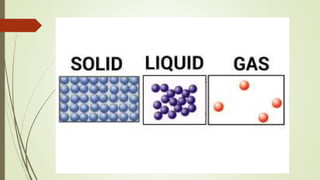
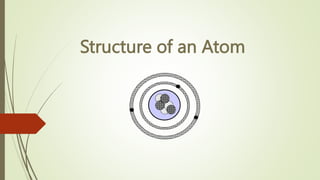
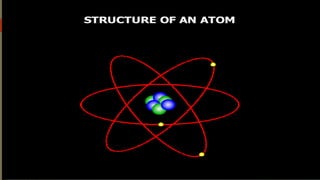
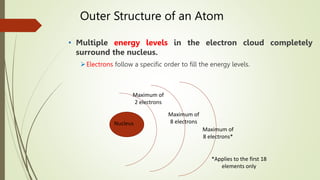
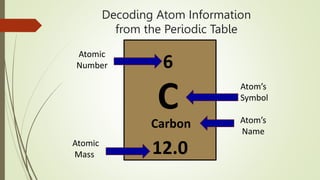
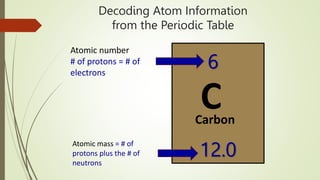
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, composed of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, is surrounded by an electron cloud with various energy levels where electrons reside. The atomic number indicates the number of protons, while atomic mass is the combined mass of protons and neutrons.