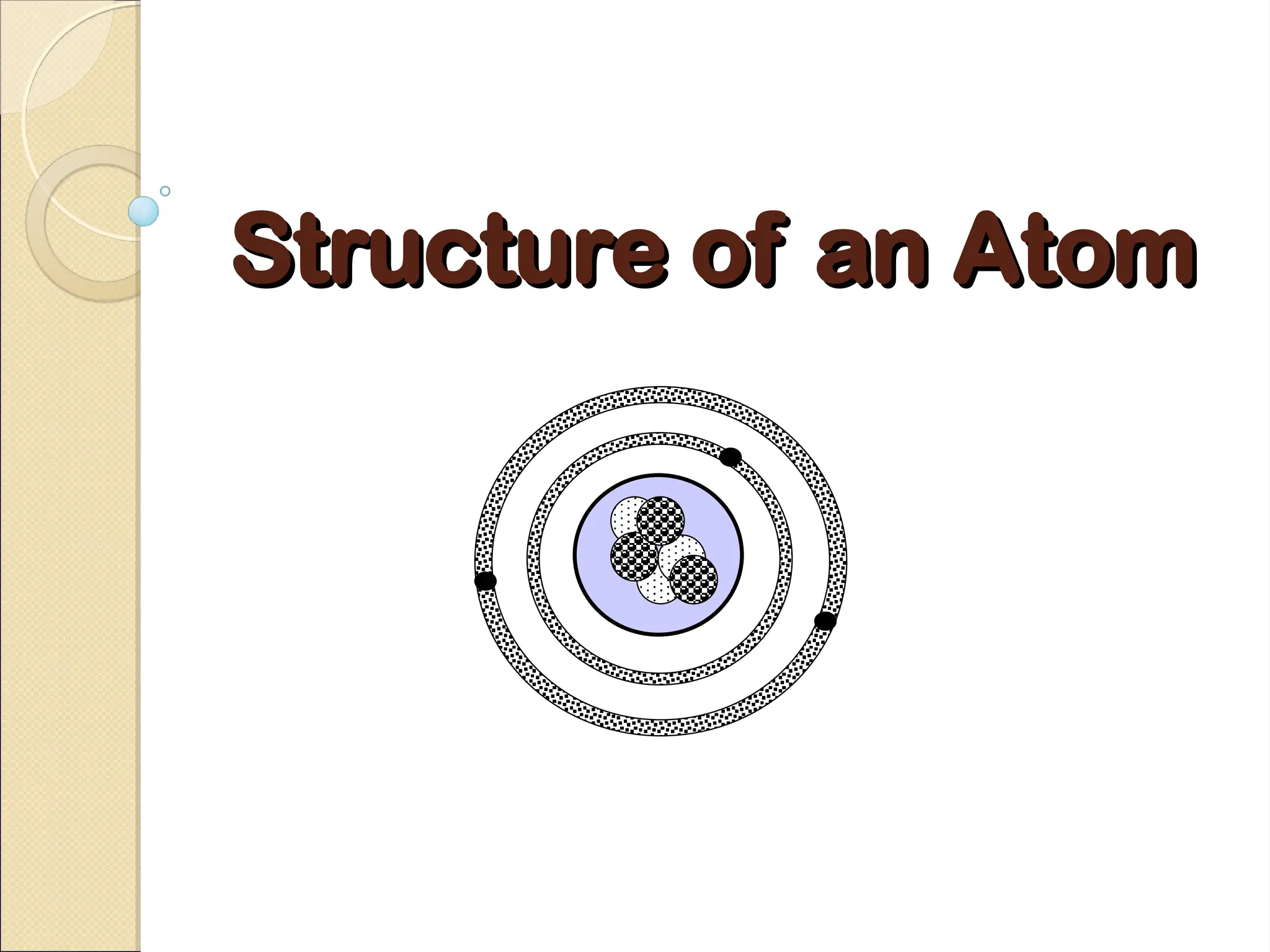
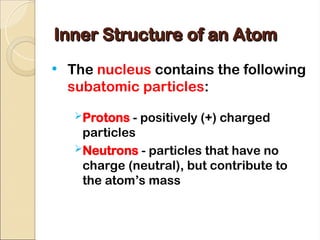
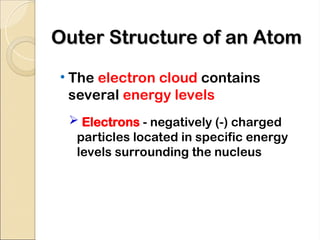
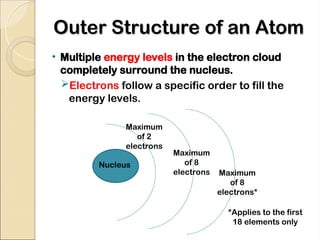
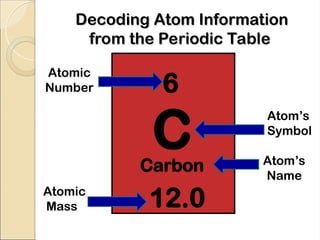
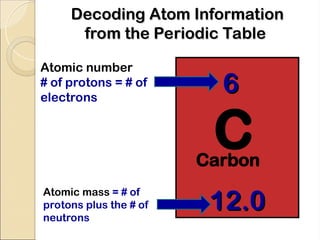
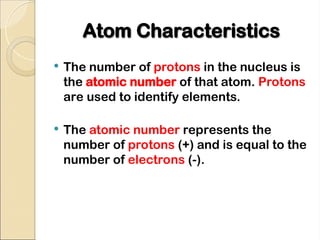
Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, with a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. The nucleus contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, while the electron cloud includes negatively charged electrons in defined energy levels. The atomic number signifies the number of protons and electrons, while atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons.